Which Gametes Can A Rryy Plant Produce
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
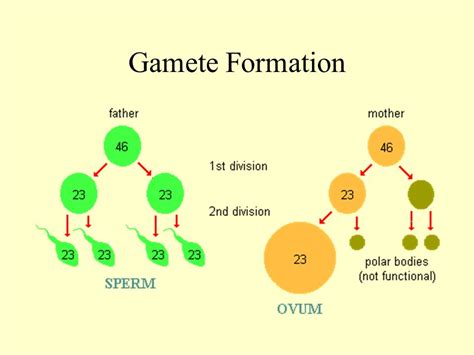
Table of Contents
Which Gametes Can a RRYY Plant Produce? Understanding Mendelian Genetics
Understanding gamete production in plants is fundamental to comprehending inheritance patterns. This article delves into the specifics of gamete formation in a plant with the genotype RRYY, explaining the principles of Mendelian genetics and how they dictate the possible gametes produced. We'll explore the concept of alleles, homozygous conditions, and the process of meiosis, ultimately demonstrating how the genotype dictates the genetic makeup of the resulting gametes.
Understanding Genotypes and Alleles
Before we explore the gametes a RRYY plant can produce, let's define some key terms. A genotype represents the genetic makeup of an organism, detailing the specific alleles present for a given trait. In our case, RRYY represents the genotype of the plant. Alleles are different versions of a gene that determine the expression of a particular trait. In this example, we're dealing with two genes: one controlling trait "R" and another controlling trait "Y".
- R and r represent different alleles for the first gene (let's say, flower color, where R=Red and r=white). Since the plant is RRYY, it has two copies of the dominant "R" allele.
- Y and y represent different alleles for the second gene (let's say, seed shape, where Y=Yellow and y=green). Again, our plant has two copies of the dominant "Y" allele.
A plant is homozygous for a given gene if it carries two identical alleles for that gene (e.g., RR or yy). Our RRYY plant is homozygous for both the "R" gene and the "Y" gene. This homozygous condition significantly impacts the types of gametes it can produce.
Meiosis: The Foundation of Gamete Formation
Gametes, also known as sex cells (sperm and egg in animals, pollen and ovules in plants), are haploid cells, meaning they contain only one set of chromosomes. This halving of the chromosome number is achieved through meiosis, a specialized type of cell division. Meiosis consists of two successive divisions: Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
Meiosis I is a reductional division, where homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) pair up and then separate, resulting in two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This separation is crucial because it ensures that each gamete receives only one allele for each gene. This is where the principle of segregation comes into play, ensuring that each gamete carries only one allele for each trait.
Meiosis II is an equational division, similar to mitosis, where the sister chromatids (identical copies of each chromosome) separate, resulting in four haploid daughter cells (gametes).
In the context of our RRYY plant, during Meiosis I, the two homologous chromosomes carrying the R alleles will separate, and similarly, the two homologous chromosomes carrying the Y alleles will separate. This separation ensures that each resulting gamete receives one allele for each gene.
Determining the Possible Gametes
Because the RRYY plant is homozygous for both genes, the separation of alleles during meiosis is straightforward. Each gamete will receive one R allele and one Y allele. Therefore, there is only one type of gamete this plant can produce: RY.
Let's illustrate this:
| Meiosis I | Meiosis II | Gametes |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosome pair RR separates into two cells, each with one R. | Sister chromatids of R separate. | RY |
| Chromosome pair YY separates into two cells, each with one Y. | Sister chromatids of Y separate. | RY |
All four resulting gametes will have the same genetic makeup: RY. This is because the plant is homozygous for both traits. If the plant were heterozygous for either trait (e.g., RrYY or RRYy), the number of possible gametes and their genetic makeup would be different.
Contrast with Heterozygous Genotypes
To further emphasize the impact of homozygosity, let's contrast the RRYY plant with a plant that is heterozygous for one or both genes.
RrYY Plant: This plant is heterozygous for the "R" gene and homozygous for the "Y" gene. During meiosis, the R and r alleles will segregate independently. This results in two possible gametes: RY and rY.
RRYy Plant: Similar to the previous example, this plant is heterozygous for the "Y" gene and homozygous for the "R" gene. This yields two possible gametes: RY and Ry.
RrYy Plant: This plant is heterozygous for both genes. This signifies independent assortment of alleles during gamete formation leading to four possible gametes: RY, Ry, rY, and ry. This exemplifies the fundamental concept of Mendelian genetics where different traits are inherited independently.
This contrast clearly illustrates how the homozygous nature of the RRYY plant simplifies gamete production, resulting in only one possible combination.
Punnett Squares and Predicting Offspring
The knowledge of the possible gametes produced by a plant is crucial for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of its offspring. Using a Punnett square, we can visualize the possible combinations of alleles when this RRYY plant is crossed with another plant.
If we cross the RRYY plant (producing only RY gametes) with another RRYY plant (also producing only RY gametes), all offspring will have the genotype RRYY. This demonstrates the principle of homozygous dominance where the offspring will inherit the dominant traits from both parents.
However, if we cross the RRYY plant with a plant of a different genotype, the outcome changes. For instance, crossing RRYY with rrYy would produce a variety of offspring genotypes and phenotypes, depending on the gametes contributed by the second parent. The Punnett square would help predict the probability of each genotype and phenotype.
The Importance of Understanding Gamete Formation
Understanding the principles governing gamete formation is critical in various aspects of plant breeding, genetic engineering, and agricultural practices. Predicting the genetic makeup of offspring is essential for:
- Developing new crop varieties: Breeders can select and cross plants with desirable traits to generate offspring with improved characteristics.
- Genetic engineering: Modifying genes requires a thorough understanding of gamete formation and inheritance patterns to ensure successful gene transfer and expression.
- Disease resistance: Understanding gamete formation aids in developing disease-resistant crops by carefully selecting and crossing plants with resistance genes.
- Crop improvement: Optimizing crop yields and quality requires manipulating genes and understanding their inheritance, which is intricately linked to gamete formation.
The seemingly simple concept of gamete formation in a homozygous plant like RRYY underlines the complex mechanisms of heredity and its wide-ranging applications in plant science and agriculture. The principles of Mendelian genetics laid the groundwork for many advancements in agricultural technologies, contributing to enhanced crop production and food security.
Conclusion: The Simplicity of Homozygous Inheritance
In conclusion, a RRYY plant, being homozygous for both genes, can only produce one type of gamete: RY. This simplicity stems directly from the homozygous nature of its genotype, resulting in the straightforward segregation of alleles during meiosis. Understanding this fundamental aspect of Mendelian genetics is crucial for predicting the inheritance patterns in plants and has wide-ranging implications in agriculture and plant science. The ability to predict offspring genotypes allows for strategic plant breeding and genetic manipulation techniques, ultimately contributing to improved crop yields, enhanced disease resistance, and a more sustainable food system. Further exploration into heterozygous crosses and more complex genetic scenarios can build upon this foundation, revealing the intricate beauty and power of Mendelian inheritance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Homologous Chromosomes Separate During Which Phase Of Meiosis
Mar 19, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Mcg And Mg
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Type Of Symmetry Do Sponges Have
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Hormone Is Not Produced By The Anterior Pituitary Gland
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Lenses Does A Compound Microscope Have
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Gametes Can A Rryy Plant Produce . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
