The Figure Displays A 13.1 V Battery
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
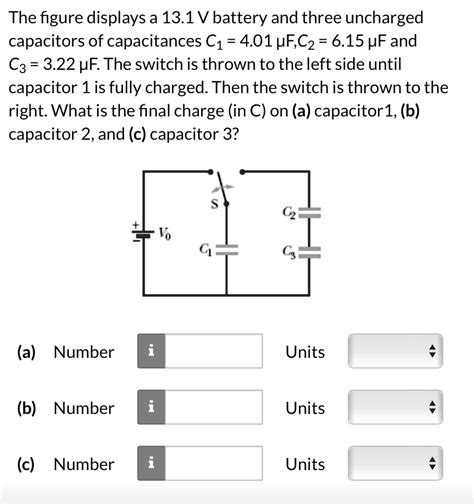
Table of Contents
Decoding the 13.1V Battery: Understanding Voltage, Applications, and Safety
The figure displays a 13.1V battery. This seemingly simple statement opens a door to a world of electrical engineering, specific applications, and important safety considerations. While a 12V battery is far more common, the 13.1V designation hints at a specialized purpose, often involving higher power demands or specific charging requirements. This article will delve into the intricacies of 13.1V batteries, exploring their voltage characteristics, typical applications, and crucial safety protocols.
Understanding Voltage and its Significance
Before diving into the specifics of a 13.1V battery, it's crucial to understand the concept of voltage. Voltage, also known as electromotive force, is the electrical potential difference between two points. It's the "push" that drives electrons through a circuit, enabling the flow of electrical current. A higher voltage means a greater potential difference, leading to a potentially stronger current flow. The unit of voltage is the volt (V).
A 13.1V battery isn't a standard voltage like 12V or 24V. This slight deviation from typical battery voltages suggests a specific design purpose. This non-standard voltage is often a result of:
- Battery chemistry: The specific chemical composition of the battery cells influences the overall output voltage. Different chemistries (like Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, Nickel-Cadmium) yield varying voltages.
- Cell configuration: Batteries are often composed of multiple individual cells connected in series or parallel. The number of cells and their connection determines the total voltage. A 13.1V battery might be a series arrangement of cells designed to deliver this specific voltage.
- Manufacturing tolerances: Slight variations in manufacturing processes can lead to minor deviations from the nominal voltage rating.
Common Applications of 13.1V Batteries
The slightly elevated voltage of a 13.1V battery suggests applications requiring more power than standard 12V systems while not needing the higher voltages of 24V or 48V systems. This niche voltage often appears in:
1. Specialized Power Tools
Certain high-performance power tools, such as cordless drills with exceptionally high torque, angle grinders demanding significant power, and impact wrenches designed for heavy-duty tasks may utilize 13.1V batteries. The slightly higher voltage allows for greater power output compared to a standard 12V battery without necessitating the jump to a heavier and bulkier 24V system.
2. Industrial Automation and Robotics
In industrial settings, precise control and robust power delivery are crucial. Automated systems and robots often require custom-designed power supplies, and a 13.1V battery might be specifically chosen to meet the voltage requirements of specific motors or actuators within the system. This specialized voltage could be integral to the system’s precise performance.
3. Automotive Applications (Specific Systems)
While not a standard automotive battery voltage, certain automotive systems might utilize 13.1V batteries for specific components. These systems may require slightly higher voltages for optimal performance but cannot use a standard 24V system. For example, certain advanced electronic modules or high-power actuators may leverage this voltage.
4. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) for Specialized Equipment
In situations where uninterrupted power is crucial, a 13.1V UPS tailored to a specific device or system's power needs may use a 13.1V battery bank. This ensures consistent and reliable power delivery, avoiding disruptions caused by power outages.
Battery Chemistry and Technology
The battery chemistry significantly influences the performance and characteristics of a 13.1V battery. Possible chemistries include:
-
Lithium-ion (Li-ion): Li-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and relatively long lifespan. They are frequently used in portable electronics and power tools, and are a likely choice for a 13.1V battery due to their ability to deliver high power output in a compact form factor. Variations in Li-ion chemistry (e.g., LCO, NMC, LFP) might be employed depending on the specific needs of the application.
-
Lead-acid: Lead-acid batteries are a more mature technology, characterized by lower energy density and shorter lifespan compared to Li-ion. However, they are typically less expensive and offer good performance in applications where high power output is not the primary concern. While less likely for a 13.1V battery given the need for higher power in most applications employing this voltage, they might be used in niche situations.
Safety Precautions with 13.1V Batteries
Regardless of the specific application, safety should always be the paramount concern when handling 13.1V batteries. These batteries, even if relatively low voltage, still carry significant electrical potential. Here are critical safety precautions:
- Proper handling: Always use insulated gloves and tools when working with 13.1V batteries to avoid electrical shock.
- Avoid short circuits: Never allow the battery terminals to come into contact with each other or conductive materials. A short circuit can cause rapid heat generation, potentially leading to fire or explosion.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation when charging or discharging the battery, particularly for batteries that generate gas during operation (like some lead-acid batteries). Accumulation of flammable gases can be extremely dangerous.
- Charging: Use only the appropriate charger designed specifically for the 13.1V battery. Using an incorrect charger can damage the battery or create a fire hazard. Always adhere to the manufacturer's charging instructions.
- Disposal: Dispose of used 13.1V batteries according to local regulations and guidelines. Improper disposal can contaminate the environment and pose hazards.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Avoid extreme temperatures, which can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan. Always store batteries away from children.
- Inspect for damage: Regularly inspect the battery for any signs of damage, such as swelling, leaks, or corrosion. Damaged batteries should be immediately replaced to avoid potential hazards.
Choosing the Right 13.1V Battery
The choice of a 13.1V battery depends critically on the specific application and its unique requirements. Factors to consider include:
- Capacity (mAh or Ah): This determines how long the battery will power the device before needing recharging. A higher capacity is generally better for longer runtimes.
- Discharge rate (C-rate): This specifies the maximum current the battery can safely deliver. Applications requiring high power output need batteries with a high C-rate.
- Battery chemistry: The choice of chemistry (Li-ion, lead-acid, etc.) impacts performance, lifespan, safety, and cost.
- Physical dimensions and weight: The size and weight of the battery are important considerations, especially in portable applications.
- Cost: The price of the battery will vary based on capacity, chemistry, and features.
The Future of 13.1V and Similar Niche Voltages
While 12V and 24V remain dominant in many applications, niche voltages like 13.1V will likely continue to appear where specific performance requirements necessitate a tailored power solution. Advances in battery technology, particularly in Li-ion chemistries, will likely lead to more efficient and safer batteries operating at these non-standard voltages. The demand for higher power in smaller, more portable devices will further drive the development and adoption of such specialized battery systems. Therefore, understanding the nuances of 13.1V and similar voltage batteries is crucial for engineers, technicians, and consumers alike.
By understanding the voltage characteristics, applications, safety precautions, and selection criteria of a 13.1V battery, we can leverage its power efficiently and safely in specialized applications. Remember, safety should always be the primary concern when working with any battery, regardless of its voltage. Proper handling and disposal practices are essential for ensuring both personal safety and environmental protection.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Equilibrium
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Major Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Wire Loop Of Radius 10 Cm And Resistance
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Figure Displays A 13.1 V Battery . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
