What Is The Conjugate Base For H2so4
News Leon
Apr 07, 2025 · 5 min read
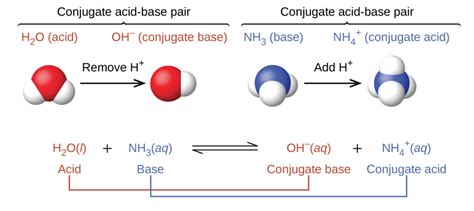
Table of Contents
What is the Conjugate Base for H₂SO₄? A Deep Dive into Acid-Base Chemistry
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), a strong diprotic acid, plays a crucial role in numerous industrial processes and chemical reactions. Understanding its behavior, particularly its conjugate bases, is fundamental to comprehending its reactivity and applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of conjugate bases, explores the conjugate bases of H₂SO₄, and examines their properties and significance.
Understanding Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
The concept of conjugate acid-base pairs is central to Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory. According to this theory, an acid is a substance that donates a proton (H⁺), while a base is a substance that accepts a proton. When an acid donates a proton, it forms its conjugate base, which is the species remaining after the proton is lost. Conversely, when a base accepts a proton, it forms its conjugate acid.
The relationship between an acid and its conjugate base is characterized by a single proton difference. They are essentially the same molecule, differing only by the presence or absence of a proton. A strong acid will have a weak conjugate base, and vice-versa. This is because a strong acid readily donates its proton, leaving behind a stable, weak conjugate base that has little tendency to accept a proton back.
H₂SO₄: A Diprotic Acid
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a diprotic acid, meaning it can donate two protons. This distinguishes it from monoprotic acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl), which can only donate one proton. This diprotic nature leads to the formation of two conjugate bases.
The Conjugate Bases of H₂SO₄
Because H₂SO₄ can donate two protons, it forms two conjugate bases:
1. Hydrogen Sulfate Ion (HSO₄⁻): The First Conjugate Base
When H₂SO₄ donates its first proton, it forms the hydrogen sulfate ion (HSO₄⁻). This is the first conjugate base. The reaction can be represented as:
H₂SO₄ ⇌ H⁺ + HSO₄⁻
The double arrow (⇌) indicates that this is an equilibrium reaction. In aqueous solution, the equilibrium lies heavily to the right because H₂SO₄ is a strong acid for its first proton donation. This means that a significant amount of H₂SO₄ dissociates, generating a substantial concentration of H⁺ and HSO₄⁻ ions.
Properties of HSO₄⁻:
- Weak Acidic Properties: Although formed from a strong acid, HSO₄⁻ itself is a weak acid. It can further donate its proton:
HSO₄⁻ ⇌ H⁺ + SO₄²⁻
-
Amphoteric Nature: Due to its ability to both donate and accept a proton (acting as both an acid and a base), HSO₄⁻ is considered amphoteric.
-
Prevalence: This ion is commonly found in various chemical environments and plays a significant role in many reactions.
2. Sulfate Ion (SO₄²⁻): The Second Conjugate Base
When HSO₄⁻ donates its proton, it forms the sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻). This is the second conjugate base of H₂SO₄. The reaction is:
HSO₄⁻ ⇌ H⁺ + SO₄²⁻
This equilibrium lies significantly further to the left compared to the first dissociation of H₂SO₄, reflecting the weaker acidic nature of HSO₄⁻.
Properties of SO₄²⁻:
-
Very Weak Acidity: The sulfate ion is a very weak acid, showing negligible tendency to donate a proton.
-
Stable Anion: It is a highly stable anion, found extensively in various sulfate salts.
-
Important in Biological Systems: Sulfate ions play crucial roles in various biological systems, including enzyme function and metabolism.
Comparing the Conjugate Bases
The two conjugate bases of H₂SO₄ differ significantly in their acidic strengths:
| Conjugate Base | Formula | Acid Strength | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Sulfate Ion | HSO₄⁻ | Weak Acid | Moderately Stable |
| Sulfate Ion | SO₄²⁻ | Very Weak Acid | Highly Stable |
The relative strengths of the acids and their conjugate bases highlight the stepwise dissociation of a diprotic acid. The first proton is readily released, while the second proton is held more tightly.
Applications and Significance of Conjugate Bases
The conjugate bases of sulfuric acid, HSO₄⁻ and SO₄²⁻, find numerous applications across various fields:
-
Industrial Processes: Sulfate salts, derived from SO₄²⁻, are widely used in various industrial applications, including fertilizer production, paper manufacturing, and metal processing.
-
Chemical Synthesis: HSO₄⁻ and SO₄²⁻ participate in numerous chemical reactions as reactants or catalysts.
-
Analytical Chemistry: These ions play crucial roles in titrations and other analytical techniques.
-
Environmental Science: Understanding the behavior of sulfate ions is critical in assessing water quality and environmental impacts.
-
Biological Systems: As mentioned earlier, sulfate ions are integral components of biological processes.
Further Considerations: Factors Affecting Conjugate Base Strength
Several factors influence the strength of a conjugate base:
-
Electronegativity: Highly electronegative atoms within the conjugate base can stabilize the negative charge, leading to a weaker conjugate base.
-
Resonance: The presence of resonance structures can delocalize the negative charge, enhancing the stability and weakening the conjugate base's ability to accept a proton.
-
Size and Polarizability: Larger anions with greater polarizability can better accommodate the negative charge, resulting in a weaker conjugate base.
-
Solvent Effects: The solvent environment can significantly influence the stability and reactivity of conjugate bases.
Conclusion: Understanding the Conjugate Bases of H₂SO₄ is Key
The conjugate bases of sulfuric acid, HSO₄⁻ and SO₄²⁻, are crucial components in a wide array of chemical processes and applications. Their properties, including their acidic strengths and stabilities, stem from the inherent nature of sulfuric acid as a diprotic acid and are influenced by several factors. This comprehensive understanding is essential for various fields, ranging from industrial chemistry to environmental science and biological research. Further exploration into the specific reactions and applications of these ions would provide an even deeper understanding of their significant roles in the chemical world. By grasping the fundamental concepts of conjugate acid-base pairs and the factors affecting conjugate base strength, one can effectively navigate the complexities of acid-base chemistry and its numerous applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Oxidation State Of Sulphur In So2
Apr 09, 2025
-
What Is The Freezing Point On The Kelvin Scale
Apr 09, 2025
-
How Long Is A Tooth Brush
Apr 09, 2025
-
Are All Physical Changes Accompanied By Chemical Changes
Apr 09, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Following Figure Have
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Conjugate Base For H2so4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.