What Is The Purpose Of A Switch In A Circuit
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
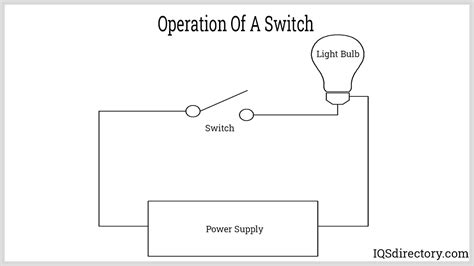
Table of Contents
What is the Purpose of a Switch in a Circuit?
A switch, in its simplest form, is a device that controls the flow of electricity in a circuit. Its purpose is to interrupt or complete an electrical circuit, thereby turning a device or system on or off. While this seems straightforward, the role of a switch extends far beyond this basic function, encompassing crucial roles in safety, efficiency, and the complex operation of modern electrical systems. This article will delve deep into the multifaceted purpose of switches, exploring their various types, applications, and importance in everyday life.
The Fundamental Role: Breaking and Making Circuits
The primary purpose of a switch in any circuit is to control the path of electrical current. When the switch is closed (or "on"), it creates a continuous pathway for electrons to flow, completing the circuit and allowing electricity to power the connected device. Conversely, when the switch is open (or "off"), it breaks the circuit, interrupting the flow of current and turning the device off. This simple on/off functionality is the foundation upon which all other switch functions are built.
Understanding Circuit Completion
A complete circuit requires an unbroken path for current to flow from the power source (e.g., battery or mains supply), through the load (e.g., light bulb, motor), and back to the source. The switch acts as a gatekeeper in this pathway. Without a closed switch, the circuit is incomplete, and no current flows, even if the power source is active and the load is functional.
The Importance of Safety
The ability of a switch to interrupt the flow of electricity is paramount for safety. In situations where high voltages or currents are involved, a properly functioning switch can prevent electrical shocks, fires, and other hazards. This is why switches are incorporated into virtually all electrical appliances and systems, from simple light switches to complex industrial control panels.
Types of Switches and Their Applications
Switches come in a wide variety of types, each designed for specific applications and purposes. These differences primarily relate to their operating mechanism, voltage and current ratings, and the type of circuit they control.
1. Mechanical Switches
These are the most common type of switch, relying on physical contact to make or break the circuit.
-
Toggle Switches: These are familiar from light switches in homes and offer a simple on/off mechanism. They're robust and reliable for low-power applications.
-
Push-Button Switches: Used in a variety of applications, from momentary activation (e.g., doorbell) to latching on/off functions (e.g., some computer peripherals). Their design allows for quick, simple operation.
-
Rotary Switches: These switches offer multiple positions, allowing for selection among various circuits or settings (e.g., fan speed control).
-
Knife Switches: Typically found in high-current applications, these switches use a blade-like conductor to make contact with fixed terminals. Their design ensures a firm and reliable connection.
-
DIP Switches: Small, compact switches often used on circuit boards for configuration and setting adjustments. They are usually a series of multiple switches mounted closely together.
2. Electronic Switches
These switches utilize electronic components to control the flow of current, often offering more sophisticated control features.
-
Transistor Switches: Semiconductors like transistors act as electronic switches, controlled by a small electrical signal. They're highly efficient and can handle faster switching speeds than mechanical switches.
-
Solid-State Relays (SSRs): These switches use a semiconductor device to control a much larger electrical load, offering isolation between the control circuit and the high-power circuit. This is beneficial in high-voltage or high-current environments.
-
MOSFET Switches: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) are another type of semiconductor switch, known for their low on-resistance, making them efficient for handling significant currents.
3. Specialized Switches
Certain applications require specialized switches with unique functionalities.
-
Safety Switches: These switches incorporate safety features to prevent accidental operation or to ensure safety in hazardous environments. They often include lockout/tagout mechanisms or emergency stop functions.
-
Limit Switches: Used in industrial automation and robotics to detect the position or movement of a machine part. They signal a controller when a specific limit is reached.
-
Mercury Switches: These switches use mercury to make and break contact, often employed in tilt sensors or other applications requiring a small, reliable switch.
-
Proximity Switches: These switches detect the presence of an object without physical contact, often using inductive, capacitive, or optical sensing technologies.
Switches in Different Systems and Applications
The purpose of a switch varies depending on the specific system or application it's integrated into.
1. Household Appliances
Switches are ubiquitous in household appliances, allowing users to control the operation of devices like lights, fans, ovens, washing machines, and more. The simple on/off functionality is vital for user convenience and safety.
2. Automotive Systems
In vehicles, switches control various functions, including headlights, wipers, turn signals, power windows, and more. These switches must withstand vibration, temperature variations, and other environmental stresses.
3. Industrial Control Systems
Industrial systems employ a wide array of switches, often for safety-critical functions or in complex automation processes. These switches may be part of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) or other control systems, ensuring precise and reliable operation of machinery and equipment.
4. Computer Systems
Within computers and electronic devices, switches play a crucial role in controlling data flow and signal routing. From simple power switches to complex integrated circuits, switches are essential components in the intricate workings of digital systems.
5. Telecommunications Networks
Switches are integral to telecommunications networks, directing and routing signals between different nodes. These switches handle massive amounts of data and ensure reliable communication.
Choosing the Right Switch: Key Considerations
Selecting the appropriate switch requires careful consideration of several factors:
-
Voltage and Current Rating: The switch must be rated to handle the voltage and current of the circuit it will control. Using an under-rated switch can lead to overheating, damage, or even fire.
-
Switching Mechanism: The type of switch (toggle, push-button, rotary, etc.) should be chosen based on the application's requirements for ease of use, durability, and functionality.
-
Mounting Style: The switch should be designed for the intended mounting location, whether it's a panel-mount switch or a surface-mount switch.
-
Environmental Conditions: The switch should be able to withstand the environmental conditions it will be exposed to, including temperature, humidity, vibration, and other factors.
-
Safety Features: For safety-critical applications, switches with built-in safety features, such as lockout/tagout mechanisms, are essential.
The Future of Switches
While the basic principle of switches remains unchanged, technological advancements continue to refine their design and functionality. The increasing integration of smart technology is leading to the development of intelligent switches, capable of remote control, energy monitoring, and integration with smart home systems. Moreover, the use of solid-state switches is expected to increase, driven by their efficiency, durability, and ability to handle high-speed switching applications.
In conclusion, the purpose of a switch in a circuit goes far beyond a simple on/off function. It plays a crucial role in safety, efficiency, and the control of complex electrical systems. Understanding the different types of switches and their applications is crucial for selecting the right component for any given application, ensuring both safety and reliable operation. The continuous evolution of switch technology promises even more advanced and integrated solutions in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Kg Is 5000 G
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Vertices On A Sphere
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Largest Gulf In The World
Mar 22, 2025
-
Advertising Is A Form Of Paid And Non Personal Promotion
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Close Is South America To Antarctica
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Purpose Of A Switch In A Circuit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
