What Is The Order Of Rotational Symmetry Of A Rhombus
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
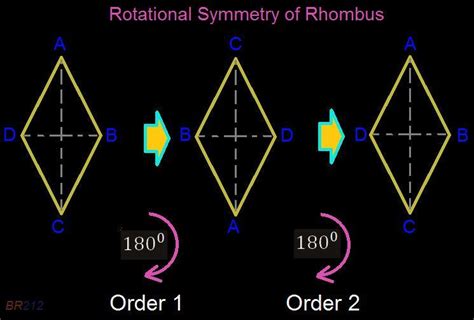
Table of Contents
What is the Order of Rotational Symmetry of a Rhombus? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding rotational symmetry is crucial in geometry, especially when dealing with shapes like the rhombus. This article delves deep into the concept of rotational symmetry, focusing specifically on the rhombus and explaining its order of rotational symmetry in a clear, comprehensive, and engaging manner. We'll explore the definition, properties, and applications of rotational symmetry, providing a solid foundation for anyone wanting to master this geometrical concept.
Understanding Rotational Symmetry
Rotational symmetry describes the property of a shape where it can be rotated about a central point (the center of rotation) by a certain angle and still look exactly the same. This means that after the rotation, the shape perfectly overlaps its original position. The order of rotational symmetry refers to the number of times a shape can be rotated by less than 360 degrees and still maintain its original appearance. A shape with no rotational symmetry has an order of 1.
Key Terms to Remember:
- Rotation: The act of turning a shape around a fixed point.
- Center of Rotation: The fixed point around which a shape is rotated.
- Angle of Rotation: The angle by which a shape is rotated.
- Order of Rotational Symmetry: The number of times a shape can be rotated (by less than 360 degrees) and still look identical.
Exploring the Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) with all four sides having equal length. It's important to distinguish the rhombus from other quadrilaterals, such as squares and rectangles. While a square is a special type of rhombus (with right angles), a rhombus doesn't necessarily have right angles. This difference significantly impacts its rotational symmetry.
Properties of a Rhombus:
- Four equal sides: All four sides of a rhombus have the same length.
- Opposite sides are parallel: Opposite sides of a rhombus are parallel to each other.
- Opposite angles are equal: Opposite angles within a rhombus are equal in measure.
- Consecutive angles are supplementary: Consecutive angles (angles next to each other) in a rhombus add up to 180 degrees.
- Diagonals bisect each other at right angles: The diagonals of a rhombus intersect at a point, and this point divides each diagonal into two equal halves. The intersection also forms four right angles.
Determining the Rotational Symmetry of a Rhombus
To determine the order of rotational symmetry of a rhombus, we need to visualize rotating it around its center point. The center of rotation is the point where the diagonals intersect.
Let's consider the rotations:
- 0° Rotation: Rotating the rhombus by 0° (no rotation) leaves it unchanged. This is always the case for any shape.
- 180° Rotation: Rotating the rhombus by 180° about its center will result in the shape overlapping its original position. The opposite vertices will swap places, but the overall shape remains the same.
- Any other rotation: Rotating the rhombus by any angle other than 0° or 180° (e.g., 90°, 270°) will not result in the shape perfectly overlapping its original position. The shape will appear differently.
Therefore, a rhombus only has two positions where it looks exactly the same after rotation – 0° and 180°.
The Order of Rotational Symmetry: It's 2!
Based on the above analysis, the order of rotational symmetry for a rhombus is 2. This means it can be rotated two times (by 0° and 180°) and still look identical.
Comparing Rhombus to Other Shapes
Let's compare the rotational symmetry of a rhombus to other quadrilaterals:
- Square: A square has an order of rotational symmetry of 4. It can be rotated by 90°, 180°, and 270° and still look identical.
- Rectangle (not a square): A rectangle (that is not a square) has an order of rotational symmetry of 2, just like the rhombus.
- Parallelogram (not a rhombus or rectangle): A parallelogram (that is not a rhombus or rectangle) also has an order of rotational symmetry of 2.
- Trapezoid: A trapezoid typically has an order of rotational symmetry of 1 (no rotational symmetry).
Applications of Rotational Symmetry
Understanding rotational symmetry has numerous applications in various fields:
- Art and Design: Artists and designers utilize rotational symmetry to create aesthetically pleasing and balanced designs in various forms, such as mandalas, logos, and patterns.
- Architecture: Architects incorporate rotational symmetry in building designs to create visually appealing and structurally sound buildings. Many iconic buildings exhibit rotational symmetry.
- Engineering: Engineers use rotational symmetry principles in designing mechanical parts, wheels, and other components to ensure balanced function and efficient operation.
- Nature: Rotational symmetry is prevalent in nature, observed in snowflakes, starfish, and many flowers.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper, here are some advanced concepts related to rotational symmetry:
- Point symmetry: A shape possesses point symmetry if it can be rotated by 180° around a point and still look the same. A rhombus exhibits point symmetry.
- Line symmetry (Reflectional Symmetry): While not directly related to rotational symmetry, understanding line symmetry is also crucial in geometry. A rhombus has two lines of symmetry.
- Higher-order rotational symmetry: Shapes such as regular polygons (e.g., equilateral triangle, square, pentagon) exhibit higher orders of rotational symmetry.
Conclusion: Mastering the Rhombus's Rotational Symmetry
The order of rotational symmetry of a rhombus is 2. This fundamental geometrical concept is important to understand, not only for academic purposes but also for its broader applications in various fields. By mastering the concepts explained in this article, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the properties of the rhombus and rotational symmetry in general. Remember to practice visualizing the rotations and comparing the rhombus to other shapes to solidify your understanding. The more you practice, the better you'll become at identifying and applying rotational symmetry principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups In 9 Ounces
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Ones Are There Between 1 And 100
Mar 29, 2025
-
025 Expressed As A Percentage Is
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Democracy And Dictatorship
Mar 29, 2025
-
Bill Is To Law As Larva Is To
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Order Of Rotational Symmetry Of A Rhombus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
