Which Cell Structure Has A Double Membrane Surrounding It
News Leon
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
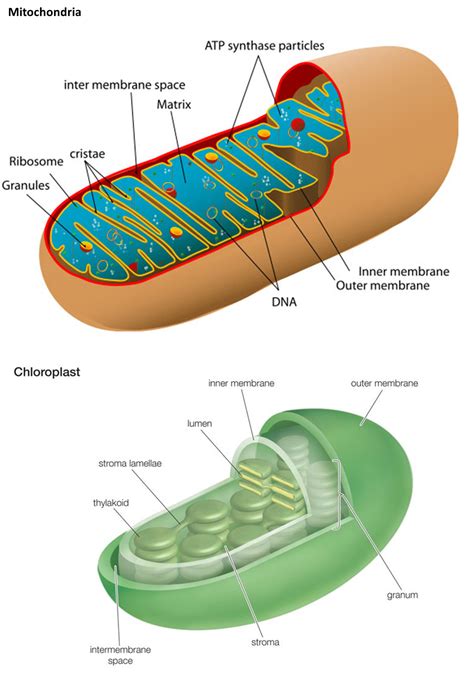
Table of Contents
Which Cell Structure Has a Double Membrane Surrounding It? Delving into the Nucleus and Other Double-Membraned Organelles
The question, "Which cell structure has a double membrane surrounding it?" immediately points to the nucleus, the control center of eukaryotic cells. However, the answer isn't quite that simple. While the nucleus is the most prominent example of a double-membraned organelle, other crucial cellular structures also boast this unique architectural feature. Understanding these structures and their functions is key to comprehending the complex machinery of life.
The Nucleus: The Command Center with a Double Membrane
The nucleus, undoubtedly, is the most well-known organelle with a double membrane. This double membrane, known as the nuclear envelope, separates the genetic material (DNA) from the cytoplasm, providing a protected environment for crucial cellular processes.
The Nuclear Envelope's Structure and Function:
The nuclear envelope isn't just a simple barrier; it's a highly regulated gatekeeper. It comprises two lipid bilayers:
- Inner Nuclear Membrane: This membrane is closely associated with the nuclear lamina, a protein meshwork that provides structural support to the nucleus. It also plays a role in regulating gene expression and anchoring chromatin.
- Outer Nuclear Membrane: This membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and is often studded with ribosomes, actively synthesizing proteins.
Between these two membranes lies the perinuclear space, a narrow compartment approximately 20-40 nm wide. This space allows for selective transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
The nuclear envelope is punctuated by nuclear pores, complex protein structures that regulate the passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. These pores are highly selective, allowing only specific molecules, such as mRNA, ribosomal subunits, and proteins necessary for DNA replication and transcription, to pass through. The regulation of nuclear pore complexes is critical for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the nucleus.
The Nucleus's Role in Cellular Processes:
The nucleus houses the cell's genetic material, organized into chromatin, a complex of DNA and proteins. Within the nucleus, several key cellular processes occur:
- DNA Replication: The precise duplication of the entire genome before cell division.
- Transcription: The synthesis of RNA molecules from DNA templates. This process creates mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, all essential for protein synthesis.
- RNA Processing: Modifications to RNA molecules, such as splicing and capping, to prepare them for translation.
- Regulation of Gene Expression: Controlling which genes are expressed and at what levels, a crucial process for cellular differentiation and response to environmental stimuli.
Mitochondria: The Powerhouses with a Double Membrane
Mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell, are another vital organelle enclosed by a double membrane. These organelles are responsible for cellular respiration, the process of converting nutrients into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's primary energy currency.
The Mitochondrial Membrane System:
The mitochondrial double membrane comprises:
- Outer Mitochondrial Membrane: A relatively permeable membrane containing porins, proteins that form channels allowing the passage of small molecules.
- Inner Mitochondrial Membrane: A highly folded membrane with numerous cristae, which significantly increase its surface area. This membrane is impermeable to most molecules and contains the electron transport chain and ATP synthase, key components of oxidative phosphorylation.
The space between the two membranes is called the intermembrane space, while the space enclosed by the inner membrane is the mitochondrial matrix. The matrix contains mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), ribosomes, and enzymes involved in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle).
Mitochondria's Role in Energy Production:
The intricate structure of the mitochondrial membranes is crucial for its role in ATP production. The electron transport chain embedded in the inner membrane establishes a proton gradient across the membrane, driving ATP synthesis by ATP synthase. This process is highly efficient and provides the cell with the majority of its energy.
Chloroplasts: Solar Power Plants with a Double Membrane
In plant cells and some algae, chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of sugars. Similar to mitochondria, chloroplasts also possess a double membrane.
Chloroplast Membrane Structure:
The chloroplast's double membrane comprises:
- Outer Chloroplast Membrane: Relatively permeable, allowing the passage of small molecules.
- Inner Chloroplast Membrane: Less permeable, surrounding the stroma, and enclosing the thylakoid system.
Inside the chloroplast, the inner membrane encloses the stroma, a fluid-filled space containing enzymes for carbon fixation (the Calvin cycle). Within the stroma lies the thylakoid system, a network of flattened, interconnected sacs. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll and other pigments involved in light absorption and the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts' Role in Photosynthesis:
The double membrane system of chloroplasts, together with the thylakoid structure, creates compartments essential for the two stages of photosynthesis:
- Light-Dependent Reactions: Occur in the thylakoid membranes, converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): Occur in the stroma, using ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
Other Organelles with Double Membranes (Less Commonly Discussed):
While the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are the most frequently cited examples, other organelles might also be considered to possess a double membrane, depending on the interpretation:
- Some argue that peroxisomes have a double membrane, although the consensus leans toward a single membrane. The formation of peroxisomes is debated; some suggest budding from the endoplasmic reticulum, others from the self-assembly of proteins. This ongoing debate affects the classification of their membrane structure.
- The nuclear envelope itself is a double membrane, but this is often not considered an organelle itself, but a defining feature of the nucleus.
Conclusion: The Significance of Double Membranes
The presence of a double membrane in these organelles is not merely coincidental. This structure is crucial for several reasons:
- Compartmentalization: Creating distinct internal compartments for specialized processes, preventing interference and enhancing efficiency.
- Regulation of Transport: Controlling the movement of molecules between the organelle and the cytoplasm, ensuring the proper functioning of cellular pathways.
- Protection: Protecting sensitive molecules and processes from the surrounding environment.
Understanding the structure and function of double-membraned organelles is essential for comprehending the complex interplay of cellular processes that sustain life. Further research continues to refine our understanding of these intricate structures and their dynamic roles within the cell. This ongoing investigation underscores the continuous evolution of our knowledge in cell biology and related fields. The intricacies of the double membrane, its protein composition, and its influence on various cellular processes remain an area of ongoing exploration and discovery, promising further insights into the fundamental mechanisms of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Volume Of 1 Drop Of Water
Apr 04, 2025
-
Make Meaningful Sentences With The Following Words
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Light Reactions Of Photosynthesis Occur In The
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Body At Rest Can Have
Apr 04, 2025
-
Router Operate At Which Layer Of The Osi Model
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Cell Structure Has A Double Membrane Surrounding It . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
