Which Of The Following Is Not True About Insulin
News Leon
Apr 08, 2025 · 6 min read
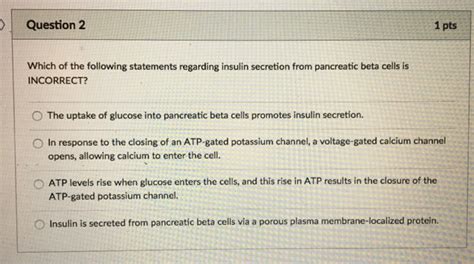
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is NOT True About Insulin? Debunking Common Myths
Insulin. The word itself often conjures images of diabetes, needles, and strict diets. While it's undeniably crucial for managing blood sugar, many misconceptions surround this vital hormone. This comprehensive article will delve into common beliefs about insulin, separating fact from fiction and clarifying its role in the body. We'll explore its functions, production, and the consequences of imbalances, aiming to provide a clear and accurate understanding of this complex yet essential molecule.
Insulin's Primary Role: Regulating Blood Glucose
Before debunking myths, let's establish the fundamental truth: insulin's primary function is to regulate blood glucose levels. After we eat, our bodies break down carbohydrates into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. This rise in blood sugar triggers the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin then acts as a key, unlocking the doors of cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles. Without sufficient insulin, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia – a hallmark of diabetes.
Understanding the Insulin Resistance Phenomenon
A common misconception is that insulin simply “lowers blood sugar.” While it does lower blood sugar, it's more accurate to say it facilitates glucose uptake into cells. This process can be impaired in a condition called insulin resistance. In insulin resistance, cells become less responsive to insulin's signals, meaning glucose struggles to enter cells even when insulin is present. This forces the pancreas to produce more insulin to compensate, eventually leading to exhaustion and potentially type 2 diabetes.
Debunking Common Myths About Insulin
Now, let's address some common misconceptions surrounding insulin:
Myth 1: Insulin is Only for Diabetics
False. While individuals with diabetes often require insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar, insulin is essential for everyone. Even people without diabetes rely on insulin to regulate their blood glucose levels. The difference lies in the amount of insulin produced and the body's sensitivity to it. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas doesn't produce insulin at all, necessitating external supplementation. In type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or doesn't use it efficiently (insulin resistance). However, everyone needs insulin for proper glucose metabolism.
Myth 2: Insulin is a "Fat Storage" Hormone
Partially True, but Oversimplified. Insulin does promote fat storage, but this is a secondary effect of its primary function. When glucose levels are high, insulin facilitates glucose uptake into fat cells, leading to fat storage. However, to label it solely as a "fat storage" hormone is misleading. Its primary role is glucose regulation. Moreover, insulin also plays a role in protein synthesis and other metabolic processes. Viewing insulin solely as a fat storage hormone ignores its broader metabolic functions and can lead to unhealthy dietary choices and misconceptions about weight management.
Myth 3: All Insulin is the Same
False. There are various types of insulin, differing in their onset of action, peak effect, and duration. Some act rapidly, while others have a longer-lasting effect. The type of insulin prescribed depends on an individual's needs and the specific requirements of their treatment plan. Ranging from rapid-acting insulins used before meals to long-acting basal insulins providing a continuous background level, the variety ensures tailored management of blood glucose. The choice of insulin involves careful consideration by healthcare professionals and is highly individualized.
Myth 4: Insulin Injections are Painful and Inconvenient
Overstated. While the initial thought of needles might be daunting, modern insulin delivery systems have significantly improved the process. Many find injections less painful than initially anticipated, and pain management strategies are available. Furthermore, insulin pens are now widely used, offering a more user-friendly and discreet method of administration compared to traditional syringes. In addition, insulin pumps provide continuous subcutaneous insulin delivery, minimizing the need for multiple daily injections and providing better glycemic control.
Myth 5: Insulin Causes Weight Gain
Complex and Context-Dependent. While weight gain is a common side effect of insulin therapy, it isn't an inevitable consequence. Weight gain can be attributed to multiple factors, including increased insulin levels leading to increased glucose uptake and storage as fat, the potential for increased appetite, or the nature of the associated dietary changes necessary to manage blood sugar effectively. However, proper management of insulin dosage and diet can often mitigate this side effect.
Myth 6: Insulin Can Be Taken Orally
False. Insulin is a protein hormone, and if taken orally, it would be broken down by digestive enzymes in the stomach and intestines before it could reach the bloodstream and exert its effects. Therefore, insulin must be administered via injection or infusion to bypass the digestive system and directly enter the bloodstream.
Myth 7: High Insulin Levels Always Mean Diabetes
False. While persistently high insulin levels are often associated with diabetes (particularly type 2), temporary elevations can occur due to various factors, including carbohydrate intake, stress, and certain medications. It's crucial to interpret insulin levels within the context of other factors, such as blood glucose levels and overall health status.
Myth 8: Once You Start Insulin, You're on it for Life
Oversimplification. This statement depends entirely on the underlying cause of insulin deficiency or resistance. In type 1 diabetes, insulin is a lifelong necessity. However, in type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes, weight loss, and other medications may allow some individuals to discontinue insulin therapy, especially if it was initially used to temporarily manage blood sugar during a crisis. Consult your physician for advice specific to your condition.
The Importance of Accurate Information and Professional Guidance
Misconceptions about insulin can lead to poor health management, especially for those with diabetes. Accurate information is crucial for understanding insulin's role in the body, managing diabetes effectively, and making informed decisions about health. It’s vital to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans related to insulin and blood sugar management.
Conclusion: Understanding Insulin for Optimal Health
Insulin is a fundamental hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels, a process critical for maintaining overall health. While several myths surround insulin, a clear understanding of its function and the realities of insulin therapy is essential for informed decision-making. By debunking common misconceptions, we aim to empower individuals with knowledge that promotes health and well-being. Remember, seeking professional guidance from healthcare providers is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and overall health. This detailed exploration aimed to clear up some common misconceptions and provide a more comprehensive understanding of this crucial hormone.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Happens When A Star Exhausts Its Core Hydrogen Supply
Apr 08, 2025
-
Find The Value Of X In A Kite
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Regarding The Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Apr 08, 2025
-
Draw Significant Resonance Structures For The Following Compound
Apr 08, 2025
-
Difference Between A Mirror And A Lens
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Not True About Insulin . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.