Which Of The Following Is True About Sexual Reproduction
News Leon
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
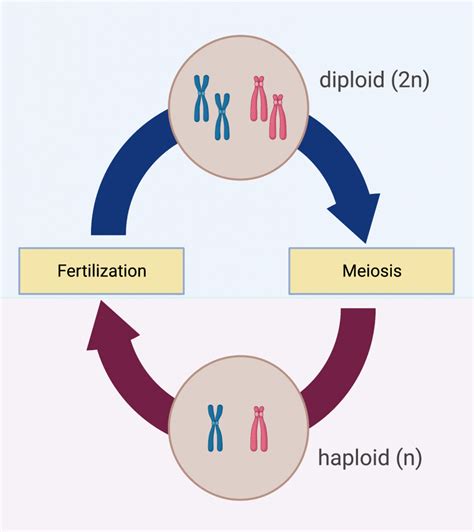
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is True About Sexual Reproduction? A Deep Dive into the Fundamentals
Sexual reproduction, a cornerstone of biological diversity, is a complex process with far-reaching consequences for the evolution and survival of species. While the basic concept might seem straightforward—two parents contributing genetic material to create offspring—the intricacies of sexual reproduction are surprisingly vast and varied. This article delves into the fundamental truths surrounding sexual reproduction, exploring its mechanisms, advantages, disadvantages, and evolutionary significance. We will unpack several common statements about sexual reproduction, analyzing their accuracy and exploring the nuances behind them.
Statement 1: Sexual Reproduction Increases Genetic Variation
This statement is TRUE. This is arguably the most significant advantage of sexual reproduction. Unlike asexual reproduction, which produces genetically identical clones, sexual reproduction combines the genetic material of two parents through the process of meiosis and fertilization.
Meiosis: The Foundation of Genetic Diversity
Meiosis, a specialized type of cell division, is the cornerstone of genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms. During meiosis, the diploid cells (containing two sets of chromosomes) undergo two rounds of division, resulting in four haploid cells (containing one set of chromosomes). Crucially, crossing over occurs during meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This process shuffles alleles (different versions of a gene), creating new combinations of genes that were not present in either parent.
Fertilization: The Fusion of Genetic Material
Fertilization, the fusion of two haploid gametes (sperm and egg), further contributes to genetic variation. The combination of chromosomes from two different individuals ensures that the offspring inherits a unique blend of genetic information. This random assortment of chromosomes from each parent vastly increases the potential for genetic diversity within a population. The sheer number of possible chromosome combinations is astronomical, even in organisms with relatively few chromosomes.
The Evolutionary Significance of Genetic Variation
The increased genetic variation generated by sexual reproduction is vital for the long-term survival of a species. It allows populations to adapt more effectively to changing environmental conditions. Individuals with advantageous gene combinations are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their beneficial traits to the next generation. This process of natural selection drives evolution and shapes the diversity of life on Earth.
Statement 2: Sexual Reproduction Requires Two Parents
This statement is TRUE. By definition, sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two separate parents. Each parent contributes a haploid gamete, which fuses during fertilization to form a diploid zygote. This fundamental requirement distinguishes sexual reproduction from asexual reproduction, which can occur in a single parent organism.
Statement 3: Sexual Reproduction Produces Offspring Genetically Identical to the Parents
This statement is FALSE. As discussed previously, sexual reproduction inherently generates genetic variation. Offspring inherit a unique combination of genes from both parents, resulting in offspring that are genetically distinct from either parent. While offspring may share some similarities with their parents, they are never genetically identical. This is a key differentiator between sexual and asexual reproduction, where offspring are essentially clones of the parent.
Statement 4: Sexual Reproduction is More Energy-Intensive Than Asexual Reproduction
This statement is TRUE. Sexual reproduction demands a significant energy investment compared to asexual reproduction. The process involves finding a mate, courtship rituals, gamete production, and the energetic demands of pregnancy and offspring care in many species. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, is significantly simpler and requires less energy expenditure. A single parent can reproduce without the need for a mate, leading to faster population growth under ideal conditions.
