Which Of The Following Is A Combination Reaction
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
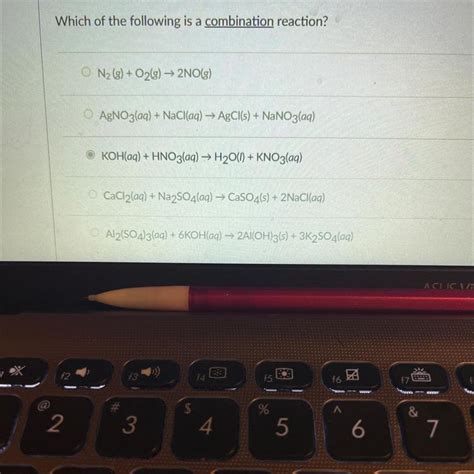
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Is A Combination Reaction
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following is a Combination Reaction? A Deep Dive into Chemical Reactions
- What is a Combination Reaction?
- Key Characteristics of Combination Reactions
- Examples of Combination Reactions
- 1. Formation of Metal Oxides:
- 2. Formation of Non-metal Oxides:
- 3. Formation of Metal Halides:
- 4. Formation of Water:
- 5. Formation of Compounds from their elements:
- Differentiating Combination Reactions from Other Reaction Types
- Identifying Combination Reactions: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Combination Reactions in Everyday Life
- Combination Reactions in Industry
- Advanced Topics in Combination Reactions
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following is a Combination Reaction? A Deep Dive into Chemical Reactions
Understanding chemical reactions is fundamental to grasping the world around us. From the rusting of iron to the burning of wood, countless processes involve the transformation of matter. One crucial type of reaction is the combination reaction, also known as a synthesis reaction. This article will delve into the intricacies of combination reactions, explaining what they are, how to identify them, and providing numerous examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also explore how to differentiate combination reactions from other reaction types, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of this essential chemical concept.
What is a Combination Reaction?
A combination reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. This contrasts with decomposition reactions, where a single reactant breaks down into two or more products. The general form of a combination reaction can be represented as:
A + B → AB
Where A and B are reactants, and AB is the single product formed. The reaction involves the formation of new chemical bonds between the reactants, resulting in a completely new substance with different chemical and physical properties. It's important to note that the reactants can be elements or compounds, but the product is always a single compound.
Key Characteristics of Combination Reactions
Several key characteristics help distinguish combination reactions from other types of chemical reactions:
- Formation of a single product: This is the most defining feature. Regardless of the number of reactants, only one product is formed.
- Increase in complexity: The product is generally more complex than the individual reactants. This increased complexity reflects the formation of new chemical bonds.
- Energy changes: Combination reactions can be either exothermic (releasing heat) or endothermic (absorbing heat). The energy change depends on the specific reactants and the strength of the bonds formed.
- Often irreversible: While some combination reactions can be reversed under specific conditions, many are essentially irreversible under normal circumstances.
Examples of Combination Reactions
Let's examine several examples to illustrate the diverse nature of combination reactions:
1. Formation of Metal Oxides:
Many metals react with oxygen in the air to form metal oxides. A classic example is the reaction between iron and oxygen to produce iron(III) oxide (rust):
4Fe(s) + 3O₂(g) → 2Fe₂O₃(s)
This reaction is exothermic and responsible for the corrosion of iron. Similarly, the reaction of magnesium with oxygen produces magnesium oxide:
2Mg(s) + O₂(g) → 2MgO(s)
This reaction is also exothermic and produces a bright white light, often used in flares.
2. Formation of Non-metal Oxides:
Non-metals also react with oxygen to form non-metal oxides. For instance, the combustion of carbon in the presence of oxygen yields carbon dioxide:
C(s) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g)
This reaction is crucial in various combustion processes, including the burning of fossil fuels. Similarly, the reaction of sulfur with oxygen produces sulfur dioxide:
S(s) + O₂(g) → SO₂(g)
Sulfur dioxide is a significant air pollutant.
3. Formation of Metal Halides:
Metals react vigorously with halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine) to form metal halides. For example, the reaction between sodium and chlorine produces sodium chloride (common table salt):
2Na(s) + Cl₂(g) → 2NaCl(s)
This reaction is highly exothermic and releases considerable heat.
4. Formation of Water:
The reaction between hydrogen and oxygen is a classic combination reaction that forms water:
2H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2H₂O(l)
This reaction is highly exothermic and is crucial for various industrial processes.
5. Formation of Compounds from their elements:
Many compounds can be synthesized by combining their constituent elements. For instance, combining nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature produces ammonia:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2NH₃(g)
This reaction is known as the Haber-Bosch process and is crucial for the production of fertilizers.
Differentiating Combination Reactions from Other Reaction Types
It's essential to distinguish combination reactions from other types of chemical reactions, such as decomposition, single displacement, and double displacement reactions.
- Decomposition reactions: These involve a single compound breaking down into two or more simpler substances. The opposite of a combination reaction.
- Single displacement reactions: Involve one element replacing another element in a compound.
- Double displacement reactions: Involve the exchange of ions between two compounds.
Understanding the differences between these reaction types is crucial for accurately classifying and predicting chemical reactions.
Identifying Combination Reactions: A Step-by-Step Guide
To identify a combination reaction, follow these steps:
- Count the number of reactants: Combination reactions always have two or more reactants.
- Count the number of products: Combination reactions always have only one product.
- Examine the chemical formulas: Determine if the product is a more complex molecule than the reactants.
- Consider the overall change: The reaction should involve the formation of new chemical bonds between the reactants.
If all these conditions are met, the reaction is likely a combination reaction.
Combination Reactions in Everyday Life
Combination reactions are ubiquitous in our daily lives. From the rusting of a nail to the burning of a candle, numerous processes involve the formation of a new compound from simpler reactants. Understanding these reactions helps us comprehend various phenomena and design processes for synthesizing new materials.
Combination Reactions in Industry
Combination reactions play a critical role in various industrial processes. The Haber-Bosch process for ammonia synthesis, for example, is fundamental to the production of fertilizers, impacting global food production. The synthesis of various metal oxides and halides is essential in the manufacturing of numerous materials and chemicals.
Advanced Topics in Combination Reactions
Further exploration of combination reactions can encompass:
- Reaction kinetics: Studying the rate at which combination reactions occur, including the effects of temperature, pressure, and catalysts.
- Thermodynamics: Analyzing the energy changes associated with combination reactions, including enthalpy and entropy changes.
- Mechanism: Investigating the step-by-step process through which combination reactions occur at a molecular level.
Conclusion
Combination reactions, or synthesis reactions, represent a fundamental class of chemical reactions characterized by the formation of a single product from two or more reactants. Understanding their key features, recognizing their examples, and differentiating them from other reaction types are crucial for developing a strong foundation in chemistry. This knowledge finds widespread application in various fields, from explaining everyday phenomena to driving industrial processes. By mastering the principles of combination reactions, you gain a deeper appreciation of the intricate processes shaping our physical world. Remember to always consider the number of reactants and products, and the overall complexity of the molecules involved, when determining if a reaction is a combination reaction.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Iupac Name For No2 Is
Apr 09, 2025
-
Protein Digestion Takes Place In The
Apr 09, 2025
-
What Is The Relation Between Momentum And Force
Apr 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are True About The Brain
Apr 09, 2025
-
A Line Segment Has Two Endpoints True Or False
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Combination Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.