When Two Pipes Fill A Pool Together
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 7 min read
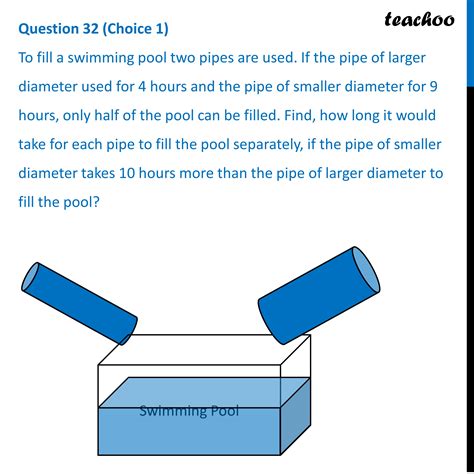
Table of Contents
When Two Pipes Fill a Pool Together: A Comprehensive Guide to Solving Rate Problems
This article delves into the fascinating world of rate problems, specifically focusing on scenarios where two pipes fill a pool concurrently. We'll explore various approaches to solving these problems, from basic arithmetic to more advanced algebraic techniques. Understanding these methods will not only help you solve these specific types of problems but also build a stronger foundation in problem-solving and rate calculations.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Rates and Work
Before diving into complex scenarios, let's establish a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts. The core idea revolves around rates of work. A rate is simply a measure of how much work is done per unit of time. In our pool-filling scenario, the rate represents the fraction of the pool filled by a single pipe in a given time unit (e.g., hours, minutes).
Key Terms:
- Rate (R): The fraction of the pool filled per unit of time. This is often expressed as a fraction or a decimal.
- Time (T): The amount of time it takes to complete the work (fill the pool).
- Work (W): The total amount of work done (filling the entire pool, which we'll consider as 1 unit).
The fundamental relationship between these three elements is:
Work = Rate x Time or W = R x T
This simple equation forms the bedrock of solving all rate problems.
Solving Single Pipe Problems: Building the Foundation
Before tackling two pipes simultaneously, let's practice solving problems involving a single pipe. This will help us develop a strong understanding of the fundamental concepts.
Example 1:
A single pipe fills a pool in 6 hours. What is its rate of work per hour?
Solution:
- Work (W) = 1 (the entire pool)
- Time (T) = 6 hours
- We need to find the Rate (R)
Using the formula W = R x T, we get:
1 = R x 6
Solving for R:
R = 1/6 (This means the pipe fills 1/6 of the pool per hour)
Tackling Two Pipes: Simultaneous Filling
Now, let's move on to the core of our topic: situations where two pipes fill a pool together. The key here is to understand that their rates of work simply add up when they work simultaneously.
Example 2:
Pipe A fills a pool in 6 hours, and Pipe B fills the same pool in 4 hours. How long will it take for both pipes to fill the pool together?
Solution:
-
Find the individual rates:
- Pipe A's rate (Ra) = 1/6 pool per hour
- Pipe B's rate (Rb) = 1/4 pool per hour
-
Find the combined rate:
When both pipes work together, their rates add up:
Combined rate (Rc) = Ra + Rb = 1/6 + 1/4
To add these fractions, we need a common denominator (12):
Rc = (2/12) + (3/12) = 5/12 pool per hour
-
Find the time to fill the pool together:
We know:
Work (W) = 1 (the entire pool) Combined Rate (Rc) = 5/12 pool per hour
Using the formula W = R x T:
1 = (5/12) x T
Solving for T:
T = 12/5 hours = 2.4 hours or 2 hours and 24 minutes
Different Scenarios and Problem-Solving Strategies
Let's explore different variations of the two-pipe problem to strengthen our problem-solving skills.
Scenario 1: One Pipe Fills, One Pipe Empties
This introduces a new dynamic. One pipe fills the pool, while another empties it. The combined rate is the difference between the filling rate and the emptying rate.
Example 3:
Pipe A fills a pool in 5 hours, while Pipe B empties it in 10 hours. If both pipes are open, how long will it take to fill the pool?
