Which Part Of The Brain Contains The Arbor Vitae
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
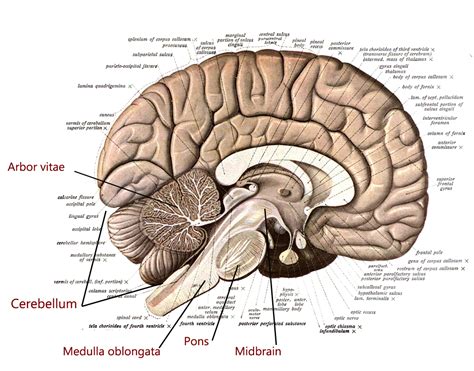
Table of Contents
Which Part of the Brain Contains the Arbor Vitae? A Deep Dive into Cerebellar Anatomy
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, is a complex organ composed of various interconnected structures, each with specialized functions. Understanding its intricate architecture is crucial to comprehending its overall operation. This article delves into a specific, fascinating structure: the arbor vitae, exploring its location, composition, function, and clinical significance.
What is the Arbor Vitae?
The arbor vitae, Latin for "tree of life," is a striking, branching white matter structure found deep within the cerebellum. Its name is derived from its distinctive, tree-like appearance when viewed in a midsagittal section of the cerebellum. This characteristic pattern of white matter tracts radiates outward from the cerebellar hilum, resembling the branches of a tree.
The arbor vitae is not a functional unit in itself but rather a vital pathway facilitating communication within the cerebellum and between the cerebellum and other brain regions. It's crucial for the cerebellar functions we'll discuss later.
Cerebellar Anatomy: Locating the Arbor Vitae
To understand the precise location of the arbor vitae, we need to grasp the basic anatomy of the cerebellum. The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, beneath the cerebrum, is crucial for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. It's divided into two cerebellar hemispheres and a midline vermis.
The arbor vitae resides within the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. It's nestled between the gray matter of the cerebellar cortex (the outer layer) and the deep cerebellar nuclei (clusters of gray matter located deep within the white matter). The white matter tracts of the arbor vitae connect the cerebellar cortex with the deep cerebellar nuclei, and the deep cerebellar nuclei with other brain regions. Therefore, it's not a structure on its own but rather a network of pathways vital for cerebellar function.
Key Cerebellar Structures and their Relationship with the Arbor Vitae:
- Cerebellar Cortex: The outermost layer, composed of gray matter, responsible for processing sensory input related to movement and coordination.
- Deep Cerebellar Nuclei: Clusters of gray matter found deep within the cerebellum. They are essential relay stations for cerebellar output to other brain areas. These nuclei include the dentate nucleus, emboliform nucleus, globose nucleus, and fastigial nucleus.
- White Matter: The arbor vitae itself forms the bulk of the cerebellum's white matter. This white matter comprises myelinated axons, providing the communication pathways between the cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei.
- Cerebellar Peduncles: These bundles of nerve fibers connect the cerebellum to the brainstem, acting as crucial pathways for information exchange between the cerebellum and other brain regions.
The Arbor Vitae: A Closer Look at its Composition and Function
The arbor vitae is primarily composed of myelinated axons. Myelin, a fatty substance that surrounds axons, allows for rapid and efficient transmission of nerve impulses. These axons form the intricate network of pathways within the cerebellar white matter. The myelin's presence accounts for the arbor vitae's characteristic white appearance.
Functional Roles of the Arbor Vitae:
The arbor vitae’s primary function is to facilitate communication within the cerebellum. It acts as a vital conduit, allowing for seamless information exchange between:
-
Cerebellar Cortex and Deep Cerebellar Nuclei: The arbor vitae transmits processed sensory information from the cerebellar cortex to the deep cerebellar nuclei. The deep nuclei then relay this information to other brain regions to fine-tune motor control.
-
Deep Cerebellar Nuclei and Other Brain Regions: The arbor vitae also plays a role in transmitting signals from the deep cerebellar nuclei to other brain areas involved in motor control, including the thalamus, brainstem, and motor cortex.
In essence, the arbor vitae is the cerebellum's internal communication system, ensuring the coordinated function of different cerebellar regions and allowing for seamless interaction with other parts of the brain responsible for motor control, balance, and coordination.
Clinical Significance: Conditions Affecting the Arbor Vitae
Damage to the arbor vitae can significantly impact cerebellar function, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. Various conditions can affect this crucial structure:
1. Stroke:
Cerebellar strokes, particularly those affecting the blood supply to the cerebellar white matter, can damage the arbor vitae. This can result in symptoms such as:
- Ataxia: Impaired coordination of movement, leading to difficulties with gait, balance, and fine motor skills.
- Dysmetria: Difficulty judging distances, leading to inaccurate movements.
- Tremor: Involuntary shaking or trembling.
- Nystagmus: Involuntary eye movements.
2. Tumors:
Tumors within the cerebellum can compress or infiltrate the arbor vitae, disrupting its structure and function. Depending on the tumor's size and location, symptoms can range from mild incoordination to severe ataxia and other neurological deficits.
3. Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
MS is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the central nervous system, including the white matter of the brain. In MS, the myelin sheath surrounding axons is damaged, disrupting nerve impulse transmission. Damage to the arbor vitae in MS can result in cerebellar dysfunction similar to that seen in stroke or tumors.
4. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI):
Traumatic brain injuries, such as those caused by falls or car accidents, can cause damage to the cerebellum, including the arbor vitae. The severity of the symptoms depends on the extent of the injury.
5. Cerebellar Atrophy:
This condition involves the gradual loss of cerebellar tissue, including the arbor vitae. It can be caused by various factors, including genetic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and prolonged alcohol abuse. Symptoms include progressive ataxia, dysmetria, and other cerebellar signs.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Several imaging techniques can be used to visualize the arbor vitae and detect abnormalities:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides high-resolution images of the brain and is particularly useful for visualizing the intricate structure of the arbor vitae. MRI can detect lesions, tumors, or other abnormalities affecting the white matter.
-
Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans can also be used to visualize the cerebellum, although the resolution is not as high as with MRI. CT scans are useful for detecting acute injuries, such as hemorrhages.
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI): DTI is a specialized MRI technique that allows for the visualization of white matter tracts, including the arbor vitae. DTI is particularly useful for assessing the integrity of white matter pathways and detecting subtle abnormalities not readily apparent on standard MRI.
Conclusion: The Arbor Vitae – A Crucial Component of Cerebellar Function
The arbor vitae, with its striking resemblance to a tree of life, is far more than just a visually appealing structure. It's a crucial component of the cerebellum, facilitating the intricate communication necessary for coordinated movement, balance, and posture. Understanding its anatomy, function, and clinical significance is essential for neurologists and other healthcare professionals involved in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebellar disorders. Damage to the arbor vitae, whether through stroke, tumor, MS, TBI, or other conditions, can lead to significant neurological deficits, highlighting the importance of this often-overlooked, yet vital, brain structure. Further research continues to unveil the intricacies of cerebellar function and the arbor vitae's specific roles within this complex system. As our understanding deepens, we can expect to develop even more effective diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for conditions impacting this crucial brain region.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Hours Is In 3 Weeks
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Y Axis Of A Velocity Time Graph Represents
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Moles In 22g Of Co2
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Toiroidal Solenoid Has A Central Radius Of 0 5m
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Blood Is A Connective Tissue
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Part Of The Brain Contains The Arbor Vitae . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
