Which Chemical Equation Is Correctly Balanced
News Leon
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
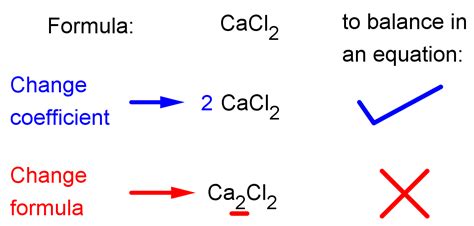
Table of Contents
- Which Chemical Equation Is Correctly Balanced
- Table of Contents
- Which Chemical Equation Is Correctly Balanced? A Deep Dive into Balancing Chemical Equations
- Understanding the Law of Conservation of Mass
- The Balancing Act: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 1. Write the Unbalanced Equation
- 2. Count the Atoms
- 3. Balancing Act: Adjust Coefficients
- 4. Iterate and Verify
- 5. Final Check
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Examples of Balanced and Unbalanced Equations
- Advanced Techniques for Balancing Complex Equations
- Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Balancing Chemical Equations
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Chemical Equation Is Correctly Balanced? A Deep Dive into Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental concept in chemistry. It's crucial for understanding stoichiometry, predicting reaction yields, and accurately representing chemical processes. A correctly balanced equation adheres to the law of conservation of mass, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element remains the same on both the reactant and product sides. This article will explore the principles of balancing chemical equations, provide strategies for achieving balance, and delve into examples to clarify the process. We will also examine common mistakes and how to avoid them, ultimately empowering you to confidently determine which chemical equation is correctly balanced.
Understanding the Law of Conservation of Mass
Before diving into the mechanics of balancing equations, it's essential to grasp the underlying principle: the law of conservation of mass. This law dictates that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Therefore, the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. This translates directly into the requirement that the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the chemical equation.
The Balancing Act: A Step-by-Step Guide
Balancing chemical equations is a systematic process. While some equations may seem straightforward, others can be quite complex, requiring careful attention to detail and a strategic approach. Here's a step-by-step guide to effectively balance chemical equations:
1. Write the Unbalanced Equation
Begin by writing the skeletal equation, including the correct chemical formulas for all reactants and products. This is the foundation upon which you will build your balanced equation. Ensure you are familiar with the chemical formulas and their correct representations.
2. Count the Atoms
Carefully count the number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides of the unbalanced equation. This provides a clear picture of where imbalances exist. Create a table to organize your atom counts for better clarity.
3. Balancing Act: Adjust Coefficients
The key to balancing is adjusting the coefficients—the numbers placed in front of the chemical formulas. Never change the subscripts within the chemical formulas themselves; this alters the identity of the substance.
Start by balancing elements that appear in only one reactant and one product. Often, it is best to balance metals first, followed by nonmetals, and then hydrogen and oxygen last. This method often simplifies the process and minimizes the potential for errors.
4. Iterate and Verify
After adjusting coefficients, recount the atoms of each element on both sides. If the counts are still unequal, continue adjusting coefficients iteratively until balance is achieved. It's a process of trial and error, often requiring multiple adjustments until all elements are balanced.
5. Final Check
Once you believe the equation is balanced, conduct a final check to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is identical on both sides of the equation. This meticulous verification is crucial to avoid errors and guarantee accuracy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can hinder the process of balancing chemical equations. Recognizing these pitfalls can save you time and frustration:
-
Altering Subscripts: As previously emphasized, never change the subscripts within a chemical formula. Doing so changes the chemical identity of the substance, rendering the equation incorrect.
-
Ignoring Polyatomic Ions: If polyatomic ions (like sulfate, SO₄²⁻) appear unchanged on both sides of the equation, treat them as a single unit when balancing. This simplifies the process and maintains accuracy.
-
Rushing the Process: Balancing equations requires patience and attention to detail. Rushing can lead to errors that are difficult to detect later.
-
Not Checking Your Work: Always verify your balanced equation by recounting the atoms of each element on both sides. This final check is essential for accuracy.
Examples of Balanced and Unbalanced Equations
Let's analyze some examples to illustrate the concepts discussed:
Example 1: Combustion of Methane
-
Unbalanced: CH₄ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
-
Balanced: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
In this example, we balance the carbons first (already balanced), then the hydrogens, and finally, the oxygens.
Example 2: Reaction of Iron and Oxygen
-
Unbalanced: Fe + O₂ → Fe₂O₃
-
Balanced: 4Fe + 3O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃
This example requires a bit more work, involving fractions before multiplying to obtain whole number coefficients.
Example 3: Neutralization Reaction
-
Unbalanced: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
-
Balanced: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O (This one is already balanced!)
Example 4: A More Complex Example
-
Unbalanced: C₆H₁₂O₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
-
Balanced: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
This example, representing cellular respiration, demonstrates how balancing can become more intricate with larger molecules.
Advanced Techniques for Balancing Complex Equations
For extremely complex equations, particularly those involving redox reactions (reactions involving electron transfer), advanced techniques might be necessary. These techniques include the half-reaction method and the oxidation number method. These methods are best suited for advanced chemistry students and beyond the scope of this introductory guide.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill in chemistry. By understanding the underlying principles of the law of conservation of mass, employing a systematic approach, and avoiding common mistakes, you can confidently determine whether a chemical equation is correctly balanced. Remember, patience and meticulous attention to detail are key to success in this essential aspect of chemical calculations. The ability to accurately balance equations is crucial for numerous applications in chemistry and related fields, and this guide has provided the foundational knowledge to excel in this critical area. Practice is key; the more equations you balance, the more proficient you will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Negative Income Elasticity Of Demand Indicates That The Product
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Pairs Is Correct
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Does After A Number Mean
Apr 08, 2025
-
How To Write A Letter For A Bank
Apr 08, 2025
-
Where Does Glycolysis Occur In A Prokaryotic Cell
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Chemical Equation Is Correctly Balanced . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.