Why Is The Wall Of The Left Ventricle Thicker
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
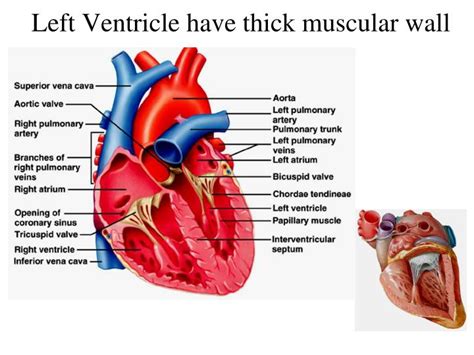
Table of Contents
Why is the Left Ventricle Wall Thicker? A Deep Dive into Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology
The human heart, a remarkable organ, tirelessly pumps blood throughout our bodies. Its four chambers – two atria and two ventricles – each play a crucial role in this vital process. A striking anatomical feature is the significantly thicker wall of the left ventricle compared to the right. This difference isn't arbitrary; it's a direct consequence of the vastly different workloads these chambers bear. Understanding this difference requires exploring the circulatory system's mechanics and the physiological demands placed on each ventricle.
The Systemic and Pulmonary Circuits: A Tale of Two Pressures
The heart's work is divided into two distinct circulatory circuits: the systemic and the pulmonary. The systemic circulation involves the left side of the heart, pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs to the rest of the body. The pulmonary circulation, handled by the right side of the heart, circulates deoxygenated blood from the body to the lungs for oxygenation.
The key difference lies in the pressure each circuit demands. The systemic circulation requires significantly higher pressure to overcome the extensive resistance offered by the vast network of blood vessels supplying the entire body. This high pressure is necessary to effectively deliver oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues. In contrast, the pulmonary circulation operates at a much lower pressure. The distance the blood travels in the pulmonary circuit is shorter, and the resistance within the pulmonary vessels is lower.
Pressure Differences and Ventricular Wall Thickness
This disparity in pressure is directly reflected in the thickness of the left and right ventricular walls. The left ventricle, tasked with pumping blood against the high pressure of the systemic circulation, has a significantly thicker muscular wall. This thicker wall allows it to generate the substantial force needed to propel blood effectively throughout the body. Conversely, the right ventricle, working against the much lower pressure of the pulmonary circulation, has a thinner wall. It needs less muscular power to deliver blood to the lungs.
The Myocardium: The Engine of the Heart
The walls of the ventricles are composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue, known as the myocardium. The thickness of the myocardium is directly proportional to the pressure the ventricle must generate. The left ventricle's significantly thicker myocardium reflects its greater workload in propelling blood against the high pressure of the systemic circulation.
Microscopic Structure and Contractile Force
At a microscopic level, the increased thickness of the left ventricle's myocardium translates to a greater number of cardiac muscle cells arranged in a more complex and robust structure. These cells contain more contractile proteins, allowing for a more forceful contraction. This increased contractile force is crucial for overcoming the high resistance of the systemic circulation. The right ventricle, with its thinner myocardium, possesses fewer cardiac muscle cells and less robust contractile capabilities. This is perfectly adequate for its lower-pressure workload.
Consequences of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
While a thicker left ventricular wall is essential for normal function, excessive thickening, a condition known as left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), can be problematic. LVH can be caused by various factors, including high blood pressure (hypertension), aortic stenosis (narrowing of the aortic valve), and chronic heart failure.
The Detrimental Effects of LVH
Over time, LVH can lead to several adverse consequences, including:
- Increased oxygen demand: The enlarged and thickened left ventricle requires more oxygen to function effectively. This increased oxygen demand can strain the heart's blood supply, potentially leading to ischemia (reduced blood flow) and angina (chest pain).
- Impaired diastolic function: LVH can impair the ventricle's ability to relax and fill with blood during diastole (the relaxation phase of the heartbeat). This impaired filling can reduce the heart's overall efficiency and lead to heart failure.
- Increased risk of arrhythmias: LVH can disrupt the heart's electrical conduction system, increasing the risk of irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias). These arrhythmias can range from benign palpitations to life-threatening conditions like ventricular fibrillation.
- Heart failure: In advanced stages, LVH can lead to heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This can cause shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles, and other debilitating symptoms.
Assessing Left Ventricular Thickness: Diagnostic Tools
Several diagnostic tools are employed to assess left ventricular thickness and identify potential problems. These include:
- Echocardiography: This non-invasive ultrasound technique provides detailed images of the heart's structure and function, allowing accurate measurement of left ventricular wall thickness.
- Electrocardiography (ECG): While not directly measuring wall thickness, ECG can reveal signs of LVH, such as changes in the electrical activity of the heart.
- Cardiac MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging provides high-resolution images of the heart, offering a more comprehensive assessment of LVH and other cardiac abnormalities.
- Cardiac Catheterization: A more invasive procedure, cardiac catheterization involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel to directly measure pressures within the heart chambers and assess the function of the heart valves.
Maintaining Cardiovascular Health: Prevention and Management
Maintaining cardiovascular health is crucial in preventing the development of LVH and its associated complications. This involves:
- Managing blood pressure: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for LVH. Regular blood pressure monitoring and appropriate management with lifestyle modifications or medication are essential.
- Controlling cholesterol levels: High cholesterol levels contribute to atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of arteries, which increases the workload on the heart.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity puts added strain on the heart, increasing the risk of LVH.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity helps strengthen the heart and improve cardiovascular health.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Pressure and Structure
The thicker wall of the left ventricle is not a flaw but a testament to the heart's remarkable adaptability. Its increased thickness reflects the higher pressures and greater workload required to supply oxygenated blood to the entire body. Understanding this fundamental difference in ventricular structure is crucial for appreciating the intricacies of the cardiovascular system and the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health. While a thicker left ventricle is necessary for healthy function, excessive thickening, or LVH, can have significant health implications. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt medical attention are vital in preventing and managing conditions that can lead to LVH and its potential complications. The human heart, a masterpiece of engineering, constantly adapts to the demands placed upon it, highlighting the complex interplay between physiology, anatomy, and the overall well-being of the organism.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Figure Shows A Rectangular Array Of Charged Particles
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Major Function Of Political Parties
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Best Describes Mitochondrial Dna Mtdna
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Largest Lymphoid Organ
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is A Non Permanent Magnet
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Is The Wall Of The Left Ventricle Thicker . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
