What Does A Pyramid Of Biomass Represent
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
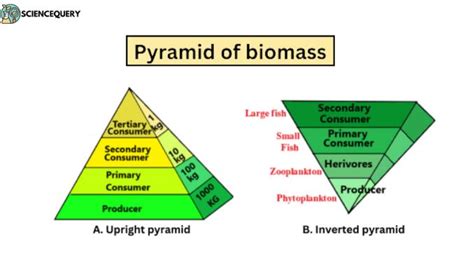
Table of Contents
- What Does A Pyramid Of Biomass Represent
- Table of Contents
- What Does a Pyramid of Biomass Represent? Unraveling the Ecological Hierarchy
- Understanding the Building Blocks: Trophic Levels and Biomass
- The Visual Representation: Structure of a Biomass Pyramid
- Interpreting the Pyramid:
- Variations in Biomass Pyramids: Inverted Pyramids and Other Anomalies
- Inverted Biomass Pyramids:
- Other Deviations from the Classic Pyramid:
- The Importance of Biomass Pyramids in Ecological Studies
- Comparing Biomass Pyramids with Other Ecological Pyramids
- Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Ecological Understanding
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What Does a Pyramid of Biomass Represent? Unraveling the Ecological Hierarchy
A pyramid of biomass offers a compelling visual representation of the ecological hierarchy within a given ecosystem. Unlike a pyramid of numbers, which simply counts organisms, a biomass pyramid depicts the total dry mass of organisms at each trophic level. Understanding this representation is crucial for grasping the intricate relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers within an ecosystem, as well as comprehending concepts like energy flow and ecological efficiency.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Trophic Levels and Biomass
Before delving into the intricacies of biomass pyramids, it's essential to define key terms.
-
Trophic Levels: These represent the different feeding levels within a food chain or food web. The first trophic level always comprises producers, organisms that synthesize their own food (typically plants). The subsequent levels are occupied by consumers, ranging from primary consumers (herbivores) to secondary and tertiary consumers (carnivores and omnivores). Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) are often not explicitly represented in a pyramid but play a vital role in recycling nutrients.
-
Biomass: This refers to the total dry mass of living organisms at a particular trophic level. It's important to note that "dry mass" is used to exclude the water content, which can significantly vary between organisms and environments. Biomass is usually expressed in units such as grams per square meter (g/m²) or kilograms per hectare (kg/ha).
The Visual Representation: Structure of a Biomass Pyramid
A typical biomass pyramid is constructed as a pyramid, with each level representing a trophic level. The base of the pyramid represents the producers, which typically have the highest biomass. As you move up the pyramid to higher trophic levels (consumers), the biomass generally decreases. This decrease reflects the energy loss at each trophic level, as only a fraction of the energy consumed is converted into biomass.
Interpreting the Pyramid:
A pyramid of biomass illustrates several key ecological concepts:
-
Energy Flow: The pyramid visually demonstrates the flow of energy through the ecosystem. Energy from the sun is captured by producers through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to higher trophic levels through consumption. However, a significant portion of energy is lost at each transfer, primarily as heat, through respiration, and as undigested waste.
-
Ecological Efficiency: The pyramid reflects ecological efficiency, which is the percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next. This efficiency is typically low (around 10%), meaning only a small fraction of the energy available at one level is converted into biomass at the next. This inefficiency explains why biomass decreases as you ascend the pyramid.
-
Carrying Capacity: The biomass at each level influences the carrying capacity of the higher levels. The total biomass of producers sets a limit on the number of herbivores that can be supported. Similarly, the biomass of herbivores limits the number of carnivores that can exist within the ecosystem.
-
Nutrient Cycling: Though not directly represented visually, the pyramid is implicitly linked to nutrient cycling. Decomposers break down dead organic matter from all trophic levels, releasing nutrients back into the environment to be taken up by producers, thus completing the cycle.
Variations in Biomass Pyramids: Inverted Pyramids and Other Anomalies
While the typical pyramid shape reflects a general ecological pattern, exceptions exist.
