Which Is A Correct Way Of Stating Boyle's Law
News Leon
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
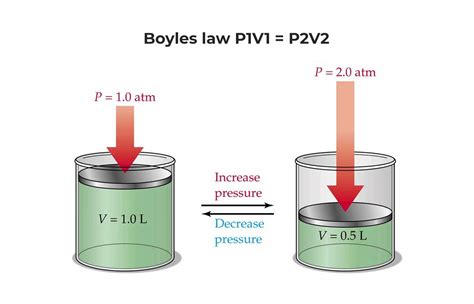
Table of Contents
Which is the Correct Way of Stating Boyle's Law? Understanding Pressure-Volume Relationships
Boyle's Law, a cornerstone of ideal gas behavior, describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas when temperature and the amount of gas are held constant. While the fundamental concept is straightforward, the precise way to state Boyle's Law can be nuanced, leading to potential confusion. This article delves deep into the various ways Boyle's Law is expressed, clarifies the correct and most accurate formulations, and explores common misconceptions. We’ll also examine the implications of Boyle's Law in various applications and its limitations when applied to real gases.
Understanding the Core Principle: Inverse Proportionality
At the heart of Boyle's Law lies the concept of inverse proportionality. This means that as one variable (pressure) increases, the other variable (volume) decreases proportionally, and vice-versa, provided the temperature and the amount of gas remain unchanged. This inverse relationship can be visually represented by a hyperbola on a pressure-volume graph.
Common Ways to State Boyle's Law: A Comparative Analysis
Boyle's Law is often presented in several ways, each with subtle differences in emphasis and mathematical representation. Let's examine some common formulations and assess their accuracy:
1. The Qualitative Statement:
- "For a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature, the volume is inversely proportional to the pressure."
This is a perfectly acceptable qualitative statement. It accurately captures the essence of the law without resorting to mathematical equations. It emphasizes the relationship between pressure and volume. While not as precise as the mathematical expressions, it's effective in conveying the fundamental principle to a broader audience.
2. The Proportional Statement:
- "At constant temperature and amount of gas, the product of pressure and volume is constant."
This is another accurate statement, although mathematically oriented. It expresses the relationship using the concept of a constant product. This form is frequently used in introductory physics and chemistry texts due to its simplicity and direct link to the mathematical equation. The constant (often denoted as 'k') represents a value specific to the given amount of gas at a specific temperature.
3. The Mathematical Equation:
- P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
This is the most concise and commonly used representation of Boyle's Law. It utilizes subscripts to represent the initial (1) and final (2) states of the gas. This equation is particularly useful for solving problems involving pressure and volume changes under constant temperature conditions. This is the most direct and practical way to use Boyle's Law in calculations.
- PV = k (where k is a constant)
This is an alternative mathematical representation. It expresses the constant relationship between pressure and volume more directly. This form highlights the unchanging product of pressure and volume. While less frequently used for problem-solving compared to P₁V₁ = P₂V₂, it provides a concise mathematical summary of the law.
Debunking Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions often surround the statement and application of Boyle's Law:
-
Ignoring the constant conditions: A critical error is forgetting that Boyle's Law only applies when both temperature and the amount of gas (number of moles) remain constant. Any changes in these parameters invalidate the law. The law specifically describes an isothermal process (constant temperature).
-
Confusing direct and inverse proportionality: Some students mistakenly interpret the relationship as a direct proportionality, where increasing pressure increases volume. It's crucial to emphasize the inverse relationship.
-
Incorrect unit usage: Using inconsistent units for pressure and volume will lead to incorrect results. Ensure consistent units (e.g., atm and L, kPa and m³, etc.) throughout the calculation.
-
Extrapolation beyond ideal gas conditions: Boyle's Law accurately predicts the behavior of ideal gases. However, real gases deviate from ideal behavior, especially at high pressures and low temperatures. Applying Boyle's Law to real gases under such conditions may lead to significant errors.
Applications of Boyle's Law in Real-World Scenarios
Boyle's Law finds practical application in numerous fields:
-
Pneumatics: The design and operation of pneumatic systems, such as air brakes, rely heavily on Boyle's Law. Understanding pressure-volume relationships is crucial for predicting the performance of such systems.
-
Respiratory Physiology: Boyle's Law plays a vital role in the mechanism of breathing. The expansion and contraction of the lungs alter the lung volume, resulting in changes in pressure that drive air into and out of the lungs.
-
Diving: Divers must understand Boyle's Law to account for the effects of pressure changes on gas volume at different depths. Failure to do so can result in serious injury or death due to gas expansion or compression.
-
Weather Balloons: The expansion of weather balloons as they rise to higher altitudes is a direct consequence of Boyle's Law. The decreasing atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes causes the balloon's gas to expand.
-
Aerosol Cans: Aerosol cans utilize Boyle's Law. When the valve is pressed, the pressure inside the can decreases, causing the propellant to expand and push the product out.
Limitations of Boyle's Law: The Ideal Gas Assumption
Boyle's Law, while a powerful tool for understanding gas behavior, is based on the assumption of an ideal gas. Ideal gases are hypothetical gases that follow certain assumptions, such as having negligible intermolecular forces and negligible molecular volume. Real gases, however, deviate from this ideal behavior, particularly at high pressures and low temperatures.
At high pressures, the volume occupied by the gas molecules themselves becomes significant, and intermolecular forces become more substantial, leading to deviations from the inverse proportionality predicted by Boyle's Law. At low temperatures, intermolecular attractions become more pronounced, reducing the gas's tendency to expand.
Beyond Boyle's Law: Incorporating Temperature and Amount of Gas
To accurately describe gas behavior under conditions where temperature and the amount of gas are not constant, we must consider the Ideal Gas Law:
- PV = nRT
Where:
- P = Pressure
- V = Volume
- n = Number of moles of gas
- R = Ideal gas constant
- T = Temperature (in Kelvin)
The Ideal Gas Law is a more comprehensive equation that encompasses Boyle's Law as a special case (when n and T are constant). It provides a more accurate description of gas behavior over a wider range of conditions.
Conclusion: Accuracy and Context in Stating Boyle's Law
The most accurate way to state Boyle's Law depends on the context. The qualitative statement effectively conveys the fundamental principle. The proportional statement and the mathematical equations (P₁V₁ = P₂V₂ or PV = k) offer precise quantitative representations. Choosing the most appropriate statement depends on the target audience and the specific application. However, it is crucial always to remember the inherent limitations of Boyle's Law and its reliance on the ideal gas assumption. Understanding these limitations and the conditions under which it applies is essential for correct interpretation and application of this fundamental gas law. When dealing with real gases, especially under extreme conditions, employing the Ideal Gas Law or more sophisticated models that account for intermolecular forces is necessary for accurate predictions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is A Circle Not A Polygon
Apr 09, 2025
-
Center Of Mass Of Quarter Circle
Apr 09, 2025
-
Rate Constant Units For Third Order Reaction
Apr 09, 2025
-
What Protects And Supports The Cell
Apr 09, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Following Parts Of A Mature Sperm
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is A Correct Way Of Stating Boyle's Law . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.