The Most Abundant Metal In The Earth's Crust Is
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
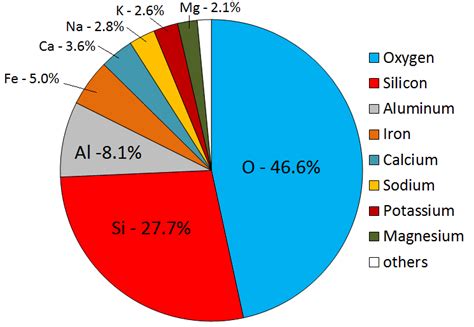
Table of Contents
The Most Abundant Metal in the Earth's Crust Is... Aluminum!
Aluminum. A name synonymous with lightweight cans, sleek smartphones, and durable cookware. But beyond its ubiquitous presence in modern life, aluminum holds a remarkable distinction: it's the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust. This seemingly simple fact unlocks a wealth of geological, economic, and environmental considerations, which we’ll explore in detail in this comprehensive article.
Understanding Abundance: More Than Just Surface Level
Before diving into the specifics of aluminum’s dominance, it’s crucial to define what we mean by “abundance.” We're talking about the relative concentration of an element within the Earth's crust – the outermost solid shell of our planet. This doesn't simply mean the total mass, but rather the proportion of the element compared to the total mass of the crust. Aluminum's claim to fame isn't just about being plentiful; it's about its significantly higher concentration compared to other metallic elements.
While other elements might exist in larger overall quantities within the Earth (including the mantle and core), the focus here remains firmly on the accessible crust. This layer is where mining operations extract the raw materials that fuel our industries and technology.
Aluminum's Geological Significance: A Deep Dive
Aluminum's dominance isn't accidental. Its high abundance is a direct consequence of the processes that shaped our planet billions of years ago.
The Formation of the Earth and Aluminum's Role
During the Earth's formation, the lighter elements rose to the surface, forming the crust. Aluminum, relatively light compared to elements like iron and nickel (which constitute the core), found its place in this outermost layer. The planet's early molten state and subsequent cooling and crystallization significantly influenced the distribution of elements, leading to the concentration of aluminum within the crustal rocks.
Key Aluminum-Bearing Minerals: Feldspars and More
Aluminum doesn't exist freely in nature. Instead, it's found bound within various minerals, most notably feldspars. These silicate minerals are the most abundant minerals in the Earth's crust, and a significant proportion of their composition is aluminum. Other important aluminum-containing minerals include:
- Bauxite: This aluminum hydroxide mineral is the primary ore used for aluminum production. Its formation involves complex weathering processes that selectively leach out other elements, leaving behind a concentrated deposit of aluminum.
- Clay minerals: These are widespread secondary minerals formed by the weathering of other aluminosilicate minerals, like feldspars. They contain significant amounts of aluminum, although they are generally not as economically viable for aluminum extraction as bauxite.
- Micas: These sheet silicate minerals also incorporate aluminum into their crystal structures.
The prevalence of these aluminum-bearing minerals directly contributes to its status as the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust.
Aluminum Extraction: From Ore to Metal
While aluminum is abundant, extracting it from its ores is a complex and energy-intensive process. The most common method involves several key steps:
1. Bauxite Mining: Unearthing the Raw Material
Bauxite deposits are often found in tropical and subtropical regions, where weathering processes are intense. Mining involves the excavation of these deposits, often using open-pit methods. This process can have significant environmental consequences, including deforestation, habitat loss, and water pollution, issues we will address later.
2. The Bayer Process: Refining Bauxite
The Bayer process is crucial for transforming bauxite into alumina (aluminum oxide), a key intermediate in aluminum production. This involves dissolving the bauxite in a caustic soda solution, separating out impurities, and then precipitating the pure alumina.
3. The Hall-Héroult Process: Electrolysis to Freedom
This is where the metallic aluminum is finally liberated. Alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite, and then subjected to electrolysis – a process using electricity to separate the aluminum from the oxygen. This process is highly energy-intensive, requiring substantial amounts of electricity, which raises concerns about its carbon footprint.
The Economic Significance of Aluminum: A Global Commodity
The economic importance of aluminum is undeniable. Its widespread use in various industries makes it a cornerstone of modern economies. Here's a glimpse into its key applications:
- Transportation: Aluminum is essential in the automotive and aerospace industries due to its lightweight yet strong nature. Cars, airplanes, and trains all benefit from its use.
- Packaging: Aluminum cans and foils are ubiquitous in food and beverage packaging. Their recyclability further adds to their economic value.
- Construction: Aluminum's corrosion resistance makes it suitable for building materials, including windows, doors, and cladding.
- Electronics: Aluminum plays a significant role in the electronics industry, from circuit boards to smartphone casings.
- Electrical Transmission: Aluminum's high conductivity makes it an excellent material for electrical transmission lines.
The Environmental Impact: A Double-Edged Sword
Aluminum production, while economically vital, presents significant environmental challenges.
Mining and its Consequences: Land Use and Pollution
Bauxite mining can lead to substantial land degradation, deforestation, and biodiversity loss. Furthermore, the process generates large quantities of red mud, a waste product containing heavy metals that can contaminate water sources.
Energy Consumption: A Carbon Footprint Concern
The Hall-Héroult process is highly energy-intensive, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The electricity used for electrolysis often comes from fossil fuel-based power plants, exacerbating the environmental impact.
Recycling's Importance: Mitigating the Impact
Aluminum is highly recyclable, and recycling significantly reduces the environmental burden of aluminum production. Recycling aluminum requires far less energy than producing it from raw bauxite, conserving resources and reducing emissions.
Aluminum's Future: Sustainability and Innovation
Addressing the environmental concerns associated with aluminum production is crucial for its long-term sustainability. Research and development are focused on several key areas:
Improved Refining Processes: Lower Energy Consumption
Scientists are exploring alternative refining processes that require less energy and produce fewer emissions. Innovations in electrolysis technology and the use of renewable energy sources are key aspects of this effort.
Enhanced Recycling Technologies: Closing the Loop
Improving the efficiency and accessibility of aluminum recycling is crucial. This involves developing better separation techniques and improving the collection and processing infrastructure.
Exploring Alternative Aluminum Sources: Beyond Bauxite
Researchers are investigating potential alternative sources of aluminum, such as clay minerals. However, these alternatives currently face technological and economic challenges.
Conclusion: Aluminum – Abundant, Essential, and Challenged
Aluminum's status as the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust is a testament to the geological forces that shaped our planet. Its widespread use in modern society reflects its exceptional properties – lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant. However, the environmental impact of its extraction and production necessitates a focus on sustainable practices, including improvements in refining processes, increased recycling rates, and exploration of alternative sources. The future of aluminum depends on our ability to balance its economic benefits with environmental responsibility, ensuring its continued contribution to society while minimizing its ecological footprint. The journey towards a more sustainable aluminum industry is ongoing, and the innovations and advancements in the coming years will shape the future of this indispensable metal.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Most Abundant Metal In The Earth's Crust Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.