Inverted Biomass Pyramids:
In some aquatic ecosystems, an inverted biomass pyramid can be observed. This means the biomass of consumers exceeds the biomass of producers. This apparent anomaly can be explained by the high turnover rate of producers. Phytoplankton, the primary producers in many aquatic ecosystems, reproduce rapidly, having a short lifespan and a relatively low biomass at any given time. However, their rapid production sustains a large population of zooplankton (primary consumers), resulting in a higher consumer biomass.
It’s crucial to understand that an inverted biomass pyramid doesn't negate the fundamental principle of energy loss. Even in these ecosystems, a significant amount of energy is lost as you move up the trophic levels; the anomaly is in the biomass representation rather than the energy transfer itself.
Other Deviations from the Classic Pyramid:
Other factors can influence the shape of a biomass pyramid, including:
-
Seasonal Variations: Biomass can fluctuate seasonally, depending on factors like temperature, rainfall, and resource availability. This can lead to temporary changes in the shape of the pyramid.
-
Human Intervention: Human activities, such as fishing or harvesting, can significantly alter the biomass of different trophic levels, potentially disrupting the pyramid's structure.
-
Specific Ecosystem Dynamics: The complexity of individual food webs and unique environmental conditions can create deviations from the idealized pyramid shape.
The Importance of Biomass Pyramids in Ecological Studies
Biomass pyramids are invaluable tools for ecologists for several reasons:
-
Ecosystem Monitoring: They help in monitoring ecosystem health and stability by tracking changes in biomass at different trophic levels. Significant changes may indicate problems like pollution, habitat loss, or overexploitation.
-
Resource Management: Understanding biomass distribution is critical for managing resources sustainably. For instance, it helps in setting sustainable fishing quotas to prevent overfishing and the collapse of fish populations.
-
Conservation Efforts: By visualizing the energy flow and biomass distribution, pyramids aid in conservation planning. It allows for better understanding of the impact of human activities on endangered species and their ecosystems.
-
Predictive Modeling: Biomass data can be incorporated into ecological models to predict the effects of environmental changes or human interventions on the ecosystem's structure and function.
Comparing Biomass Pyramids with Other Ecological Pyramids
It's crucial to differentiate biomass pyramids from other ecological pyramids, such as pyramids of numbers and pyramids of energy.
-
Pyramids of Numbers: These simply count the number of organisms at each trophic level. While easy to understand, they don’t accurately reflect the relative importance of each organism based on its biomass or energy contribution. A forest with numerous insects and a few large trees might show an inverted pyramid of numbers.
-
Pyramids of Energy: These depict the energy flow at each trophic level, usually expressed in units like kilocalories per square meter per year (kcal/m²/year). They provide a more accurate reflection of the actual energy transfer, although they are generally more complex to construct than biomass pyramids. While biomass pyramids show the amount of organic matter at each level, energy pyramids show the energy transferred. This difference highlights the energy losses during each trophic level transfer.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Ecological Understanding
The pyramid of biomass is a powerful visual tool for understanding the structure and function of ecosystems. While it may not capture the entire complexity of ecological interactions, it provides a clear and concise representation of the hierarchical distribution of biomass within a trophic structure. By understanding the limitations and variations of biomass pyramids, we can utilize this tool effectively to monitor ecosystem health, manage resources sustainably, and inform conservation efforts. The visual simplicity of the pyramid, coupled with its representation of fundamental ecological concepts, makes it an indispensable tool in ecological research and education. Understanding the interplay between biomass, energy flow, and ecological efficiency as represented by the pyramid allows us to appreciate the intricate balance of life within our planet's diverse ecosystems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Blood Plasma Without The Clotting Factors Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
Matter Anything That Has Mass And Takes Up Space
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Percent Of 84 Is 21
Mar 26, 2025
-
Request Letter For Increment In Salary
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is Copper A Good Conductor Of Electricity
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does A Pyramid Of Biomass Represent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
