The Movement Of Earth Around The Sun Is Called
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 7 min read
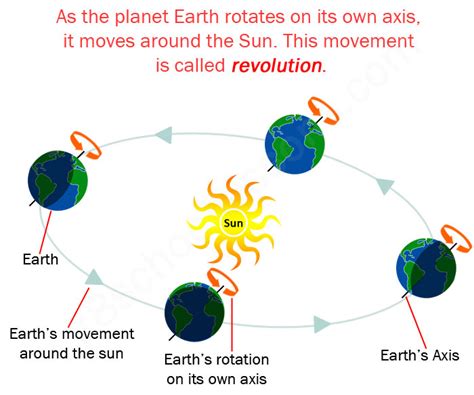
Table of Contents
The Movement of Earth Around the Sun is Called: A Deep Dive into Revolution and its Implications
The movement of Earth around the Sun is called revolution. This seemingly simple statement belies a complex interplay of gravitational forces, celestial mechanics, and profound implications for life on our planet. Understanding Earth's revolution isn't just about memorizing a scientific term; it's about grasping the fundamental processes that shape our world and our place within the vast cosmos. This article delves deep into the concept of Earth's revolution, exploring its mechanics, consequences, and significance.
Understanding Earth's Revolution: More Than Just a Trip Around the Sun
Earth's revolution is its orbital movement around the Sun. It's not a perfectly circular path, but rather an ellipse, with the Sun positioned at one of the two foci (plural of focus). This elliptical orbit means that Earth's distance from the Sun varies throughout the year. The point in Earth's orbit where it is closest to the Sun is called perihelion, and the point where it is farthest is called aphelion. This variation in distance, while influencing seasonal temperatures to a minor extent, isn't the primary driver of our seasons.
The Mechanics of Revolution: Gravity and Inertia
The driving force behind Earth's revolution is gravity. The Sun's immense gravitational pull keeps Earth in its orbit, preventing it from drifting off into the vast expanse of space. However, Earth doesn't simply fall into the Sun. This is due to inertia, the tendency of an object in motion to stay in motion in a straight line. Earth's revolution is a delicate balance between the Sun's gravitational pull, constantly trying to pull Earth inward, and Earth's inertia, trying to keep it moving in a straight line. The result is a continuous elliptical path around the Sun.
The Orbital Period: A Year Defined
One complete revolution of Earth around the Sun takes approximately 365.25 days. This is what defines our year. The extra 0.25 days accumulate over time, necessitating the addition of a leap day every four years (with some exceptions for century years) to keep our calendar synchronized with Earth's actual orbital period. This slight discrepancy highlights the complexity of accurately measuring and predicting celestial movements.
The Impact of Revolution: Seasons and More
While Earth's revolution is a continuous process, its impact is most dramatically felt through the changing seasons. However, the seasons aren't directly caused by the varying distance between Earth and the Sun during perihelion and aphelion. Instead, they are primarily a consequence of Earth's axial tilt.
Earth's Axial Tilt: The Key to Seasonal Variation
Earth's axis is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees relative to its orbital plane. This tilt is crucial because it determines the angle at which sunlight strikes different parts of the Earth throughout the year. During summer in the Northern Hemisphere, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, receiving more direct sunlight and experiencing longer days. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted away, resulting in shorter days and cooler temperatures. Six months later, the situation reverses, with the Southern Hemisphere experiencing summer and the Northern Hemisphere winter.
Beyond Seasons: The Influence on Climate and Ecosystems
The revolution of Earth around the Sun has profound implications beyond simply determining the seasons. The varying amount of sunlight received throughout the year influences climate patterns, affecting weather systems, precipitation levels, and the distribution of plant and animal life. Different regions of the Earth experience different climates due to their latitude and proximity to oceans and mountain ranges, all of which interact with the fundamental influence of Earth's revolution and axial tilt.
Revolution and Other Celestial Movements: A Complex Dance
Earth's revolution around the Sun is not an isolated event. It's part of a much larger, more intricate celestial dance involving the entire solar system. Earth's revolution is intertwined with its rotation, its spinning on its axis, which causes day and night. The interaction of these two movements shapes the patterns of sunlight and darkness across the globe, contributing to the diversity of life on Earth.
