What Energy Tranformation Happens In A Motot
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
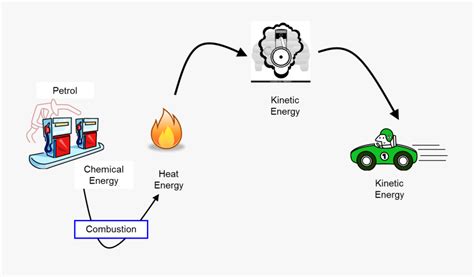
Table of Contents
Energy Transformation in a Motor: From Electrical Input to Mechanical Output
Internal combustion engines, electric motors, and even jet engines all perform the same fundamental task: converting one form of energy into mechanical energy to do work. This article dives deep into the energy transformations that occur within a motor, focusing primarily on electric motors due to their increasing prevalence and complexity. We'll explore the underlying physics, different motor types, and the efficiency considerations involved in this crucial energy conversion process.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Energy and its Transformations
Before delving into the specifics of motor operation, it's crucial to understand the basic principles of energy and its transformations. Energy, simply put, is the capacity to do work. It exists in various forms, including:
- Electrical Energy: The energy associated with the movement of electric charges. This is the primary input for electric motors.
- Magnetic Energy: The energy stored in a magnetic field. This plays a central role in the operation of most electric motors.
- Mechanical Energy: The energy associated with the motion of objects. This is the desired output of a motor, used to power machinery, vehicles, and countless other applications.
- Thermal Energy (Heat): An inevitable byproduct of energy conversion processes, some energy is always lost as heat due to friction and resistance.
The Law of Conservation of Energy dictates that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In a motor, electrical energy is primarily converted into mechanical energy, with some unavoidable energy loss as heat.
The Heart of the Matter: How Electric Motors Work
Electric motors utilize the principles of electromagnetism to convert electrical energy into mechanical rotational energy. This conversion relies on the interaction between magnetic fields generated by electric currents and permanent magnets. The fundamental principle is Lorentz force, which describes the force experienced by a charged particle moving in a magnetic field.
Here's a simplified breakdown:
-
Electrical Input: The motor receives electrical energy from a power source, typically a battery, power grid, or generator. This electrical energy creates a current that flows through the motor's windings.
-
Magnetic Field Generation: The current flowing through the motor windings generates a magnetic field. This field interacts with the magnetic field of permanent magnets or electromagnets within the motor.
-
Electromagnetic Interaction: The interaction between these magnetic fields produces a force, causing the motor's rotor (the rotating part) to turn. This force is the result of the attraction and repulsion between the magnetic poles.
-
Mechanical Output (Rotation): The rotational motion of the rotor is the motor's mechanical output. This rotating shaft can then be coupled to machinery to perform work.
-
Energy Loss (Heat): Throughout this process, some energy is lost as heat due to resistance in the windings, friction in the bearings, and other inefficiencies.
Different Types of Electric Motors and Their Energy Transformations
Several types of electric motors exist, each with its unique design and energy conversion characteristics:
1. DC Motors (Direct Current):
DC motors operate using direct current electricity. The energy transformation is relatively straightforward:
- Commutator: A key component in DC motors, the commutator reverses the current direction in the rotor windings at precisely the right moments, ensuring continuous rotation. This switching action itself introduces some energy loss as heat.
- Energy Conversion: DC motors directly convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of the magnetic field produced by the stator (stationary part) and the rotor. The commutator's role is essential for maintaining unidirectional torque.
- Efficiency: DC motors are relatively simple but can be less efficient than AC motors, especially at higher speeds.
2. AC Motors (Alternating Current):
AC motors are more prevalent due to their wider availability and often higher efficiency. They come in several types, including:
-
Induction Motors (Asynchronous Motors): These are the most common type of AC motor. They utilize a rotating magnetic field created in the stator to induce current in the rotor. This induced current interacts with the stator's field, producing torque and rotation. The rotor doesn't directly connect to a power source, leading to simplicity and robustness. Energy transformation involves converting alternating current into a rotating magnetic field that induces current in the rotor, ultimately resulting in mechanical energy. Slip (the difference between the stator field's speed and rotor speed) represents energy loss as heat.
-
Synchronous Motors: In synchronous motors, the rotor's speed is synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply. These motors are typically more efficient than induction motors, particularly at constant speeds, but require more complex control systems. They achieve synchronization using either permanent magnets or DC excitation to the rotor windings.
-
Stepper Motors: Stepper motors provide precise rotational control, moving in discrete steps rather than continuously rotating. They're ideal for applications requiring precise positioning, such as robotics and 3D printers. Energy transformation is similar to other AC motors but involves precise control of the current flow to achieve stepwise rotation.
3. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC):
BLDC motors combine the advantages of both DC and AC motors. They utilize permanent magnets in the rotor and electronically controlled switching to create a rotating magnetic field in the stator. This eliminates the need for brushes and commutators, resulting in higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and reduced maintenance. The energy transformation is similar to DC motors but with superior efficiency due to the absence of mechanical switching.
Efficiency Considerations and Energy Losses
No energy conversion process is perfectly efficient. In motors, various factors contribute to energy losses:
- Copper Losses (I²R Losses): Resistance in the motor windings generates heat, leading to energy loss. This is proportional to the square of the current and the resistance.
- Iron Losses (Core Losses): These losses occur due to hysteresis (energy loss associated with the magnetization and demagnetization of the core material) and eddy currents (circulating currents induced in the core).
- Mechanical Losses: Friction in bearings, windage (air resistance), and other mechanical components lead to energy losses.
- Stray Losses: These are miscellaneous losses that are difficult to quantify, including leakage flux and other electromagnetic phenomena.
Motor efficiency is often expressed as a percentage, representing the ratio of mechanical output power to electrical input power. High-efficiency motors minimize energy losses, leading to significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Advanced Motor Technologies and Future Trends
Ongoing research and development continuously strive to improve motor efficiency and performance:
- High-Temperature Superconductors: Utilizing superconducting materials can drastically reduce resistance in windings, leading to significantly higher efficiency.
- Advanced Materials: The development of new materials for motor components improves efficiency and durability.
- Optimized Designs: Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and other advanced simulation techniques are used to optimize motor designs, minimizing losses.
- Smart Motor Control: Sophisticated control systems adjust motor operation based on real-time conditions, maximizing efficiency and performance.
Conclusion
The energy transformation within a motor is a fascinating and complex process. Understanding the underlying principles of electromagnetism, the different types of motors, and the factors influencing efficiency is crucial for engineers, designers, and anyone interested in the technology that powers our world. As technology advances, we can expect even more efficient and sophisticated motors, further optimizing the conversion of electrical energy into the mechanical energy that drives our modern society. The continuous improvement in motor technology is essential for achieving sustainability goals and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In 1991 The Soviet Union Collapsed Mainly Because
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Much Does A Drop Of Water Weigh
Mar 20, 2025
-
34 5 As A Mixed Number
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Size Of A Cell Is Limited By The
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Trips Around The Sun In A Year
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Energy Tranformation Happens In A Motot . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
