What Is The Product Of Replication
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
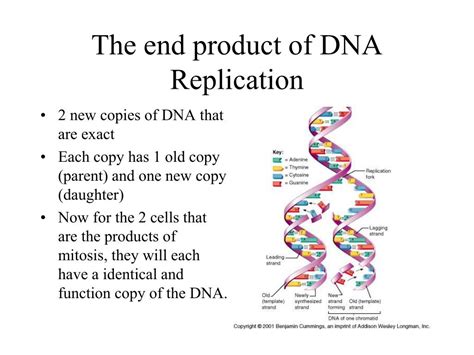
Table of Contents
What is the Product of Replication? Understanding the Outcomes of DNA Copying
The process of replication, primarily associated with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), is fundamental to life itself. It's the precise duplication of genetic material, ensuring the accurate transmission of hereditary information from one generation to the next. Understanding the product of replication—the outcome of this intricate molecular machinery—is crucial for grasping the mechanics of inheritance, cell division, and even the potential for genetic errors that can lead to disease. This article delves into the complexities of replication, examining its product from various perspectives, including accuracy, potential errors, and its vital role in biological processes.
The Primary Product: Two Identical DNA Molecules
The most straightforward answer to the question "What is the product of replication?" is: two identical DNA molecules. Starting from a single double-stranded DNA molecule, the replication process results in two daughter molecules, each possessing an identical sequence of nucleotides. This precise duplication is vital for cell division (both mitosis and meiosis), ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete and accurate copy of the genome.
Semiconservative Replication: A Key Feature
The method of replication is described as semiconservative. This means that each new DNA molecule retains one strand from the original parent molecule and synthesizes a new complementary strand. This mechanism ensures fidelity and allows for efficient error correction during the replication process. The parent strand acts as a template, guiding the precise assembly of the new strand.
The Accuracy of Replication: A Remarkable Feat
The fidelity of DNA replication is astonishingly high. DNA polymerases, the enzymes responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands, possess an intrinsic proofreading capability. This means they can detect and correct errors during the process, minimizing mistakes. The error rate is estimated to be approximately one error per billion nucleotides incorporated. This incredible accuracy is crucial for maintaining genetic stability and preventing the accumulation of harmful mutations.
Mechanisms Ensuring Accuracy
Several mechanisms contribute to the accuracy of DNA replication:
- Proofreading activity of DNA polymerases: As mentioned, DNA polymerases can backtrack and remove incorrectly incorporated nucleotides.
- Mismatch repair: This post-replication process detects and corrects mismatched base pairs that escaped the proofreading activity of DNA polymerases.
- Excision repair: This mechanism targets and removes damaged or modified bases, ensuring that the integrity of the DNA sequence is maintained.
Potential Errors and Their Consequences: Mutations
Despite the high accuracy of DNA replication, errors can still occur. These errors are known as mutations, and they can result in changes to the DNA sequence. Mutations can have various consequences, ranging from benign to severely deleterious:
- Point mutations: These involve changes in a single nucleotide base. They can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence of proteins, affecting their function.
- Insertions and deletions: These involve the addition or removal of nucleotides. They can cause frameshift mutations, dramatically altering the reading frame of the gene and resulting in non-functional proteins.
- Chromosomal mutations: These are large-scale changes that affect entire chromosomes, including deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. These mutations can have profound effects on the organism.
Beyond DNA: Replication of Other Genetic Material
While DNA replication is the most well-known example, the concept of replication applies to other types of genetic material as well. RNA (ribonucleic acid) also undergoes replication, though the process is often less precise and error-prone than DNA replication. This is particularly true for RNA viruses, where the high mutation rate contributes to their rapid evolution and adaptation.
RNA Replication: A Different Landscape
RNA replication typically involves RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which utilize an RNA template to synthesize a new RNA molecule. The lack of proofreading mechanisms in many RNA polymerases results in higher mutation rates compared to DNA replication. This high mutation rate is a crucial factor in the evolution and pathogenicity of RNA viruses.
The Product of Replication in Different Biological Contexts
The product of replication plays a vital role in various biological processes:
- Cell division: Accurate DNA replication is essential for cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. This is fundamental for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms.
- Sexual reproduction: Meiosis, the type of cell division that produces gametes (sperm and egg cells), relies on accurate DNA replication to generate haploid cells with half the number of chromosomes. The subsequent fusion of gametes during fertilization restores the diploid chromosome number.
- Genetic engineering: Understanding DNA replication is crucial for genetic engineering techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which amplifies specific DNA sequences. This technique has revolutionized various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and forensics.
The Broader Impact: Evolution and Adaptation
The product of replication, with its inherent potential for error (mutation), is a driving force behind evolution. Mutations introduce variations in the genetic material, and these variations can be selected for or against by environmental pressures. This process of natural selection leads to the adaptation and diversification of species over time.
Conclusion: A Fundamental Process with Far-Reaching Consequences
The product of replication—two identical DNA molecules—is far more than just a simple duplication. It’s the cornerstone of life, enabling inheritance, cell division, and the evolution of species. The remarkable accuracy of the process, while not perfect, maintains genetic stability, and the occasional errors contribute to the incredible diversity of life on Earth. Understanding the intricate mechanisms of replication, its potential for error, and its implications for various biological processes remains a crucial area of ongoing research with far-reaching applications in medicine, biotechnology, and our understanding of the natural world. The study of replication continues to unravel the secrets of life, and its ongoing exploration promises to yield even more significant discoveries in the years to come. Its importance transcends simple cell biology, touching upon fields such as evolutionary biology, genetics, and medicine, highlighting its fundamental position in biological systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is The Start Codon
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Meters In 200 Cm
Mar 16, 2025
-
6 Is 30 Percent Of What
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not An Organic Compound
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is An Animal With A Backbone Called
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Product Of Replication . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