Statement 5: Sexual Reproduction is Less Efficient in Producing Offspring
This statement is TRUE, in terms of sheer numbers. Asexual reproduction often leads to a greater number of offspring in a shorter time frame. A single parent can produce numerous offspring without the need to invest time and energy in finding a mate. Sexual reproduction, however, limits the number of offspring produced by the need for two parents and the biological constraints of reproduction. This trade-off, however, is compensated for by the advantages of increased genetic diversity.
Statement 6: Sexual Reproduction is Essential for the Evolution of Complex Organisms
This statement is largely TRUE. While some simple organisms utilize asexual reproduction successfully, the prevalence of sexual reproduction in complex organisms suggests its importance in driving evolutionary innovation. The increased genetic variation produced by sexual reproduction provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, leading to the evolution of complex adaptations and specialized traits. The shuffling of genes and the introduction of new gene combinations through sexual reproduction are crucial for generating the diversity necessary for complex life forms to evolve and adapt to diverse environments.
Statement 7: Sexual Reproduction is Always Advantageous
This statement is FALSE. While sexual reproduction offers significant advantages in terms of genetic diversity and adaptability, it also has drawbacks. The energy investment required and the slower rate of reproduction compared to asexual reproduction can be disadvantages, particularly in stable environments where rapid population growth is advantageous. Furthermore, the process of finding a mate can be challenging and risky, potentially exposing organisms to predation or disease.
Statement 8: All Organisms Reproduce Sexually
This statement is FALSE. Many organisms reproduce asexually, a process that produces offspring genetically identical to the parent. This can be advantageous in stable environments, allowing for rapid population growth. Asexual reproduction occurs through various mechanisms, including budding, binary fission, and fragmentation. Examples of organisms that reproduce asexually include bacteria, some protists, certain plants, and even some invertebrates.
Statement 9: Sexual Reproduction Guarantees the Survival of a Species
This statement is FALSE. While sexual reproduction enhances the chances of survival for a species by increasing genetic diversity and adaptability, it does not guarantee survival. Environmental factors, disease outbreaks, catastrophic events, and other factors can still lead to the extinction of species, regardless of their reproductive strategy. Genetic diversity is a crucial factor in resilience, but it is not a guarantee against extinction.
Statement 10: The Evolution of Sexual Reproduction Remains a Mystery
This statement is partially TRUE. While the basic mechanisms of sexual reproduction are well-understood, the evolutionary origins of sexual reproduction are still debated. The transition from asexual to sexual reproduction represents a significant evolutionary shift, and the selective pressures that drove this transition are complex and not fully elucidated. Several hypotheses attempt to explain the evolution of sexual reproduction, including the "Red Queen Hypothesis," which suggests that sexual reproduction is advantageous in an arms race against parasites and pathogens.
Conclusion: Understanding the Nuances of Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a powerful driving force behind biological diversity and the evolution of complex life. While it offers significant advantages in terms of generating genetic variation and adaptability, it also comes with energetic costs and risks. Understanding the complexities of sexual reproduction and its evolutionary implications is essential for comprehending the vast tapestry of life on Earth. The statements explored above highlight the multifaceted nature of sexual reproduction, demonstrating that the seemingly simple process is underpinned by intricate biological mechanisms and evolutionary pressures. The ongoing research into sexual reproduction continues to uncover new insights, further illuminating its significance in shaping the biodiversity we observe today.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Codon Is Composed Of How Many Nucleotides
Apr 04, 2025
-
Is The First Step In The Decision Making Process
Apr 04, 2025
-
Pressure In A Liquid Depends On The
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Region Of The Nephron Is Impermeable To Water
Apr 04, 2025
-
Whats The Thinnest Layer Of The Earth Called
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True About Sexual Reproduction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
