The Study Of Tissue Is Called
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 7 min read
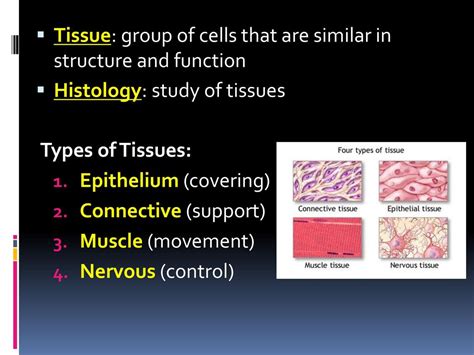
Table of Contents
The Study of Tissue is Called Histology: A Deep Dive into the Microscopic World
The study of tissue is called histology. Histology is a cornerstone of biology and medicine, providing crucial insights into the structure and function of living organisms. This detailed exploration delves into the fascinating world of histology, covering its techniques, applications, and significance across various scientific disciplines.
What is Histology?
Histology, derived from the Greek words "histos" (tissue) and "logos" (study), is the microscopic study of the microanatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It's a powerful tool that bridges the gap between macroscopic anatomy (the study of structures visible to the naked eye) and the microscopic world of cells and their interactions. By examining thin sections of tissue under a microscope, histologists can identify different cell types, their organization into tissues, and the overall architecture of organs. This detailed understanding is essential for comprehending the complex processes of life and diagnosing diseases.
Key Aspects of Histology
Histology encompasses several key aspects:
- Tissue Preparation: This critical first step involves fixing, processing, sectioning, and staining tissues to make them suitable for microscopic examination. Different methods are used depending on the type of tissue and the information sought.
- Microscopy: Histologists utilize various types of microscopes, including light microscopes and electron microscopes, to visualize tissues at different magnifications and resolutions. Light microscopy provides a general overview, while electron microscopy allows for visualization of ultrastructural details.
- Microscopic Analysis: Histologists analyze the stained tissue sections to identify different cell types, their arrangement, and the presence of any abnormal structures. This detailed analysis is crucial for diagnosis and research.
- Interpretation and Reporting: The final step involves interpreting the microscopic findings and preparing a report that communicates the results clearly and concisely. This often involves correlation with clinical information to provide a complete picture.
Techniques Used in Histology
A range of techniques are employed in histology to prepare and visualize tissue samples. These techniques are crucial for obtaining high-quality images that enable accurate interpretation and analysis.
1. Tissue Fixation
The initial step in histology is tissue fixation. This process aims to preserve the tissue's structure and prevent degradation by enzymes or bacteria. Common fixatives include formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, and alcohol. The choice of fixative depends on the type of tissue and the specific structures of interest. Proper fixation is essential for maintaining the integrity of cellular components and preventing artifacts.
2. Tissue Processing
After fixation, the tissue undergoes processing. This involves a series of steps that prepare the tissue for sectioning. These steps typically include dehydration (removing water from the tissue), clearing (replacing water with a solvent miscible with embedding medium), and embedding (infiltrating the tissue with a solid medium like paraffin wax or resin). The embedding medium provides support to the tissue, allowing for the creation of thin sections suitable for microscopy.
3. Sectioning
The processed tissue is then sectioned using a microtome, a specialized instrument that produces thin slices (typically 3-10 micrometers thick). These thin sections are essential for allowing light to pass through the tissue for microscopic examination. The thickness of the section is critical; too thick, and detail is lost, too thin, and the section may be fragile and difficult to handle.
4. Staining
Staining is a crucial step that enhances the visibility of different cellular components. Different stains have affinities for specific cellular structures. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the most common method, where hematoxylin stains the nuclei blue and eosin stains the cytoplasm pink. Other specialized stains are used to highlight specific structures, such as connective tissue fibers or microorganisms. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in situ hybridization (ISH) are more advanced techniques that use antibodies or labeled probes to identify specific proteins or nucleic acids within the tissue.
