What Is The Lowest Part Of A Wave Called
News Leon
Apr 07, 2025 · 5 min read
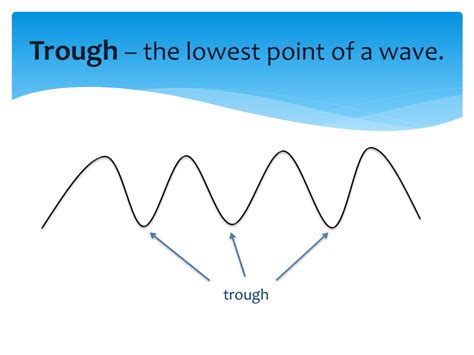
Table of Contents
What is the Lowest Part of a Wave Called? Understanding Wave Anatomy and Terminology
The ocean, a vast and powerful force of nature, is characterized by its dynamic waves. These rhythmic undulations of water, driven by wind, tides, or seismic activity, possess a fascinating structure. While the crest, the highest point of a wave, is easily recognizable, understanding the lowest point requires a deeper dive into wave anatomy. This comprehensive guide will explore what the lowest part of a wave is called, examining its characteristics, formation, and significance in various fields of study.
Defining the Trough: The Lowest Point of a Wave
The lowest point of a wave is called the trough. This is a crucial component in understanding wave dynamics and is essential terminology for anyone studying oceanography, coastal engineering, or related disciplines. It's the opposite of the crest, forming the valley between successive wave crests. Imagine a wave as a sine curve; the trough represents the lowest point on that curve.
Understanding Wave Anatomy: Beyond Crests and Troughs
Waves are complex phenomena, and their anatomy extends beyond simply crests and troughs. Several other key features help define their properties:
-
Wavelength: The horizontal distance between two consecutive crests (or troughs). This is a crucial parameter for characterizing wave size and energy.
-
Wave Height: The vertical distance between the crest and the trough of a wave. This directly reflects the wave's energy and potential impact.
-
Wave Period: The time it takes for two consecutive crests (or troughs) to pass a fixed point. This measures the frequency of wave arrival.
-
Wave Steepness: The ratio of wave height to wavelength. Steep waves are more likely to break.
Understanding these components allows for a comprehensive analysis of wave behavior and prediction.
The Formation of Troughs: A Consequence of Wave Propagation
Troughs aren't formed independently; they are an integral part of the wave's overall structure. Their formation is a direct consequence of how waves propagate. The movement of water particles in a wave follows a circular or elliptical path. As the wave travels, water particles are displaced upwards forming the crest and then downwards forming the trough. This cyclical motion is the essence of wave propagation.
Wind-Generated Waves: The Most Common Type
The majority of ocean waves are generated by wind. As wind blows across the water's surface, friction transfers energy to the water, creating small ripples. These ripples grow in size and height as more energy is transferred, eventually forming the familiar ocean waves we see. The troughs in these waves are a direct result of the downward displacement of water particles during this energy transfer.
Other Wave-Generating Forces: Tides and Seismic Activity
While wind is the primary driver of surface waves, other forces contribute to wave generation, resulting in variations in trough formation:
-
Tides: Generated by the gravitational forces of the sun and the moon, tides create rhythmic variations in sea level. While not strictly "waves" in the same sense as wind-generated waves, they still have cyclical crests and troughs, demonstrating the broad applicability of the term "trough."
-
Seismic Activity: Earthquakes and underwater landslides can generate powerful tsunamis. These waves have incredibly long wavelengths and can have devastatingly high wave heights, resulting in exceptionally deep troughs. The trough in a tsunami can temporarily lower the sea level significantly before the destructive crest arrives.
The Significance of Troughs: Applications Across Diverse Fields
The concept of the trough, while seemingly simple, holds significance across numerous scientific and engineering disciplines:
Oceanography and Coastal Engineering: Understanding Wave Dynamics
Oceanographers and coastal engineers use trough measurements, alongside other wave parameters, to model wave behavior, predict coastal erosion, and design coastal defenses. The depth of the trough, along with the wave height, is critical for understanding the wave's energy and potential for damage. Accurate prediction of trough depth is essential for effective coastal management and hazard mitigation. Detailed analysis of trough formation and characteristics informs the development of robust seawalls, breakwaters, and other coastal protection structures.
Marine Biology and Ecology: Impact on Marine Life
Troughs play a crucial role in shaping marine ecosystems. The cyclical movement of water associated with crests and troughs creates a dynamic environment that supports diverse marine life. The depth of the trough can affect the distribution and abundance of marine organisms, influencing their feeding habits, reproduction, and overall survival. The mixing of waters caused by wave action, including the movement of water during trough formation, also impacts the distribution of nutrients and oxygen in the ocean, thereby influencing the overall health and productivity of marine ecosystems.
Surfing and Water Sports: Riding the Wave
For surfers, understanding wave anatomy is paramount. While the crest is where the action is, the trough is equally important. The shape of the wave, defined by the interaction of crest and trough, influences its suitability for riding. The depth and shape of the trough impact the wave's speed and power as it breaks. Skilled surfers utilize their knowledge of wave dynamics, including the trough's influence, to select and ride the most suitable waves.
Navigation and Maritime Safety: Understanding Wave Conditions
Knowledge of wave parameters, including the depth of the trough, is essential for safe navigation. Large waves with deep troughs can pose a significant hazard to ships, potentially leading to capsizing or damage. Meteorological and oceanographic forecasts provide information on wave height and period, indirectly allowing mariners to anticipate trough depth and adjust their course or speed accordingly. This is particularly important in areas prone to extreme wave conditions.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Wave Dynamics
While the crest often grabs attention as the most dramatic part of a wave, the trough is equally crucial for understanding the overall wave dynamics and its impact on various aspects of the natural world and human activities. From informing coastal engineering designs to influencing marine ecosystems and enabling safe navigation, the understanding and accurate measurement of the trough are indispensable to various scientific and practical applications. It's the unsung hero of wave mechanics, quietly playing a vital role in shaping the world's oceans. This deeper understanding of the trough enhances our appreciation of the complex and dynamic nature of waves, emphasizing the importance of understanding every aspect of this fundamental natural phenomenon.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Is A Tooth Brush
Apr 09, 2025
-
Are All Physical Changes Accompanied By Chemical Changes
Apr 09, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Following Figure Have
Apr 09, 2025
-
Certain White Blood Cells Engulf Microorganisms
Apr 09, 2025
-
Is N More Electronegative Than C
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lowest Part Of A Wave Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.