Which Of The Following Is An Alkaline Earth Metal
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
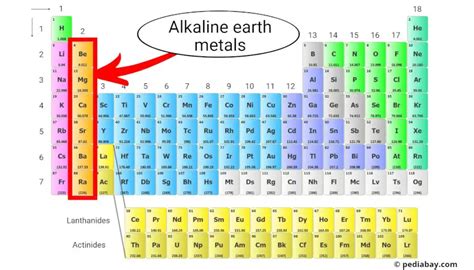
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is an Alkaline Earth Metal? A Comprehensive Guide
Alkaline earth metals are a fascinating group of elements that play crucial roles in various aspects of our lives, from the construction industry to biological processes. Understanding their properties and characteristics is key to appreciating their significance. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the properties of alkaline earth metals, helping you identify them and understand their unique place on the periodic table. We'll explore their chemical behavior, physical properties, and practical applications, ensuring you have a complete understanding of this important element group.
What are Alkaline Earth Metals?
Alkaline earth metals belong to Group 2 of the periodic table. They are characterized by having two electrons in their outermost shell, making them highly reactive. This reactivity stems from their tendency to lose these two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, similar to the noble gases. This tendency dictates their chemical and physical properties.
Key Characteristics of Alkaline Earth Metals:
- Two Valence Electrons: The defining feature is the presence of two electrons in their outermost energy level. This readily explains their reactivity.
- Relatively High Reactivity: While less reactive than the alkali metals (Group 1), they are still considerably reactive, particularly with water and oxygen.
- Electropositive Nature: They readily lose electrons, forming positively charged ions (cations) with a +2 charge.
- Metallic Properties: They exhibit typical metallic properties like good conductivity of heat and electricity, malleability, and ductility (though less so than some other metals).
- Increasing Reactivity Down the Group: As you move down Group 2 from beryllium to radium, the reactivity increases due to the increasing atomic radius and decreasing ionization energy.
Identifying Alkaline Earth Metals
Identifying an alkaline earth metal involves understanding the characteristic properties discussed above. Let's explore this with a focus on how these properties help in distinguishing them from other elements.
Differentiating from Alkali Metals (Group 1)
While both groups are highly reactive, alkaline earth metals are generally less reactive than alkali metals. This difference in reactivity is crucial for distinguishing them. For instance, alkaline earth metals react more slowly with water than alkali metals. The +2 charge of alkaline earth metal ions also contrasts with the +1 charge of alkali metal ions, influencing their chemical behavior.
Differentiating from Transition Metals
Transition metals, found in the d-block of the periodic table, are characterized by variable oxidation states and the formation of colored compounds. Alkaline earth metals, on the other hand, predominantly exhibit a +2 oxidation state and their compounds are typically colorless or white. This difference in oxidation states and color provides a clear distinction.
Differentiating from Other Groups
Comparing alkaline earth metals with elements from other groups highlights their unique characteristics. For example, unlike the halogens (Group 17) which readily gain electrons, alkaline earth metals readily lose electrons. Similarly, noble gases (Group 18) are extremely unreactive, a stark contrast to the reactivity of alkaline earth metals.
The Alkaline Earth Metals: A Closer Look
Let's examine each alkaline earth metal individually to further understand their unique characteristics and applications:
1. Beryllium (Be)
- Properties: Beryllium is a relatively rare element, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and high melting point. It is also quite toxic.
- Applications: Used in aerospace alloys, nuclear reactors, and X-ray windows.
2. Magnesium (Mg)
- Properties: Lightweight, strong, and relatively abundant. It is highly reactive but less so than other alkaline earth metals.
- Applications: Used in lightweight alloys for automobiles, airplanes, and other applications. Also used in flash photography and as a dietary supplement.
3. Calcium (Ca)
- Properties: Essential for biological processes, particularly bone formation. Reacts readily with water and oxygen.
- Applications: Used in cement, plaster, and as a reducing agent in metallurgy. Crucial in biological systems.
4. Strontium (Sr)
- Properties: Similar to calcium but slightly more reactive. Its compounds produce bright red colors in fireworks.
- Applications: Used in fireworks, some alloys, and in certain medical applications.
5. Barium (Ba)
- Properties: Highly reactive and toxic. Its compounds are used to produce green colors in fireworks.
- Applications: Used in fireworks, certain types of glass, and as a component in some catalysts.
6. Radium (Ra)
- Properties: Radioactive and highly reactive. Very rare and highly toxic.
- Applications: Limited applications due to its radioactivity and rarity. Historically used in radiotherapy.
Real-World Applications of Alkaline Earth Metals
The alkaline earth metals find numerous applications in diverse fields:
1. Construction and Materials Science: Calcium-based compounds like lime (calcium oxide) and gypsum (calcium sulfate) are fundamental materials in the construction industry for cement, plaster, and drywall. Magnesium alloys are used in lightweight construction materials.
2. Metallurgy: Magnesium and calcium are used as reducing agents in the extraction of other metals. Beryllium alloys are used in aerospace applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
3. Biological Systems: Calcium and magnesium are essential elements for biological life. Calcium plays a vital role in bone formation and muscle function, while magnesium is crucial for enzyme activity and other metabolic processes.
4. Pyrotechnics: Strontium and barium compounds are widely used in fireworks to produce bright red and green colors, respectively. Magnesium is also used for its bright white light.
5. Medical Applications: Certain strontium compounds are used in medical imaging and treatments.
Conclusion
Alkaline earth metals represent a group of elements with distinctive properties and widespread applications. Understanding their characteristic two valence electrons, high reactivity (though less than alkali metals), and formation of +2 ions is key to their identification and appreciation of their significance. From construction materials to essential biological roles and vibrant fireworks displays, these elements play a vital role in our world. By understanding their properties and applications, we can better appreciate their importance in various fields and utilize their unique characteristics effectively. This in-depth look provides a robust foundation for further study and exploration of this fascinating group of elements. Remember, always handle these metals and their compounds with care, paying attention to safety precautions due to their varying levels of reactivity and toxicity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Part Of The Scapula Articulates With The Clavicle
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Languages Did Helen Keller Know
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Ribs Do Rabbits Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
30 Is What Percent Of 48
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Only Language That A Computer Can Understand
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Alkaline Earth Metal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
