Which Has The Correct Name Formula Combination
News Leon
Apr 07, 2025 · 5 min read
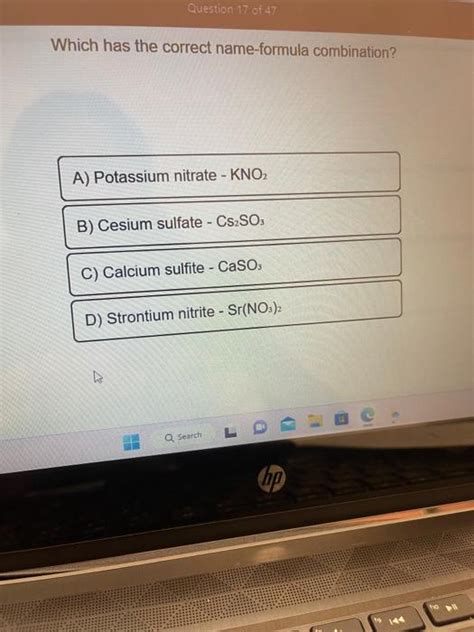
Table of Contents
Which Chemical Formula is Correct? A Deep Dive into Nomenclature and Validation
Naming chemical compounds correctly is fundamental to chemistry. A slight error in the formula or name can lead to misidentification, incorrect synthesis attempts, and potentially dangerous consequences. This article delves deep into the complexities of chemical nomenclature, providing a comprehensive guide to validating the correctness of a chemical formula and its corresponding name. We’ll explore different naming systems, common pitfalls, and practical strategies to ensure accuracy.
Understanding Chemical Nomenclature Systems
Several systems exist for naming chemical compounds, each with its own rules and conventions. The most widely used are:
1. IUPAC Nomenclature: The Gold Standard
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides a systematic approach to naming inorganic and organic compounds. It’s considered the gold standard, ensuring consistency and avoiding ambiguity. IUPAC nomenclature uses prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element (mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, etc.), suffixes to denote functional groups, and a systematic order for listing elements.
Example: Fe₂O₃ is named iron(III) oxide according to IUPAC rules, indicating two iron atoms with a +3 oxidation state and three oxygen atoms.
2. Common or Trivial Names: Historical and Practical Uses
Many compounds, especially older ones, are known by common names that predate the IUPAC system. While these names are often shorter and easier to remember, they lack the systematic nature of IUPAC nomenclature and can be ambiguous.
Example: Water (H₂O) is a common name, clearly understood, but less descriptive than its IUPAC name, dihydrogen monoxide. Similarly, ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) is commonly called ethyl alcohol.
3. Stock Nomenclature: Indicating Oxidation States
This system is especially useful for transition metals that can exhibit multiple oxidation states. It uses Roman numerals in parentheses after the element's name to specify the oxidation state.
Example: Iron(II) chloride (FeCl₂) and iron(III) chloride (FeCl₃) clearly differentiate between the two possible chloride compounds of iron.
Validating Chemical Formulae: A Step-by-Step Approach
Verifying the correctness of a chemical formula requires a multi-faceted approach:
1. Checking for Correct Element Symbols
Ensure each element is represented by its correct chemical symbol, adhering to the periodic table. A simple typo can drastically alter the compound. For example, confusing Na (sodium) with N (nitrogen) leads to a completely different substance.
2. Applying Valence Rules
Atoms tend to bond in ways that achieve a stable electron configuration, often by fulfilling the octet rule (eight electrons in their valence shell). Examine the formula to determine if the valences of the elements are satisfied. For instance, in NaCl, sodium (Na) has a +1 valence and chlorine (Cl) has a -1 valence, forming a stable ionic bond.
3. Considering Oxidation States
Especially crucial for transition metals and compounds with covalent bonds, understanding the oxidation states of elements within the molecule helps determine the correct stoichiometry (relative ratios of atoms). Balancing charges is essential; the overall charge of a neutral compound must be zero.
4. Employing Formula Mass Calculation
Calculating the formula mass (molar mass) of the compound can help identify potential errors. If the calculated mass significantly deviates from an experimentally determined value, it indicates a problem with the formula. This method is particularly useful when dealing with empirical formulas and determining the molecular formula.
5. Consulting Reliable Databases
Numerous reputable databases provide verified chemical information, including formulas, structures, and properties. These include the National Institutes of Health (NIH) databases, PubChem, and ChemSpider. These resources are invaluable for confirmation and resolving uncertainties.
6. Utilizing Chemical Software
Specialized chemical software packages offer powerful tools for drawing chemical structures, generating formulas, and predicting properties. These programs often include built-in checks and validation routines, minimizing the chance of errors.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Several common pitfalls can lead to incorrect chemical formulas and names:
1. Incorrectly Using Prefixes and Suffixes
Misunderstanding the rules for prefixes (mono-, di-, tri-, etc.) and suffixes in IUPAC nomenclature is a frequent source of error. Carefully review the IUPAC guidelines to ensure correct usage.
2. Ignoring Oxidation States
Failing to consider oxidation states, especially for transition metals, is a major cause of incorrect formulas. Remember that a single metal can form multiple compounds with varying oxidation states.
3. Incorrectly Balancing Charges
Ionic compounds must have a neutral overall charge. Neglecting to balance charges will lead to an erroneous formula. For example, MgCl (incorrect) should be MgCl₂ (correct) to balance the +2 charge of magnesium and the -1 charge of each chlorine atom.
4. Confusing Empirical and Molecular Formulas
An empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound, while a molecular formula indicates the actual number of atoms. Confusion between the two can lead to inaccurate representations.
5. Neglecting Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions (like sulfate, SO₄²⁻, or phosphate, PO₄³⁻) act as single units in compounds. Understanding their charges and incorporating them correctly in the formula is essential.
6. Not Checking for Consistency
Cross-referencing different sources and methods of validation helps ensure accuracy. If different approaches yield inconsistent results, it's a strong indicator of an error.
Advanced Techniques for Formula Verification
For complex molecules, more advanced techniques are necessary:
1. Spectroscopic Analysis
Techniques such as infrared (IR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry provide detailed information about the structure and composition of a compound. Comparison of experimental spectra with predicted spectra allows for verification of the formula.
2. X-ray Crystallography
This powerful technique determines the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a crystal. It provides definitive confirmation of the molecular structure, allowing for unambiguous formula determination.
3. Elemental Analysis
Determining the precise elemental composition of a sample through techniques like combustion analysis or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) provides direct evidence supporting (or refuting) the proposed formula.
Conclusion: Accuracy is Paramount
The correct naming and representation of chemical compounds are of utmost importance in all aspects of chemistry. By following a systematic approach that incorporates IUPAC nomenclature, valence rules, oxidation state considerations, and various validation techniques, we can minimize errors and ensure accurate communication within the chemical community. Remembering that even a minor discrepancy can lead to significant consequences reinforces the need for rigorous attention to detail and comprehensive verification methods. Through consistent application of these principles and diligent verification, we ensure the accuracy and reliability of our chemical work.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Binomial System Of Nomenclature Was Proposed By
Apr 08, 2025
-
In The Formation Of A Covalent Bond Electrons Are
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Advantage Of Exporting
Apr 08, 2025
-
Identify The Statement Below That Is Incorrect
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True Regarding The Theory Of Natural Selection
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Has The Correct Name Formula Combination . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.