Transverse Mechanical Waves Can Pass Through
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
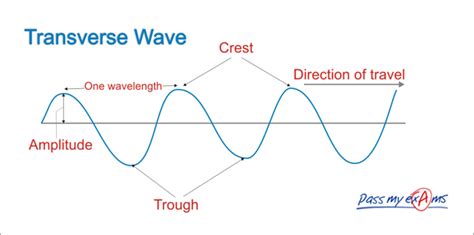
Table of Contents
Transverse Mechanical Waves: A Deep Dive into Transmission
Transverse mechanical waves, a fundamental concept in physics, are characterized by the oscillation of particles perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike longitudinal waves where particle displacement is parallel to wave movement, transverse waves exhibit a unique behavior influencing their transmission through various media. Understanding which media allow these waves to pass through, and the factors affecting their transmission, is crucial in various scientific fields. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of transverse mechanical wave transmission, exploring the different materials they can traverse and the factors influencing their propagation.
What are Transverse Mechanical Waves?
Before diving into transmission, let's solidify our understanding of transverse mechanical waves. These waves require a medium – a physical substance – for their propagation. The medium's particles vibrate perpendicular to the wave's direction of travel. Think of a wave on a string: when you pluck the string, the particles of the string move up and down (perpendicular), while the wave itself travels along the length of the string.
Key Characteristics:
- Mechanical: They require a material medium for propagation. They cannot travel through a vacuum.
- Transverse: Particle displacement is perpendicular to the wave direction.
- Energy Transfer: They transfer energy through the medium without transferring mass.
Examples abound in our everyday lives:
- Waves on a string: A classic example illustrating the perpendicular motion of particles.
- Seismic S-waves: These secondary waves generated during earthquakes are transverse waves that travel through the Earth's solid layers.
- Light waves (Electromagnetic, but analogous): While light is an electromagnetic wave and doesn't require a medium, its behavior in terms of polarization and transverse nature offers a useful analogy. Light waves oscillate perpendicular to their direction of travel.
Media Through Which Transverse Mechanical Waves Can Pass
The transmission of transverse mechanical waves depends heavily on the properties of the medium. Several factors influence whether a wave can propagate and how efficiently it does so.
1. Solids:
Solids are the most efficient transmitters of transverse mechanical waves. The strong intermolecular forces within solids provide the necessary rigidity for the particles to transfer the wave's energy effectively. The tighter the bonds between atoms, the faster the wave propagates.
- Crystalline Solids: These solids have a highly ordered atomic structure, which allows for efficient and consistent wave transmission.
- Amorphous Solids: While less ordered, amorphous solids still transmit transverse waves, although with potentially higher energy losses due to the less regular structure.
- Elasticity: The elasticity of the solid plays a crucial role. Higher elasticity implies a greater ability to restore shape after deformation, leading to more efficient wave propagation.
2. Liquids:
Liquids transmit transverse waves to a much lesser extent than solids. The weaker intermolecular forces in liquids allow for less efficient energy transfer between particles. The particles can move somewhat independently, making the propagation of a clearly defined transverse wave difficult. However, under specific conditions, such as high pressure or specific molecular structures, some limited transmission may occur.
- Viscosity: High viscosity (resistance to flow) hinders the transmission of transverse waves in liquids, as it dampens the particle oscillations.
3. Gases:
Gases are extremely poor transmitters of transverse mechanical waves. The extremely weak intermolecular forces and large distances between particles prevent efficient energy transfer for perpendicular oscillations. Therefore, transverse waves generally do not propagate effectively through gases under normal conditions.
4. The Role of Density and Rigidity:
Both density and rigidity are critical factors affecting wave transmission. A denser medium, with more tightly packed particles, generally facilitates faster wave propagation. However, the rigidity of the medium is paramount for transverse waves: a more rigid medium (higher shear modulus) will support and transmit transverse waves more effectively.
Factors Affecting Transmission of Transverse Mechanical Waves
Beyond the medium itself, several factors influence the transmission of transverse mechanical waves:
1. Frequency:
Higher frequency waves generally experience greater attenuation (energy loss) during transmission. This is because higher frequencies correspond to faster particle oscillations, leading to increased frictional losses within the medium.
2. Wavelength:
The wavelength of the wave also impacts transmission. Shorter wavelengths often encounter more obstacles and irregularities in the medium, leading to scattering and reduced transmission efficiency.
3. Temperature:
Temperature affects the intermolecular forces and the overall elasticity of the medium. Higher temperatures generally lead to weaker intermolecular forces, reducing the efficiency of transverse wave transmission in solids and liquids. In gases, increased temperature leads to more chaotic particle motion, further hindering transmission.
4. Medium Heterogeneity:
Variations in the medium's properties (density, elasticity, etc.) along the wave's path can cause scattering, refraction, and reflection of the wave, reducing the overall transmission efficiency.
5. Damping and Attenuation:
Internal friction and energy losses within the medium, often referred to as damping or attenuation, significantly reduce the wave's amplitude as it propagates. This effect is more pronounced in media with higher viscosity or internal friction.
Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding the transmission of transverse waves is crucial in numerous applications and real-world scenarios:
- Seismology: Studying seismic S-waves (transverse waves) allows seismologists to understand the Earth's internal structure and predict earthquakes. The analysis of S-wave propagation reveals information about the Earth's layers, as S-waves cannot pass through liquid (the Earth's outer core).
- Material Science: The study of how transverse waves propagate through materials provides valuable insights into the material's mechanical properties, such as elasticity and rigidity. This knowledge is crucial in designing and selecting materials for various engineering applications.
- Medical Imaging: Ultrasound imaging utilizes the transmission of both longitudinal and transverse waves through biological tissues. The analysis of wave propagation provides detailed information about tissue structure and properties, aiding in medical diagnosis.
- Nondestructive Testing: Transverse waves are employed in various nondestructive testing techniques to detect flaws and defects in materials. By analyzing the wave's reflection and transmission patterns, engineers can identify internal cracks, voids, and other imperfections.
Conclusion: A Summary of Transverse Wave Transmission
Transverse mechanical waves are a fascinating phenomenon with far-reaching applications. Their transmission is intricately linked to the properties of the medium through which they propagate. While solids are excellent transmitters, liquids exhibit limited transmission, and gases generally do not support the propagation of transverse waves effectively. Understanding the factors influencing wave transmission—frequency, wavelength, temperature, medium heterogeneity, and damping—is crucial in various fields. This knowledge helps us unravel the complexities of the Earth's interior, develop advanced materials, and improve diagnostic medical imaging and nondestructive testing techniques. Further research continues to refine our understanding of these fundamental wave phenomena and their diverse applications. The ongoing exploration of wave transmission contributes to advancements in diverse scientific and engineering domains, reinforcing their importance in our modern world. From seismic studies to medical imaging, the ability to understand and manipulate the propagation of transverse waves has profound implications for our scientific understanding and technological development.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 Functions Of A Political Party
Mar 26, 2025
-
Where Does Mitosis Take Place In The Body
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Proton Travels Through Uniform Magnetic And Electric Fields
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Transverse Mechanical Waves Can Pass Through . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
