Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Muscle
News Leon
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
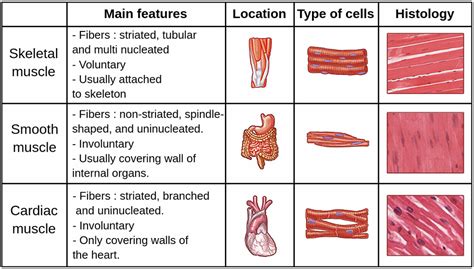
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is NOT a Type of Muscle? Understanding Muscle Tissue Classification
The human body is a marvel of engineering, and a key component of this intricate system is muscle tissue. Responsible for movement, posture, and even vital functions like breathing and digestion, muscles are crucial for our survival. But how well do you understand the different types of muscle tissue? This comprehensive guide will explore the three main types – skeletal, smooth, and cardiac – and clarify which of the options presented isn't a true muscle type.
The Three Main Types of Muscle Tissue
Before we delve into identifying the imposter, let's solidify our understanding of the three genuine types of muscle tissue. Each type possesses distinct characteristics influencing its function and location within the body.
1. Skeletal Muscle: The Voluntary Movers
Skeletal muscle tissue is what most people associate with the word "muscle." These muscles are attached to bones via tendons, enabling voluntary movement. Think about walking, lifting weights, or even smiling – these actions are all controlled by your skeletal muscles.
Key Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle:
- Voluntary Control: You consciously decide when and how to contract these muscles.
- Striated Appearance: Under a microscope, skeletal muscle shows a striped or striated pattern due to the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments.
- Multinucleated Cells: Each muscle fiber (cell) contains multiple nuclei.
- Rapid Contraction: Skeletal muscles contract quickly and powerfully but can also tire relatively easily.
- Examples: Biceps brachii, quadriceps femoris, deltoids, gastrocnemius.
2. Smooth Muscle: The Unseen Workers
Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle operates largely without conscious control. It's found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, and other structures. Its functions are critical, regulating processes like digestion, blood pressure, and respiration.
Key Characteristics of Smooth Muscle:
- Involuntary Control: You don't consciously control the contraction of smooth muscle. It's regulated by the autonomic nervous system and hormones.
- Non-Striated Appearance: Smooth muscle lacks the striated pattern seen in skeletal muscle.
- Single Nucleus per Cell: Each smooth muscle cell typically contains only one nucleus.
- Slow and Sustained Contractions: Smooth muscle contractions are slower and more sustained than skeletal muscle contractions.
- Examples: Muscles in the walls of the stomach, intestines, bladder, blood vessels.
3. Cardiac Muscle: The Heart's Engine
Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It's responsible for the rhythmic contractions that pump blood throughout the body. Like smooth muscle, it's involuntary, meaning you don't consciously control its beating.
Key Characteristics of Cardiac Muscle:
- Involuntary Control: The heart beats automatically, regulated by specialized pacemaker cells within the heart itself.
- Striated Appearance: Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle exhibits a striated pattern.
- Branching Cells: Cardiac muscle cells are branched and interconnected, forming a functional syncytium, allowing coordinated contractions.
- Intercalated Discs: These specialized junctions between cardiac muscle cells facilitate rapid communication and coordinated contraction.
- Self-Excitation: Cardiac muscle cells can generate their own action potentials, enabling the heart to beat independently.
Identifying the Non-Muscle Tissue
Now, let's address the core question: which of the following is not a type of muscle tissue? To answer accurately, we need the options to be provided. However, I can anticipate some common possibilities and explain why they wouldn't be classified as muscle tissue.
Commonly Confused Tissues:
-
Connective Tissue: This is a broad category encompassing tissues like bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and adipose (fat) tissue. While connective tissues support and connect different parts of the body, they don't have the contractile properties characteristic of muscle. They lack the specialized proteins (actin and myosin) responsible for muscle contraction.
-
Nervous Tissue: This tissue comprises neurons and glial cells, responsible for transmitting electrical signals throughout the body. While neurons can influence muscle contraction by sending signals, nervous tissue itself is not contractile.
-
Epithelial Tissue: This tissue forms linings and coverings throughout the body, including the skin, lining of organs, and blood vessels. Epithelial tissues protect, secrete, and absorb, but they are not involved in movement or contraction.
-
Adipose Tissue (Fat): This is a type of connective tissue that stores energy in the form of fat. It plays various roles, including insulation and cushioning, but lacks the contractile function of muscle.
Examples of Multiple Choice Questions & Answers:
Here are a few examples illustrating how to identify non-muscle tissue from a list:
Example 1:
Which of the following is NOT a type of muscle tissue?
a) Skeletal muscle b) Smooth muscle c) Cardiac muscle d) Connective tissue
Answer: d) Connective tissue
Example 2:
Which of the following is NOT a type of muscle tissue?
a) Skeletal muscle b) Adipose tissue c) Smooth muscle d) Cardiac muscle
Answer: b) Adipose tissue
Example 3:
Which of the following is NOT a type of muscle tissue?
a) Cardiac muscle b) Nervous tissue c) Skeletal muscle d) Smooth muscle
Answer: b) Nervous tissue
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Muscle Tissue Complexity
The classification of muscle tissue into skeletal, smooth, and cardiac is a simplification of a complex system. Within each category, there are further subdivisions and nuances based on fiber type, contractile properties, and regulatory mechanisms.
For example: Skeletal muscle fibers can be classified as slow-twitch or fast-twitch, reflecting their speed of contraction and resistance to fatigue. These differences are crucial for understanding muscle performance in various activities, from endurance running to weightlifting.
Similarly, smooth muscle can be further categorized based on its location and response to different stimuli. Understanding these nuances is vital in fields like pharmacology and physiology. For example, different drugs target specific types of smooth muscle to achieve therapeutic effects.
Clinical Significance: Understanding Muscle Disorders
Proper understanding of muscle tissue is crucial for diagnosing and treating various muscle disorders. Conditions affecting any of the three muscle types can have significant impacts on overall health.
-
Skeletal muscle disorders: These can range from relatively minor injuries like strains and sprains to serious conditions like muscular dystrophy, which involves progressive muscle degeneration.
-
Smooth muscle disorders: Dysfunction in smooth muscle can lead to problems with digestion, blood pressure regulation, and other vital processes.
-
Cardiac muscle disorders: Conditions affecting the cardiac muscle are particularly serious, including heart attacks, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Conclusion: A Deeper Appreciation for Muscle Tissue
This exploration of muscle tissue clarifies the three main types – skeletal, smooth, and cardiac – and highlights why other tissue types, such as connective tissue, nervous tissue, and adipose tissue, are not classified as muscle. Understanding the unique properties of each muscle type is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the human body, as well as diagnosing and treating various muscle disorders. The intricate interplay between these muscle types and other bodily systems showcases the remarkable efficiency and intricacy of human physiology. Remember, continuous learning and exploration are key to expanding your understanding of this fascinating subject.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Lysosomes Have A Double Membrane
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of B Cells
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Parents Are Involved In Asexual Reproduction
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Order Of The Breakdown Products Of Hemoglobin
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Muscle Subdivides The Ventral Body Cavity
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Muscle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