Solution:
-
Find the individual rates:
- Pipe A's rate (Ra) = 1/5 pool per hour (filling)
- Pipe B's rate (Rb) = 1/10 pool per hour (emptying)
-
Find the combined rate:
Since Pipe B empties the pool, we subtract its rate from Pipe A's rate:
Rc = Ra - Rb = 1/5 - 1/10 = 1/10 pool per hour
-
Find the time to fill the pool:
W = 1 (entire pool) Rc = 1/10 pool per hour
1 = (1/10) x T
T = 10 hours
Scenario 2: Variable Rates
Sometimes, the pipes might have different rates depending on the time of day or other factors. This adds another layer of complexity. These problems often require breaking down the time into intervals.
Example 4:
Pipe A fills a pool at a rate of 1/6 pool per hour for the first 2 hours and then at a rate of 1/8 pool per hour for the remaining time. Pipe B fills at a constant rate of 1/4 pool per hour. If both pipes are opened together, and the pool is filled in 4 hours, what fraction of the pool did Pipe A fill in the first two hours?
Solution:
This problem requires a step-by-step approach:
-
Calculate Pipe A's work in the first 2 hours: (1/6 pool/hour) * 2 hours = 1/3 pool
-
Calculate the remaining work: The total pool is 1, and Pipe A filled 1/3, leaving 2/3 of the pool to be filled.
-
Calculate the combined rate for the remaining 2 hours: Pipe A fills at 1/8 pool/hour and Pipe B fills at 1/4 pool/hour. The combined rate is 1/8 + 1/4 = 3/8 pool/hour.
-
Determine the fraction of the pool filled by both pipes in the remaining 2 hours: (3/8 pool/hour) * 2 hours = 3/4 pool.
-
Verify: The total work is 1/3 + 3/4 = 13/12. There's an inconsistency, indicating an error in the problem statement or assumptions. The problem needs re-evaluation or correction of values for a logical solution.
Scenario 3: Involving percentages
Some problems might express the rates as percentages instead of fractions. Remember to convert percentages to decimals or fractions before calculations.
Example 5:
Pipe A fills 25% of a pool in one hour, while Pipe B fills 40% in one hour. How long will it take for both pipes to fill the pool together?
Solution:
-
Convert percentages to fractions: Pipe A: 25% = 1/4, Pipe B: 40% = 2/5
-
Calculate the combined rate: 1/4 + 2/5 = 13/20 per hour
-
Calculate the time to fill the pool: 1 (full pool) / (13/20) = 20/13 hours
Advanced Techniques: Using Algebra
For more complex scenarios, algebraic equations can be a powerful tool. Let 'x' represent the unknown variable (often the time).
Example 6:
Pipe A fills a pool in 'x' hours, and Pipe B fills it in (x+2) hours. Together, they fill the pool in 2.4 hours. Find 'x'.
Solution:
-
Express the rates:
- Pipe A's rate: 1/x
- Pipe B's rate: 1/(x+2)
-
Write the equation:
1/x + 1/(x+2) = 1/2.4
-
Solve the equation: This requires algebraic manipulation, such as finding a common denominator and solving the resulting quadratic equation. This often leads to more than one solution. You must evaluate the solutions to ensure they make sense within the context of the problem; negative solutions are usually not practical.
Conclusion: Mastering Rate Problems
Solving problems involving two pipes filling a pool requires a systematic approach. Start with a solid understanding of rates and work. Practice with various scenarios, from simple single-pipe problems to more complex multi-pipe scenarios with variable rates or percentage rates. Remember to always check your units to ensure consistency. As you become more comfortable, consider using algebraic methods to tackle more challenging problems. Mastering these techniques will not only enhance your problem-solving abilities but also strengthen your understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. By applying these strategies, you'll confidently navigate rate problems and find solutions in various contexts. The key is practice and a clear understanding of the underlying principles.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When Two Pipes Fill A Pool Together . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.