5. Microscopy
Finally, the stained tissue sections are examined using a microscope. Light microscopes are widely used for general histological examination, providing magnification up to 1000x. Electron microscopes, including transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM), provide much higher resolution, allowing for visualization of ultrastructural details down to the nanometer scale. Confocal microscopy is another advanced technique that allows for three-dimensional imaging of tissues.
Types of Tissues Studied in Histology
Histology examines various types of tissues found in living organisms. These tissues are broadly classified into four major categories:
1. Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces, lines cavities and organs, and forms glands. It's characterized by tightly packed cells with minimal extracellular matrix. Epithelial tissues are classified based on cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) and layering (simple, stratified, pseudostratified). Histology reveals the specific arrangements of epithelial cells, providing insights into their functions, such as protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion.
2. Connective Tissue
Connective tissue supports and connects other tissues. It's characterized by abundant extracellular matrix, containing various types of fibers (collagen, elastic, reticular) and ground substance. Connective tissues include loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, and blood. Histology reveals the composition of the extracellular matrix, the types of cells present, and the overall organization of the tissue, providing information about its mechanical properties and functions.
3. Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It's characterized by specialized cells called muscle fibers that contain contractile proteins. Three types of muscle tissue exist: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Histology distinguishes these muscle types based on the arrangement of muscle fibers, the presence of striations, and the type of control (voluntary or involuntary).
4. Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue coordinates and controls bodily functions. It's composed of neurons (nerve cells) and glial cells (supporting cells). Histology reveals the structure of neurons, including their cell bodies, dendrites, and axons, and the organization of glial cells, providing insights into the function of the nervous system.
Applications of Histology
Histology has broad applications in various fields, including:
1. Disease Diagnosis
Histology plays a crucial role in disease diagnosis. Biopsies (small tissue samples) are routinely examined microscopically to identify cancerous and other pathological conditions. Histopathological examination is essential for determining the type, grade, and stage of cancer, guiding treatment decisions, and monitoring disease progression.
2. Research
Histology is essential for biological and medical research. It's used to study the structure and function of tissues and organs in both health and disease. Histological techniques are used to investigate the effects of drugs and toxins, to study developmental processes, and to understand the mechanisms of various diseases.
3. Forensic Science
Histology is used in forensic science to identify tissues and determine the cause of death. Microscopic examination of tissue samples can provide valuable clues in criminal investigations.
4. Veterinary Medicine
Histology is used in veterinary medicine to diagnose diseases in animals. The same histological techniques used in human medicine are applied to diagnose diseases in various animal species.
5. Plant Science
While often associated with animal tissues, histology is also critical in plant science (plant anatomy). Understanding the microscopic structure of plant tissues, such as xylem and phloem, is crucial for studying plant physiology and development.
The Future of Histology
Histology is a continuously evolving field. Advances in microscopy techniques, including high-resolution imaging and three-dimensional reconstruction, are providing increasingly detailed insights into tissue structure and function. New staining techniques and molecular probes are enabling the identification of specific cellular components and molecules, improving the accuracy and specificity of histological analysis. The integration of histological data with other types of data, such as genomic and proteomic data, is leading to a more comprehensive understanding of biological systems. Digital pathology, the use of digital images for histological analysis, is also transforming the field, allowing for remote consultations and improved efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of tissue, known as histology, is a vital field that underpins many areas of biology and medicine. The techniques used in histology, from tissue preparation to microscopy and analysis, are sophisticated and crucial for obtaining detailed insights into the intricate structures and functions of tissues and organs. Its applications are vast, ranging from disease diagnosis to research and forensic science, underscoring its importance in advancing our understanding of the biological world and improving human and animal health. With ongoing technological advancements, histology continues to evolve, promising further breakthroughs in our understanding of biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Pure Substances Are Made Of Only One Type Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Dpt Vaccination Is An Example Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between An Enzyme And A Hormone
Mar 14, 2025
-
An Alloy With One Of The Constituents Being Mercury
Mar 14, 2025
-
9 Is 25 Of What Number
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Study Of Tissue Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
