Which Part Of The Neuron Contains The Nucleus
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
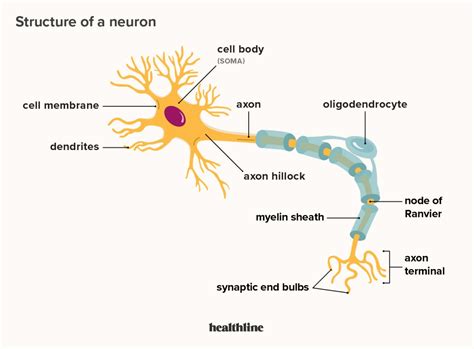
Table of Contents
Which Part of the Neuron Contains the Nucleus? A Deep Dive into Neuronal Structure and Function
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, is composed of billions of interconnected cells called neurons. These intricate cells are responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information throughout the body, forming the basis of our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Understanding the structure of a neuron is crucial to grasping its function, and a key component of this understanding lies in identifying the location of the nucleus. The nucleus of a neuron is located in the soma, also known as the cell body. This seemingly simple answer opens the door to a far richer understanding of neuronal biology.
The Neuron: A Cellular Overview
Before delving into the specifics of nuclear location, let's establish a foundational understanding of neuronal structure. A neuron, unlike many other cell types, possesses a unique morphology designed to efficiently transmit signals. It comprises three primary components:
1. Soma (Cell Body): The Control Center
The soma, or cell body, is the neuron's central hub. It's here that the nucleus resides, containing the cell's genetic material (DNA). The soma also houses other vital organelles, including:
- Mitochondria: These powerhouses generate the energy (ATP) necessary for the neuron's metabolic processes, including signal transmission.
- Ribosomes: Responsible for protein synthesis, crucial for neuronal structure and function. The abundance of ribosomes in the soma highlights its role in cellular maintenance and repair.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranes involved in protein folding, modification, and transport. The ER plays a vital role in maintaining neuronal homeostasis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Processes and packages proteins synthesized by the ribosomes, preparing them for transport to other parts of the neuron.
The soma's central location allows it to coordinate the neuron's activities, ensuring the efficient flow of information. Its size and shape vary depending on the neuron's type and location within the nervous system.
2. Dendrites: Receiving Signals
Extending from the soma are numerous dendrites, branching projections that act as the neuron's primary receivers. These dendritic branches increase the surface area available for receiving signals from other neurons. Signals arrive at the dendrites in the form of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers released into the synapse—the gap between two neurons. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the dendritic membrane, initiating electrical changes that propagate towards the soma. The intricate branching pattern of dendrites allows a single neuron to receive input from thousands of other neurons, contributing to the complexity of neuronal networks.
3. Axon: Transmitting Signals
The axon is a long, slender projection extending from the soma. Unlike dendrites, the axon's primary role is to transmit signals away from the soma. The axon's structure is uniquely adapted for efficient signal conduction. It's often covered by a myelin sheath, a fatty insulating layer that speeds up signal transmission. The myelin sheath is not continuous but is interrupted at regular intervals by the Nodes of Ranvier, allowing for saltatory conduction—a rapid "jumping" of the signal along the axon. At the axon's terminal end, the signal is converted back into a chemical form, releasing neurotransmitters into the synapse to communicate with other neurons. The length and diameter of axons vary greatly, reflecting the distance over which signals must travel.
The Nucleus: The Control Center Within the Control Center
Returning to our central question, the nucleus is undeniably located within the soma. Its role is paramount:
- Genetic Information Storage: The nucleus houses the neuron's DNA, the blueprint for all its proteins and cellular processes. This genetic information dictates the neuron's development, function, and survival.
- Gene Expression Regulation: The nucleus controls which genes are expressed (activated) and when. This precise regulation is crucial for neuronal plasticity, the ability of neurons to adapt and change in response to experience.
- Transcription and Translation: The nucleus is the site of transcription, where the DNA sequence is copied into RNA. This RNA then travels to the ribosomes in the soma and elsewhere in the neuron, where it is translated into proteins. This intricate process is essential for the synthesis of proteins vital for neuronal function and maintenance.
- Cellular Repair and Maintenance: The nucleus plays a key role in orchestrating cellular repair processes, ensuring the neuron's structural integrity and long-term survival. Damage to the nucleus can lead to neuronal dysfunction or death.
Implications of Nucleus Location and Neuronal Function
The strategic location of the nucleus within the soma has significant implications for neuronal function:
- Centralized Control: The nucleus's position in the soma allows it to centrally manage the neuron's activities. It provides a coordinated response to incoming signals and ensures the efficient allocation of resources.
- Efficient Protein Synthesis: Proximity to the ribosomes and ER in the soma facilitates efficient protein synthesis, essential for maintaining neuronal structure and function.
- Vulnerability to Damage: The soma's central location makes it a potential target for injury. Damage to the soma, including the nucleus, can have devastating consequences for the neuron's function and survival.
Types of Neurons and Nucleus Variation
While the nucleus is always located within the soma, the size and shape of both the soma and nucleus can vary significantly depending on the type of neuron. Different types of neurons are specialized for different functions, and this specialization is reflected in their morphology. For example:
- Pyramidal Neurons: Found in the cerebral cortex, these neurons are characterized by their triangular soma and large apical dendrite. Their nuclei are typically large and centrally located within the soma.
- Purkinje Cells: Located in the cerebellum, these neurons are known for their extensive dendritic arborization and large, flask-shaped soma. Their nuclei are relatively large and positioned centrally within the soma.
- Sensory Neurons: These neurons transmit sensory information from the periphery to the central nervous system. The size and shape of their soma and nucleus can vary widely depending on the type of sensory information they transmit.
Conclusion: The Nucleus – Key to Neuronal Life
In conclusion, the nucleus is unequivocally located within the soma of a neuron. Its central position within the soma is not a mere coincidence; it's a strategic placement that facilitates efficient control and coordination of the neuron's various functions. The nucleus, as the repository of genetic information and the orchestrator of gene expression, plays a crucial role in neuronal development, function, and survival. Understanding the precise location of the nucleus and its vital functions is fundamental to comprehending the complexity and sophistication of the nervous system and the intricate workings of the brain. Further research into the intricate processes within the neuronal nucleus promises to unlock even more secrets about the brain's capabilities and the mysteries of human consciousness. By understanding the fundamental structure of the neuron, including the critical role of the nucleus, we can better appreciate the remarkable complexity of the human brain and unlock the potential for advances in neuroscience and neurological treatments.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Part Of The Neuron Contains The Nucleus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.