Write The Chemical Formula For Chloric Acid
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
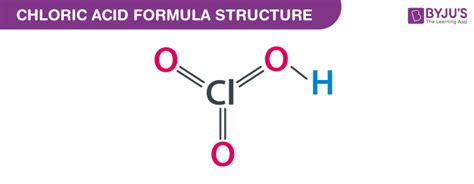
Table of Contents
The Chemical Formula for Chloric Acid: A Deep Dive into its Properties and Reactions
Chloric acid, a potent and versatile oxyacid of chlorine, holds significant importance in various chemical processes. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and reactions is crucial for anyone working with this compound. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of chloric acid, providing a detailed overview of its characteristics and applications.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: HClO₃
The chemical formula for chloric acid is HClO₃. This formula concisely represents the composition of the molecule, revealing the elements and their respective ratios. Let's break it down:
- H: Represents one hydrogen atom, contributing to the acidic nature of the compound.
- Cl: Represents one chlorine atom, the central atom around which the molecule is structured. Chlorine's variable oxidation states are key to understanding the chemistry of chloric acid and other chlorine oxyacids.
- O₃: Represents three oxygen atoms, bound to the chlorine atom. The presence of oxygen atoms significantly influences the molecule's oxidizing properties.
This simple formula, however, belies the complex behavior and reactivity of chloric acid. It's crucial to remember that this formula represents the pure compound. In reality, chloric acid is typically found in aqueous solution, meaning it's dissolved in water. Therefore, while HClO₃ is the core formula, a more realistic representation might consider its hydration state in solution.
Properties of Chloric Acid: A Closer Look
Chloric acid, despite its seemingly simple formula, exhibits a diverse range of properties:
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Chloric acid exists as a colorless or slightly yellowish liquid in its pure form. However, it's highly unstable in its concentrated form and is usually encountered in aqueous solution.
- Solubility: It's highly soluble in water, readily dissociating into its constituent ions. This high solubility contributes to its effectiveness in various chemical reactions.
- Boiling Point: Pure chloric acid has a high boiling point, though determining the exact temperature is challenging due to its instability. The boiling point of aqueous solutions varies with concentration.
- Density: The density of chloric acid solutions also depends on their concentration.
Chemical Properties:
- Strong Acid: Chloric acid is a strong acid, meaning it readily donates a proton (H⁺) when dissolved in water. This leads to a significant increase in the hydronium ion concentration ([H₃O⁺]), resulting in a low pH. The dissociation in water can be represented as: HClO₃(aq) → H⁺(aq) + ClO₃⁻(aq).
- Oxidizing Agent: Chloric acid is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it readily accepts electrons from other substances. This property stems from the relatively high oxidation state of the chlorine atom (+5). The oxidizing power of chloric acid makes it a useful reagent in various oxidation-reduction reactions.
- Instability: One of the most significant properties of chloric acid is its instability. Pure chloric acid is difficult to obtain and is prone to decomposition, even at moderate temperatures. This decomposition can produce chlorine dioxide (ClO₂), a toxic and potentially explosive gas, highlighting the need for careful handling.
- Reactivity: Chloric acid reacts readily with various metals and organic compounds. The reactions can be quite vigorous, sometimes leading to the evolution of heat and gases.
Preparation of Chloric Acid: Methods and Considerations
Due to its instability, the preparation of chloric acid requires careful control of reaction conditions. Pure chloric acid is rarely isolated; instead, aqueous solutions are typically prepared:
-
Reaction of Barium Chlorate with Sulfuric Acid: This is a common method. Barium chlorate (Ba(ClO₃)₂) reacts with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to produce chloric acid and barium sulfate (BaSO₄), an insoluble precipitate that can be easily removed by filtration. The reaction can be represented as: Ba(ClO₃)₂(aq) + H₂SO₄(aq) → 2HClO₃(aq) + BaSO₄(s). This method allows for the separation of the chloric acid solution from other components.
-
Other Methods: Other methods, though less common, involve reactions of chlorine oxides with water or the electrolysis of suitable chlorine-containing compounds. However, these methods often yield lower purities or present increased safety hazards.
Regardless of the preparation method, safety precautions are crucial. Chloric acid is a corrosive and potentially hazardous substance. Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper ventilation should always be used.
Reactions of Chloric Acid: A Diverse Palette of Transformations
The strong acidic and oxidizing nature of chloric acid leads to a wide range of reactions:
Reactions with Metals:
Chloric acid reacts vigorously with many metals, producing metal chlorates and hydrogen gas. The reactions can be highly exothermic and require careful control. For instance, the reaction with zinc (Zn) can be written as: 2HClO₃(aq) + Zn(s) → Zn(ClO₃)₂(aq) + H₂(g).
Reactions with Organic Compounds:
Chloric acid's oxidizing capabilities make it a powerful reagent in organic chemistry. It can oxidize alcohols, aldehydes, and other organic compounds, though these reactions often require careful control of temperature and concentration to avoid uncontrolled oxidation or decomposition.
Decomposition Reactions:
As mentioned earlier, chloric acid is inherently unstable and prone to decomposition. The decomposition products depend on the conditions, but chlorine dioxide (ClO₂), chlorine, oxygen, and water are common byproducts. This decomposition can be both thermal (heat-induced) or catalytic. The potential for explosive decomposition is a significant safety concern.
Applications of Chloric Acid: A Wide Range of Uses
Despite its instability, chloric acid finds application in various fields:
- Industrial Processes: Chloric acid, or its salts (chlorates), are used in the production of certain chemicals and as oxidizing agents in various industrial processes. The specific applications vary depending on the scale and nature of the process.
- Laboratory Reagent: In laboratories, chloric acid solutions find use as a strong acid and as an oxidizing agent in specific chemical syntheses and analyses. Its use is typically limited to controlled experiments due to its reactivity and instability.
- Analytical Chemistry: Chloric acid's oxidizing properties are utilized in various analytical methods, particularly in oxidation-reduction titrations and other quantitative analyses.
Safety Precautions: Handling Chloric Acid Responsibly
Chloric acid presents significant safety hazards:
- Corrosive: It's highly corrosive to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Contact can cause severe burns. Appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and lab coats, is essential when handling chloric acid.
- Oxidizing Agent: Its strong oxidizing ability poses a fire and explosion hazard, especially when in contact with organic materials or easily oxidized substances.
- Decomposition: The potential for decomposition to release toxic and explosive gases (such as chlorine dioxide) necessitates careful handling and proper ventilation.
- Toxicity: Chloric acid and its decomposition products can be toxic upon ingestion or inhalation.
Proper storage, handling, and disposal protocols are crucial for minimizing risks associated with chloric acid. Consult relevant safety data sheets (SDS) for detailed information on safe handling practices.
Conclusion: A Powerful yet Hazardous Compound
Chloric acid, with its chemical formula HClO₃, represents a potent and versatile compound. Its strong acidic and oxidizing properties make it useful in various applications, but its inherent instability and reactivity demand careful handling. Understanding its properties, reactions, and safety precautions is paramount for anyone working with this powerful yet hazardous chemical. Always prioritize safety and adhere to best practices when handling chloric acid. Remember that the information provided here is for educational purposes and should not be considered a substitute for proper laboratory training and safety protocols.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 Functions Of A Political Party
Mar 26, 2025
-
Where Does Mitosis Take Place In The Body
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Proton Travels Through Uniform Magnetic And Electric Fields
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Chemical Formula For Chloric Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
