The Amount Of Space Occupied By An Object.
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
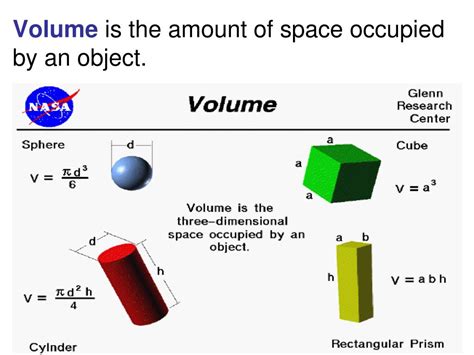
Table of Contents
The Amount of Space Occupied by an Object: Volume and its Applications
The amount of space occupied by an object is a fundamental concept in physics and mathematics, formally known as volume. Understanding volume is crucial across numerous fields, from everyday life to advanced scientific research. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the concept of volume, exploring its definition, calculation methods for various shapes, practical applications, and its connection to other physical properties like density and mass.
Defining Volume: More Than Just Space
Volume quantifies the three-dimensional extent of an object. It's essentially the measure of how much space an object takes up. While we intuitively understand the concept – a large box occupies more space than a small one – a precise definition requires considering the object's three spatial dimensions: length, width, and height. The units of volume are cubic units, reflecting the three-dimensional nature of the measurement. Common units include cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), cubic feet (ft³), and liters (L), with conversion factors readily available to switch between them.
The Importance of Units in Volume Calculation
Choosing the correct units is paramount in any volume calculation. Inconsistent units will lead to erroneous results. For instance, multiplying length in meters, width in centimeters, and height in millimeters will not yield a volume in cubic meters. Always ensure consistency in units throughout the calculation. Converting all measurements to a single unit (e.g., meters) before calculation is the best practice to avoid errors.
Calculating Volume: Shapes and Formulas
Calculating the volume of an object depends heavily on its shape. Regular, geometric shapes have well-defined formulas for calculating their volume. Irregular shapes require more sophisticated methods, often involving water displacement or numerical integration.
Volume of Regular Shapes
-
Cuboid (Rectangular Prism): The simplest shape, a cuboid's volume is calculated by multiplying its length (l), width (w), and height (h): Volume = l × w × h
-
Cube: A special case of a cuboid where all sides are equal (l=w=h), the volume of a cube is Volume = s³, where 's' is the length of a side.
-
Sphere: The volume of a sphere with radius 'r' is given by the formula: Volume = (4/3)πr³ This formula involves π (pi), a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
-
Cylinder: For a cylinder with radius 'r' and height 'h', the volume is calculated as: Volume = πr²h
-
Cone: The volume of a cone with radius 'r' and height 'h' is: Volume = (1/3)πr²h
-
Pyramid: The volume of a pyramid depends on its base area (A) and height (h): Volume = (1/3)Ah The base area 'A' varies depending on the shape of the base (square, triangle, etc.).
Volume of Irregular Shapes: Approximation Techniques
Determining the volume of irregular shapes is more challenging. Direct measurement using length, width, and height isn't feasible. Common methods for estimating volume include:
-
Water Displacement: This is a simple and widely used method. Submerge the object completely in a container filled with water and measure the volume of water displaced. This displaced volume is equal to the object's volume. Accuracy depends on the precision of the volume measurement of the water.
-
Numerical Integration: For complex shapes, numerical integration techniques (such as Simpson's rule or the trapezoidal rule) can be employed to approximate the volume. These methods involve dividing the object into smaller, manageable sections and summing up their volumes. This requires sophisticated software or a detailed understanding of calculus.
-
3D Scanning and Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Advanced techniques like 3D scanning create a digital representation of the object. CAD software can then calculate the volume from this digital model with high accuracy. This method is particularly useful for complex objects in engineering and manufacturing.
Applications of Volume Measurement: Across Diverse Fields
Understanding and calculating volume has far-reaching applications across a broad spectrum of fields:
Everyday Applications
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify ingredient volumes (e.g., cups, liters), highlighting the importance of volume measurement in culinary arts.
-
Home Improvement: Estimating paint or concrete needed for a project requires accurate volume calculations to ensure sufficient materials are purchased, preventing costly shortages or waste.
-
Storage and Packaging: Optimizing the shape and size of packages to maximize volume while minimizing material usage is crucial for logistics and efficiency in various industries.
Scientific and Engineering Applications
-
Fluid Mechanics: Volume is fundamental in fluid mechanics, governing concepts like flow rate, pressure, and buoyancy. Understanding the volume of fluids and containers is critical in designing efficient piping systems, hydraulic mechanisms, and managing water resources.
-
Material Science: Density, a crucial property of materials, is defined as mass per unit volume (Density = Mass/Volume). Accurate volume measurements are therefore essential in determining the density and characterizing material properties.
-
Medical Imaging: Medical imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans provide three-dimensional representations of internal organs and tissues. Volume calculations are employed to measure organ size, detect abnormalities, and track disease progression. Volume calculations are integral in radiotherapy treatment planning, ensuring precise dosage delivery to cancerous tissues while minimizing harm to surrounding healthy areas.
-
Environmental Science: Volume is essential in environmental studies, including hydrology (measuring water volume in rivers and reservoirs) and atmospheric science (measuring gas volumes in pollution studies). Accurate volume estimations are critical in environmental impact assessments and resource management.
-
Astronomy and Astrophysics: In astrophysics, estimating the volume of celestial bodies like planets, stars, and galaxies aids in understanding their structure, composition, and evolution.
Volume, Density, and Mass: The Interconnected Trio
Volume, density, and mass are closely related concepts. Density is defined as mass per unit volume. Therefore, knowing the volume and density of an object allows us to calculate its mass, and vice-versa:
- Mass = Density × Volume
- Density = Mass / Volume
- Volume = Mass / Density
This relationship is extensively utilized in various applications, from determining the mass of a material given its volume and density to calculating the volume of a liquid given its mass and density.
Conclusion: The Significance of Volume Measurement
The amount of space occupied by an object – its volume – is a fundamental concept with widespread relevance. Accurate volume measurement is crucial across numerous disciplines, from everyday tasks to complex scientific and engineering applications. Understanding the various methods for calculating volume, based on the shape of the object and the available tools, is essential for numerous practical and scientific endeavors. The close relationship between volume, density, and mass highlights the interconnectedness of these fundamental physical properties and their importance in describing and understanding the physical world. Whether it's cooking a meal, designing a bridge, or researching the cosmos, understanding volume forms an essential cornerstone of knowledge.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Amount Of Space Occupied By An Object. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.