What Is The Density Of Aluminum Metal
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
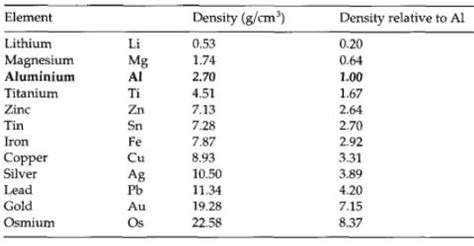
Table of Contents
What is the Density of Aluminum Metal? A Deep Dive into Properties and Applications
Aluminum, a lightweight yet remarkably strong metal, is ubiquitous in modern life. From beverage cans to aircraft components, its versatility stems from a unique combination of properties, with density being a key characteristic. Understanding the density of aluminum is crucial for engineers, scientists, and anyone interested in the material's diverse applications. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of aluminum's density, exploring its variations, influencing factors, and significance in various industries.
Understanding Density: A Fundamental Concept
Before diving into the specifics of aluminum's density, let's establish a clear understanding of the concept itself. Density is defined as the mass of a substance per unit volume. It's typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). A higher density indicates that more mass is packed into a given volume. This seemingly simple concept has profound implications in various fields, impacting everything from material selection in engineering to the behavior of fluids in physics.
The Density of Aluminum: A Definitive Answer
The density of pure aluminum at room temperature (20°C or 68°F) is approximately 2.70 g/cm³ or 2700 kg/m³. It's important to note that this value can vary slightly depending on several factors, which will be explored in detail later in this article. This density makes aluminum significantly lighter than many other common metals such as steel (around 7.85 g/cm³) or copper (around 8.96 g/cm³), contributing to its widespread use in applications where weight reduction is crucial.
Why is Density Important for Aluminum?
The relatively low density of aluminum is a cornerstone of its numerous applications. This lightness translates to:
-
Reduced weight in transportation: Aluminum's low density is paramount in the automotive, aerospace, and maritime industries. Lighter vehicles mean better fuel efficiency, improved performance, and reduced emissions. Aircraft, in particular, heavily rely on aluminum alloys for their structural components, maximizing fuel economy and payload capacity.
-
Increased portability and ease of handling: In construction and consumer goods, the lighter weight of aluminum makes it easier to handle and transport, simplifying manufacturing and installation processes.
-
Cost-effectiveness: While aluminum isn't the cheapest metal available, its lightweight nature often reduces transportation and manufacturing costs, making it a competitive option in many applications.
Factors Influencing Aluminum's Density
While the standard density of aluminum is 2.70 g/cm³, several factors can subtly influence this value:
1. Temperature:
Temperature significantly impacts the density of any material, including aluminum. As temperature increases, the atoms within the aluminum structure vibrate more vigorously, causing expansion and a decrease in density. Conversely, a decrease in temperature leads to contraction and an increase in density. This effect, while not dramatic, is important for precise engineering calculations, especially in applications involving extreme temperatures.
2. Alloying Elements:
Aluminum is rarely used in its pure form. Most aluminum applications utilize aluminum alloys, which incorporate other elements such as copper, magnesium, silicon, or zinc to enhance specific properties like strength, corrosion resistance, or machinability. The addition of these alloying elements alters the density, often slightly increasing it depending on the type and amount of the alloying element. Each aluminum alloy possesses a slightly different density, requiring careful consideration during material selection.
3. Impurities:
The presence of impurities in aluminum can also affect its density. Manufacturing processes might introduce trace amounts of other elements, potentially altering the overall density. High-purity aluminum will have a density closer to the theoretical value, while less pure aluminum might exhibit slight variations.
4. Porosity:
Porosity, or the presence of tiny voids or pores within the aluminum structure, can significantly influence density. Casting processes or other manufacturing techniques might introduce porosity, resulting in a lower overall density than expected. This is an important consideration in structural applications where integrity is paramount.
5. Processing and Manufacturing Techniques:
Different manufacturing processes, such as casting, rolling, extrusion, or forging, can affect the final density of the aluminum product. These techniques can influence the microstructure and introduce variations in density. For instance, cold working can increase density slightly due to increased atomic packing.
Applications of Aluminum Based on its Density
The lightweight nature of aluminum, a direct consequence of its low density, has revolutionized numerous industries:
1. Aerospace Industry:
Aluminum alloys are the backbone of modern aircraft construction. Their high strength-to-weight ratio is essential for fuel efficiency and maneuverability. Airframes, wings, fuselage components, and other critical parts are frequently made from various aluminum alloys tailored for specific structural requirements.
2. Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry increasingly utilizes aluminum for components like engine blocks, wheels, and body panels. This reduces vehicle weight, improving fuel economy and performance. Aluminum's corrosion resistance is also an advantage, contributing to the vehicle's longevity.
3. Packaging Industry:
Aluminum's malleability and corrosion resistance make it ideal for packaging applications. Aluminum cans for beverages are a classic example, benefiting from the metal's lightweight nature and recyclability. Aluminum foil is another common application, utilized for food preservation and other purposes.
4. Construction Industry:
Aluminum finds use in building construction, including window frames, doors, roofing materials, and cladding. Its lightweight nature simplifies handling and installation, while its corrosion resistance ensures durability. Aluminum's aesthetic appeal also contributes to its popularity in architectural applications.
5. Electrical Industry:
Aluminum's excellent electrical conductivity makes it a suitable material for electrical wiring and transmission lines. Although copper is more commonly used in certain applications due to superior conductivity, aluminum's lightweight nature and lower cost make it a cost-effective alternative in some situations.
Measuring the Density of Aluminum
Accurately determining the density of a specific aluminum sample requires precise measurement techniques. Common methods include:
-
Archimedes' principle: This classic method involves measuring the apparent weight loss of the aluminum sample when submerged in a liquid of known density (usually water). The difference in weight allows for the calculation of the sample's volume, subsequently leading to density determination.
-
Direct measurement of mass and volume: This involves accurately measuring the mass of the aluminum sample using a balance and its volume using techniques such as water displacement or caliper measurements for regular shapes. The density is then calculated by dividing the mass by the volume.
-
Density meters: Specialized instruments, such as density meters, provide a rapid and accurate measurement of the density of liquids and solids. These are particularly useful for quality control purposes in aluminum production.
Conclusion: The Significance of Aluminum Density
The density of aluminum, approximately 2.70 g/cm³, is a critical property driving its widespread use across various industries. Its relatively low density contributes to its lightweight nature, making it ideal for applications requiring weight reduction, portability, and cost-effectiveness. However, understanding the factors influencing density variations, including temperature, alloying elements, impurities, and processing techniques, is crucial for accurate material selection and engineering calculations. The continued development of aluminum alloys with enhanced properties will likely expand its role in future technologies. From aerospace engineering to everyday consumer goods, the significance of aluminum's density remains undeniable.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Density Of Aluminum Metal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.