What Is It Called When It Says Speed With Direction
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
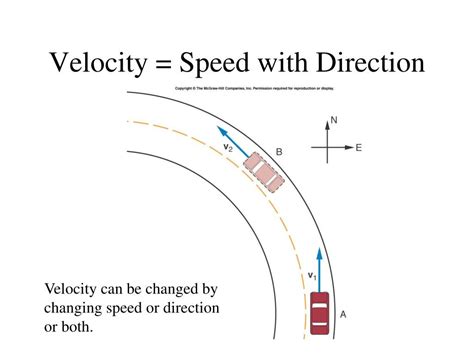
Table of Contents
What is it called when it says speed with direction? Understanding Vectors
The phrase "speed with direction" describes a fundamental concept in physics and mathematics: velocity. While speed tells us how fast something is moving, velocity tells us how fast and in what direction. This seemingly small difference is crucial for understanding many aspects of the physical world, from projectile motion to fluid dynamics. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the concept of velocity, exploring its relationship with speed, its representation, and its applications.
The Difference Between Speed and Velocity
The key distinction between speed and velocity lies in their nature:
-
Speed: A scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude (size or amount). It answers the question: "How fast?" For example, a car traveling at 60 mph has a speed of 60 mph. The direction of travel is irrelevant to its speed.
-
Velocity: A vector quantity, possessing both magnitude and direction. It answers the question: "How fast and in what direction?" A car traveling at 60 mph north has a velocity of 60 mph north. The direction is an integral part of the velocity.
Illustrative Examples
Consider these scenarios to solidify the difference:
-
Scenario 1: Two cars are traveling at 60 mph. One heads north, and the other heads south. They have the same speed but opposite velocities.
-
Scenario 2: A person walks 5 miles in an hour, then rests for an hour before walking another 5 miles in an hour. The average speed is 5 mph, but the average velocity could be 0 mph if their starting and ending points are the same (e.g., a round trip). This emphasizes the importance of direction in velocity.
-
Scenario 3: A plane flies in a circle at a constant speed. While its speed remains constant, its velocity is constantly changing because the direction of motion is constantly changing. This highlights that a changing velocity does not necessarily mean a changing speed.
Representing Velocity: Vectors
Because velocity is a vector, we need a way to represent both its magnitude and direction. This is typically done using:
-
Arrows: The length of the arrow represents the magnitude (speed), and the arrow's direction indicates the direction of motion. Longer arrows represent higher speeds.
-
Coordinates: In a Cartesian coordinate system (x, y, z), velocity can be represented by components along each axis. For example, a velocity of (3, 4) m/s represents movement 3 m/s in the x-direction and 4 m/s in the y-direction. The magnitude of this velocity can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem: √(3² + 4²) = 5 m/s.
-
Polar Coordinates: Alternatively, we can use polar coordinates (magnitude, angle). The magnitude is the speed, and the angle specifies the direction relative to a reference axis (often the positive x-axis).
Calculating Velocity
Calculating velocity involves determining both the magnitude (speed) and the direction of motion.
-
Average Velocity: The average velocity is the displacement (change in position) divided by the time taken. Displacement is a vector quantity representing the straight-line distance between the starting and ending points, considering direction. The formula is:
Average Velocity = Displacement / Time
-
Instantaneous Velocity: This represents the velocity at a specific instant in time. It's the limit of the average velocity as the time interval approaches zero. In calculus, this is represented as the derivative of the position function with respect to time.
Examples of Velocity Calculations:
-
Example 1: A car travels 100 km north in 2 hours. Its average velocity is 50 km/h north.
-
Example 2: An object moves from (1, 2) to (4, 6) in 3 seconds. The displacement is (3, 4). The average velocity is (1, 4/3) m/s.
-
Example 3: A projectile launched at an angle will have a continuously changing velocity due to the influence of gravity. Calculating the instantaneous velocity at any point requires calculus.
Applications of Velocity
The concept of velocity is fundamental to many fields, including:
-
Physics: Analyzing projectile motion, orbital mechanics, fluid flow, and collisions all rely heavily on understanding velocity. Newton's laws of motion are expressed in terms of velocity and acceleration (the rate of change of velocity).
-
Engineering: Designing vehicles, aircraft, and spacecraft requires precise calculations of velocity and its relationship to forces and energy. Control systems often use velocity feedback to maintain stability and performance.
-
Meteorology: Weather forecasting involves tracking the velocity of air masses and storm systems. Understanding wind velocity is crucial for predicting weather patterns.
-
Astronomy: Astronomers use velocity measurements to determine the movement of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. The redshift of light from distant galaxies is a measure of their velocity relative to us.
-
Navigation: GPS systems rely on precise velocity measurements to determine location and track movement. Navigation systems in ships and aircraft also use velocity data.
Advanced Concepts Related to Velocity
-
Relative Velocity: This refers to the velocity of an object as measured from a moving frame of reference. For example, the velocity of a person walking on a moving train is different relative to the train and relative to the ground.
-
Angular Velocity: This describes the rate of change of angular position (rotation). It is often expressed in radians per second.
-
Velocity Field: In fluid mechanics, a velocity field describes the velocity of a fluid at each point in space. Visualizing velocity fields helps understand fluid flow patterns.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between speed and velocity is crucial for comprehending many aspects of the physical world. Velocity, being a vector quantity, incorporates both speed and direction, making it a powerful tool for analyzing motion and change. Its applications span numerous fields, highlighting its fundamental importance in science, engineering, and technology. While seemingly simple at first glance, a thorough understanding of velocity unlocks the ability to analyze complex systems and predict their behavior, emphasizing the importance of considering both the magnitude and direction of movement. From the simple act of walking to the complex mechanics of orbital motion, velocity is the key to unlocking a deeper understanding of our physical reality.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Renewable Resource
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Faces Are There On A Standard Dice
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Function Of Skin
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Phase Is The Longest In The Cell Cycle
Mar 15, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Square
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is It Called When It Says Speed With Direction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