The Influence of Other Planets: Gravitational Interactions
The gravitational forces of other planets in our solar system also subtly influence Earth's orbit. These interactions are relatively small, but over long periods, they can cause slight variations in Earth's orbital path. These variations are studied by astronomers to better understand the dynamics of our solar system and predict future changes.
The Precession of the Equinoxes: A Slow Shift
Earth's axis of rotation isn't perfectly stable; it undergoes a slow wobble called precession. This wobble is caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun and the Moon on Earth's equatorial bulge. The precession cycle takes approximately 26,000 years, gradually shifting the position of the equinoxes and solstices over time. This slow shift has long-term implications for Earth's climate and seasons, although the effects are gradual and subtle compared to the annual cycle of seasons.
Observing Earth's Revolution: Evidence and Measurement
The understanding of Earth's revolution wasn't always as clear as it is today. Ancient civilizations observed the movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars, developing calendars and astronomical models based on their observations. Modern astronomy uses sophisticated techniques to precisely measure and track Earth's orbit.
Historical Observations: From Ancient Calendars to Modern Telescopes
Early astronomers, using simple instruments like sundials and astrolabes, carefully tracked the Sun's apparent movement across the sky. Their observations formed the basis for the development of calendars and agricultural practices, highlighting the importance of understanding Earth's revolution for human societies. The invention of the telescope revolutionized astronomical observation, allowing for far more precise measurements of celestial bodies, including Earth's orbit.
Modern Methods: Tracking Earth's Movement with Precision
Today, astronomers use advanced technologies such as satellites, radio telescopes, and sophisticated computer models to track Earth's movement with extraordinary accuracy. These tools allow for precise measurements of Earth's orbital parameters, including its distance from the Sun, its orbital speed, and the shape of its elliptical path. This precise data is essential for various applications, including navigation, space exploration, and climate modeling.
The Significance of Understanding Earth's Revolution: Past, Present, and Future
Understanding Earth's revolution is not simply an academic pursuit; it has profound implications for our past, present, and future. From the development of early agricultural practices to modern space exploration and climate change predictions, a comprehensive understanding of Earth's orbital motion is essential.
Historical Context: Shaping Human Civilization
Throughout history, the understanding of Earth's revolution has been intertwined with the development of human civilization. Early calendars and agricultural practices were directly influenced by observations of the Sun's apparent movement, highlighting the crucial role of celestial mechanics in shaping human societies. The ability to predict seasonal changes was critical for planning planting and harvesting cycles, ensuring food security and societal stability.
Modern Applications: Navigation, Space Exploration, and Climate Modeling
In the modern era, our understanding of Earth's revolution is essential for various technological advancements. Precise knowledge of Earth's orbit is crucial for navigation systems, enabling accurate GPS positioning and satellite communication. Space exploration relies heavily on precise calculations of orbital mechanics, enabling successful launches, maneuvers, and landings of spacecraft. Furthermore, understanding Earth's orbit is critical for climate modeling, allowing scientists to study long-term climatic trends and predict the potential impacts of global warming.
Future Implications: Protecting Our Planet
As we face the challenges of climate change, understanding Earth's revolution becomes even more crucial. Precise knowledge of Earth's orbital parameters is essential for developing accurate climate models, predicting the impacts of global warming, and devising strategies for mitigating its effects. The ongoing study of Earth's revolution and its interaction with other celestial bodies contributes to our ability to understand and protect our planet for future generations.
In conclusion, the movement of Earth around the Sun, called revolution, is far more than a simple orbital path. It's a complex interplay of gravitational forces, celestial mechanics, and profound implications for life on Earth. Understanding this fundamental process is crucial for appreciating our place in the cosmos and addressing the challenges facing our planet. From ancient calendars to modern space exploration and climate modeling, the study of Earth's revolution continues to shape our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Are In One Cubic Foot
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Diodes Are Required To Form A Bridge Rectifier
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Graph Of The X Component Of The Electric Field
Mar 14, 2025
-
Reactions Which Do Not Continue To Completion Are Called Reactions
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is Five Hours
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Movement Of Earth Around The Sun Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
