What Is The Index Of Refraction For Crown Glass
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
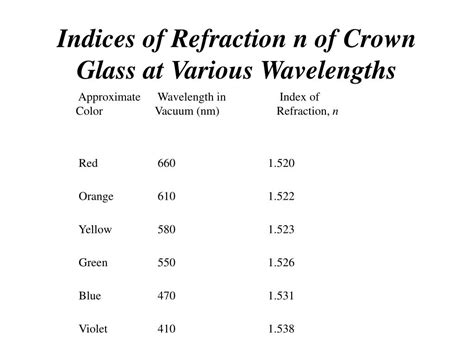
Table of Contents
What is the Index of Refraction for Crown Glass? A Deep Dive
The index of refraction (n), a fundamental optical property of materials, describes how much light slows down when passing through a medium compared to its speed in a vacuum. Crown glass, a type of optical glass, is widely used in various applications due to its specific refractive properties. Understanding its index of refraction is crucial for designing lenses, prisms, and other optical instruments. This comprehensive guide will explore the index of refraction for crown glass, examining its variations, factors influencing it, and its significance in different applications.
Understanding the Index of Refraction
Before delving into the specifics of crown glass, let's establish a clear understanding of the index of refraction itself. It's a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum (c) to the speed of light in the medium (v):
n = c/v
A higher index of refraction indicates a greater slowing of light, meaning the light bends more significantly when entering or exiting the material. This bending is described by Snell's Law, a cornerstone of geometrical optics.
Factors Affecting the Index of Refraction
The index of refraction isn't a constant value for a given material. Several factors influence it:
-
Wavelength of Light: The most significant factor is the wavelength (or color) of the light. This phenomenon is known as dispersion. Crown glass, like most transparent materials, exhibits dispersion, meaning its index of refraction is slightly different for each wavelength in the visible spectrum. Blue light, with its shorter wavelength, generally has a higher refractive index than red light with its longer wavelength. This is why prisms separate white light into its constituent colors.
-
Temperature: Temperature changes also affect the index of refraction. Generally, an increase in temperature leads to a slight decrease in the refractive index. This is because higher temperatures increase the average distance between atoms in the glass, subtly altering its optical density.
-
Composition of the Glass: The specific chemical composition of the crown glass significantly impacts its refractive index. Crown glasses are primarily composed of silica (SiO2), but variations in the proportions of other oxides (e.g., sodium oxide, potassium oxide, calcium oxide, lead oxide) significantly alter the refractive index. Different types of crown glass are designed to have specific refractive indices for particular applications.
-
Pressure: While less significant than wavelength and temperature, pressure can also subtly influence the refractive index. Higher pressure generally increases the refractive index, as it compresses the material, increasing its density.
Index of Refraction for Crown Glass: A Range, Not a Single Value
It's crucial to understand that there isn't a single, universally applicable index of refraction for crown glass. The value varies depending on the specific type of crown glass and the factors mentioned above. Instead of a single number, we typically encounter a range of values.
A common approximation for the index of refraction of crown glass for yellow sodium light (the D-line, at approximately 589 nm) is around 1.52. However, this is a broad generalization. Different manufacturers produce crown glasses with slightly different compositions, leading to variations in their refractive indices. Datasheets for specific crown glass types from manufacturers will provide more precise values for their products.
Specific Examples and Variations
To illustrate the variability, consider the following hypothetical examples (these are representative and might not correspond to actual commercial products):
-
Light Crown Glass: Might have a refractive index around 1.515 for the sodium D-line. This type is known for its relatively low dispersion.
-
Medium Crown Glass: Could have an index of refraction near 1.520 for the same wavelength. It offers a balance between refractive index and dispersion.
-
Dense Crown Glass: This type typically boasts a higher refractive index (e.g., 1.525 or even slightly higher) at the expense of increased dispersion.
These values are indicative and would vary with the exact composition and the wavelength of light considered. Furthermore, the temperature and pressure conditions would further modify these values, albeit to a smaller degree.
The Significance of Knowing the Refractive Index of Crown Glass
Accurate knowledge of the index of refraction is crucial in numerous optical applications employing crown glass:
Lens Design
In lens design, the refractive index is critical for determining the focal length, lens power, and overall optical performance. Precise values are essential for computer-aided design software used to model and optimize lens systems. Knowing the dispersion properties is vital for minimizing chromatic aberration (color fringing).
Prism Design
Prisms are used for separating light into its spectral components (spectroscopy) or for deflecting light beams. The refractive index, especially its wavelength dependence (dispersion), is crucial for calculating the angles of deviation in prism designs.
Optical Instruments
Many optical instruments, including microscopes, telescopes, and cameras, utilize crown glass lenses and prisms. Accurate refractive index values are necessary for achieving the desired magnification, resolution, and image quality.
Optical Fibers
Although crown glass isn't the primary material used in optical fibers, its refractive index characteristics serve as a basis for understanding the principles of light propagation in waveguides.
Other Applications
Beyond these core applications, crown glass finds its way into various other optical components and devices, where precise knowledge of the refractive index plays a significant role in their design and performance.
Determining the Index of Refraction of a Crown Glass Sample
Several methods can be employed to experimentally determine the refractive index of a specific crown glass sample:
-
Minimum Deviation Method (using a prism): This classical method involves precisely measuring the angle of minimum deviation of a light beam passing through a prism made of the crown glass. Using Snell's Law, the refractive index can be calculated.
-
Refractometry: Refractometers are specialized instruments that directly measure the refractive index of a material. They use the principle of total internal reflection to determine the index.
-
Ellipsometry: Ellipsometry is a sophisticated technique for characterizing optical properties, including the refractive index, by analyzing the polarization changes of light reflected from the sample surface.
These methods are employed in research labs and manufacturing settings for quality control and precise characterization of crown glass.
Conclusion: A Crucial Parameter for Optical Applications
The index of refraction is a fundamental property of crown glass that dictates its behavior with light. Understanding that it's not a fixed value, but rather varies depending on several factors, including wavelength, temperature, and composition, is essential. Accurate knowledge of the refractive index, along with its wavelength dependence (dispersion), is paramount in designing and optimizing optical systems that rely on crown glass, ensuring optimal performance and image quality in a wide array of applications. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for the precise refractive index values of specific crown glass types.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
At Which Layer Of The Osi Model Do Routers Work
Apr 06, 2025
-
Bangalore Is Capital Of Which State
Apr 06, 2025
-
Cytoplasm Divides Immediately After This Period
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Composition Of Co
Apr 06, 2025
-
In The Visible Spectrum Which Color Has The Longest Wavelength
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Index Of Refraction For Crown Glass . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
