What Is The Measure Of 3
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
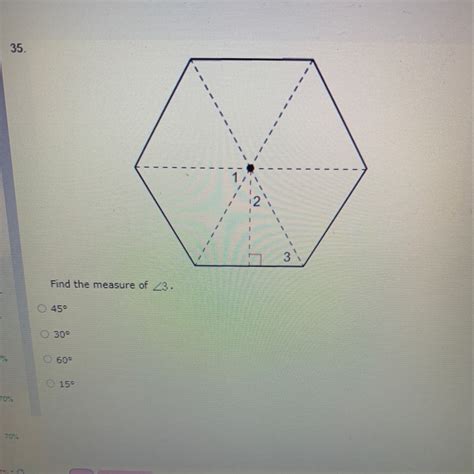
Table of Contents
- What Is The Measure Of 3
- Table of Contents
- What is the Measure of 3? Exploring the Multifaceted Nature of Measurement
- 3 as a Cardinal Number: Counting and Quantity
- Cardinality and Set Theory
- Applications of Cardinal Number 3
- 3 as an Ordinal Number: Ordering and Position
- Ordering and Ranking
- Applications of Ordinal Number 3
- 3 as a Real Number: Measurement and the Number Line
- The Number Line and its Implications
- Applications of Real Number 3
- 3 in Different Measurement Systems
- Beyond Cardinal, Ordinal, and Real: Other Interpretations
- The Significance of the Number 3
- Conclusion: The Contextual Nature of Measurement
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Measure of 3? Exploring the Multifaceted Nature of Measurement
The seemingly simple question, "What is the measure of 3?" opens a surprisingly deep and multifaceted exploration into the world of mathematics, measurement, and the very nature of quantity. The answer depends heavily on the context – what kind of "measure" are we talking about? Are we considering 3 as a cardinal number, an ordinal number, a real number, or perhaps something else entirely? This article will delve into these various interpretations, revealing the rich tapestry woven around this seemingly innocuous number.
3 as a Cardinal Number: Counting and Quantity
At its most fundamental level, 3 is a cardinal number. This signifies its role in representing the quantity of a collection of objects. When we count three apples, three cars, or three stars, we're using 3 to express the size of the set. The measure of 3 in this context is simply the quantity three. It's an absolute and inherent property of the set.
Cardinality and Set Theory
Within the framework of set theory, the cardinal number 3 represents the cardinality of sets that can be put into one-to-one correspondence with the set {a, b, c}. This means any set with three distinct elements has a cardinality of 3. This concept extends beyond tangible objects to encompass abstract entities and ideas. For example, the set of primary colors {red, blue, yellow} also has a cardinality of 3.
Applications of Cardinal Number 3
The application of cardinal number 3 is pervasive throughout our daily lives and various fields of study:
- Everyday Counting: Counting objects, people, or events is the most common application.
- Data Analysis: Representing frequencies and counts in data sets.
- Science: Measuring quantities like the number of atoms in a molecule.
- Computer Science: Representing the size of arrays or other data structures.
3 as an Ordinal Number: Ordering and Position
In contrast to its cardinal role, 3 can also function as an ordinal number. In this case, 3 signifies the third position in a sequence or ordered list. Unlike the cardinal measure which is absolute, the ordinal measure is relative to the sequence.
Ordering and Ranking
Consider the winners of a race: the third-place finisher is in position 3, signifying their rank. The measure of 3 here represents the position, not a quantity. This measure is dependent on the context of the ordered sequence. Changing the order will change the ordinal position of the elements.
Applications of Ordinal Number 3
The use of 3 as an ordinal number is ubiquitous:
- Ranking and Competition: Determining the position of participants in competitions.
- Calendar Dates: The third day of the month or the third month of the year.
- Serial Numbers: Identifying items within a numbered sequence.
- Page Numbers: Indicating the position of a page in a book or document.
3 as a Real Number: Measurement and the Number Line
Within the broader context of the real number system, 3 is a real number situated on the number line. Its measure in this context relates to its position relative to other real numbers, such as 0, 1, 2, and so forth. It's a point on a continuous scale, not just a discrete quantity or position.
The Number Line and its Implications
The number line visualizes the real numbers, providing a geometric representation of their magnitude and order. The measure of 3 on the number line is its distance from 0, which is exactly 3 units. This concept underpins many measurement systems.
Applications of Real Number 3
The real number 3 finds application in numerous areas:
- Measurement of Physical Quantities: Length, weight, volume, and many other physical attributes.
- Geometric Calculations: Determining the lengths of sides in triangles or the volume of a cube.
- Calculus: Representing variables and constants in equations and functions.
- Physics: Modeling physical phenomena using mathematical equations.
3 in Different Measurement Systems
The "measure" of 3 also varies based on the measurement system employed. For example:
- Metric System: 3 meters, 3 kilograms, 3 liters. The units significantly impact the measure's physical interpretation.
- Imperial System: 3 feet, 3 pounds, 3 gallons. A different system of units yields different practical meanings.
- Other Systems: Time (3 hours, 3 minutes, 3 seconds), angles (3 degrees, 3 radians), and other specialized systems provide their own context-specific meanings.
These variations emphasize that the measure of 3 isn't solely defined by the number itself but significantly by the units of measurement applied to it.
Beyond Cardinal, Ordinal, and Real: Other Interpretations
The measure of 3 extends beyond these core interpretations. Consider:
- Vector Spaces: In linear algebra, 3 can represent a vector in a three-dimensional space. The "measure" could refer to its magnitude (length) or direction.
- Modular Arithmetic: Within modular arithmetic, 3 has a specific meaning relative to a chosen modulus.
- Abstract Algebra: In group theory or ring theory, 3 might represent an element within a given algebraic structure. Its "measure" could then be determined by its properties within that structure.
- Complex Numbers: 3 can represent the real part of a complex number, or even the magnitude (modulus) of a complex number.
The Significance of the Number 3
Throughout history and across cultures, the number 3 holds significant symbolic meaning. It often represents:
- Trinity: In various religions, 3 symbolizes the holy trinity (father, son, holy spirit).
- Completeness: The idea of beginning, middle, and end.
- Balance: A representation of equilibrium and harmony.
- Growth and Expansion: Indicating increase or development.
Conclusion: The Contextual Nature of Measurement
The question, "What is the measure of 3?" is fundamentally a question of context. Without specifying the kind of measurement, the answer remains ambiguous. 3 can be a cardinal quantity, an ordinal position, a real number on a continuous scale, or even a component in more advanced mathematical systems. The diverse interpretations highlight the rich and multifaceted nature of measurement and the fundamental role that numbers play in quantifying and understanding the world around us. Understanding the context is paramount to accurately interpreting and applying the "measure" of 3 – or any number for that matter. The seemingly simple number 3 reveals a surprising depth and complexity when explored from various mathematical and symbolic perspectives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Organelles Are Found In Only Plant Cells
Apr 03, 2025
-
In The Prisoners Room A Candle Is Burning Dimly
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Protozoa Is True
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is 10 Of An Hour
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Organelles Does Cellular Respiration Take Place In
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Measure Of 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
