Which Of The Following Events Occur During Anaphase I
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
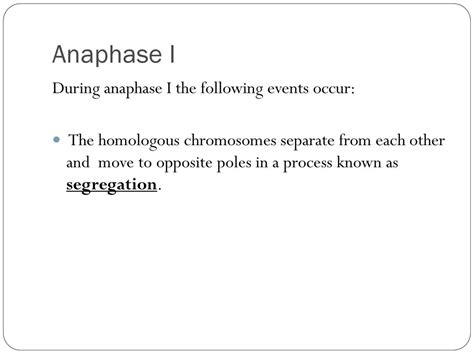
Table of Contents
Which Events Occur During Anaphase I? A Deep Dive into Meiosis
Meiosis, the specialized cell division process that produces gametes (sex cells), is crucial for sexual reproduction. Understanding the intricate steps of meiosis, particularly the events that unfold during each phase, is fundamental to grasping the mechanisms of heredity and genetic variation. This article focuses on Anaphase I, a pivotal stage in Meiosis I, detailing the key events that occur and their significance in generating genetic diversity.
The Significance of Meiosis I
Before delving into the specifics of Anaphase I, let's briefly recap the importance of Meiosis I. Meiosis is a two-part process, Meiosis I and Meiosis II, resulting in four haploid daughter cells from a single diploid parent cell. The reduction in chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) is crucial because it ensures that when two gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote retains the correct diploid chromosome number characteristic of the species. Meiosis I is particularly important because it's where homologous chromosomes separate, a process that directly contributes to genetic variation.
Anaphase I: The Separation of Homologous Chromosomes
Anaphase I is the stage of Meiosis I where the homologous chromosomes are physically separated and pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. This separation is unlike the separation of sister chromatids in mitosis or Anaphase II. The key events occurring during Anaphase I include:
1. Separation of Homologous Chromosomes: The Hallmark of Anaphase I
The most defining event of Anaphase I is the disjunction of homologous chromosomes. Remember that during Prophase I, homologous chromosomes paired up forming bivalents (tetrads). In Anaphase I, these homologous pairs are separated. It's crucial to understand that sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere; it is the homologous chromosomes that separate. This is a fundamental difference between Anaphase I and Anaphase II.
Key Players: The separation is driven by the shortening of kinetochore microtubules attached to the kinetochores of each homologous chromosome. These microtubules are part of the spindle apparatus, a complex structure responsible for chromosome movement during cell division. Motor proteins associated with the microtubules and kinetochores actively contribute to the pulling force.
2. Movement Towards Opposite Poles: A Precise Orchestration
As the kinetochore microtubules shorten, the homologous chromosomes move towards opposite poles of the cell. This movement is not random; it's a highly coordinated process ensuring that each pole receives one chromosome from each homologous pair. This ensures the correct reduction in chromosome number from diploid to haploid.
Potential for Error: Although the process is tightly regulated, errors can occur during Anaphase I. Non-disjunction, the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly, can lead to gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes. This is a significant cause of genetic disorders like Down syndrome (trisomy 21).
3. Chiasmata Resolution and Genetic Recombination: The Legacy of Crossing Over
The separation of homologous chromosomes in Anaphase I is directly linked to the events of Prophase I, specifically crossing over. During Prophase I, homologous chromosomes exchange segments of DNA at points called chiasmata. This exchange of genetic material, known as genetic recombination, is a crucial mechanism for generating genetic diversity. In Anaphase I, the chiasmata are resolved as the homologous chromosomes separate, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a chromosome with a unique combination of alleles.
Importance of Genetic Recombination: Genetic recombination is essential for the evolution and adaptation of populations. It generates new combinations of alleles that may be beneficial in changing environments. This shuffling of genetic material is a major driver of genetic diversity within a species.
4. Independent Assortment: The Random Distribution of Chromosomes
Another crucial aspect of Anaphase I is the independent assortment of homologous chromosomes. The orientation of each homologous pair on the metaphase plate (during Metaphase I) is random. This means that maternal and paternal chromosomes are distributed independently to the daughter cells. This random segregation further contributes to the genetic variation among the gametes produced.
Combinatorial Diversity: Independent assortment dramatically increases the number of possible chromosome combinations in the gametes. For example, in a species with two pairs of homologous chromosomes (2n=4), independent assortment generates four different gametes. With more chromosome pairs, the number of possible combinations increases exponentially.
5. The Role of the Cytoskeleton: Microtubules and Motor Proteins
The entire process of chromosome separation in Anaphase I is orchestrated by the cytoskeleton, specifically the microtubules of the spindle apparatus. These microtubules, along with associated motor proteins, provide the force necessary for chromosome movement. The dynamic instability of microtubules, their ability to grow and shrink, is crucial for accurate chromosome segregation.
Regulation of Microtubule Dynamics: The accurate separation of homologous chromosomes requires precise regulation of microtubule dynamics. This regulation is controlled by a complex interplay of proteins that affect microtubule polymerization and depolymerization. Disruptions to this regulation can lead to errors in chromosome segregation.
Contrasting Anaphase I with Anaphase II
It's important to distinguish Anaphase I from Anaphase II. While both phases involve chromosome separation, the nature of the separation differs significantly:
| Feature | Anaphase I | Anaphase II |
|---|---|---|
| Separating | Homologous chromosomes | Sister chromatids |
| Chromosome Number | Reduced from 2n to n | Remains n |
| Genetic Variation | Contributes significantly through disjunction and independent assortment | Does not generate significant genetic variation |
| Centromeres | Remain intact | Separate |
Consequences of Errors in Anaphase I
Errors during Anaphase I, particularly non-disjunction, have significant consequences. Non-disjunction leads to gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes – aneuploidy. When these aneuploid gametes participate in fertilization, the resulting zygote may have an abnormal chromosome number, leading to various genetic disorders. These disorders can range from mild developmental problems to severe conditions incompatible with life.
Conclusion: Anaphase I – A Cornerstone of Genetic Diversity
Anaphase I is a critical stage in Meiosis I, characterized by the separation of homologous chromosomes. This separation, coupled with crossing over and independent assortment, is the foundation of genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms. Understanding the intricate events of Anaphase I, their precise choreography, and the potential for errors is vital for appreciating the mechanisms of heredity, the generation of genetic variation, and the causes of chromosomal abnormalities. The delicate balance of microtubule dynamics, motor proteins, and regulatory mechanisms ensures the faithful segregation of chromosomes, guaranteeing the integrity of the genetic information passed on to the next generation. Errors in this process underscore the importance of meticulous cellular control and highlight the significant consequences of deviations from the precise mechanisms driving meiosis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Rational
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Word Atom Comes From A Greek Word That Means
Mar 19, 2025
-
Moment Of Inertia For Hollow Sphere
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Rhombus Have
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Hinge Joint
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Events Occur During Anaphase I . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
