Sun Distance From Earth In Light Years
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
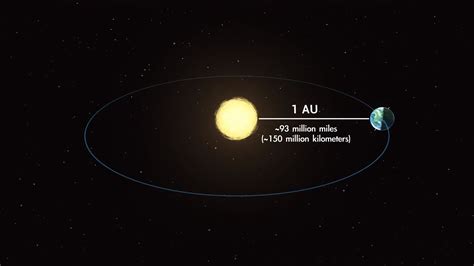
Table of Contents
The Sun's Distance from Earth: A Journey in Light Years and Astronomical Units
The Sun, our life-giving star, is the celestial body at the center of our solar system. Its distance from Earth isn't just a number; it's a fundamental concept in astronomy, shaping our understanding of planetary motion, seasons, and even life itself. While we often talk about the Sun's distance in terms of light-years, it's crucial to understand that light-years are a measure of distance, not time. This article delves into the complexities of measuring this distance, exploring the different units used, and discussing the implications of the Sun's proximity to Earth.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
Before we dive into light-years, it's important to grasp the concept of the Astronomical Unit (AU). One AU is defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. This isn't a fixed distance because the Earth's orbit is slightly elliptical, meaning the distance varies throughout the year. However, the average distance is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). The AU provides a much more practical unit for measuring distances within our solar system than kilometers or miles, as those numbers become unwieldy when dealing with planetary distances.
Why Light-Years Are Less Practical for Sun-Earth Distance
While the concept of a light-year is widely understood, it's significantly less practical for expressing the Sun's distance from Earth. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year – approximately 9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (5.879 × 10<sup>12</sup> miles). Using light-years to describe the Sun's distance results in a very small, almost insignificant, fraction of a light-year. This is because the Sun is relatively close to Earth on a cosmic scale. The precision lost using such a large unit of measurement when discussing a relatively small distance would be considerable.
Calculating the Sun's distance in light-years would yield a number less than 0.0000158 light-years, which is not very intuitive or informative for most discussions about our solar system. It’s far more convenient and accurate to use AUs for describing distances within our solar system. Light-years become far more useful when discussing distances between stars and galaxies, where AUs would be incredibly cumbersome.
Methods for Measuring the Sun-Earth Distance
Historically, determining the Sun-Earth distance was a significant challenge for astronomers. Several methods were developed over time, each building upon the advancements in technology and understanding.
-
Transit of Venus: In the 18th and 19th centuries, astronomers utilized the transit of Venus – the passage of Venus across the face of the Sun – to measure the Sun's distance. By observing the transit from different locations on Earth and utilizing parallax (the apparent shift in an object's position when viewed from different locations), they could triangulate the distance. While ingenious, this method was limited by the accuracy of available instruments and the infrequent occurrence of Venus transits.
-
Radar Measurements: With the advent of radar technology in the mid-20th century, astronomers were able to bounce radar signals off planets and precisely measure the time it took for the signal to return. By knowing the speed of light, they could calculate the distance to the planets. Through a series of measurements and calculations involving planetary orbits and Kepler's Laws, the Sun-Earth distance could be accurately derived.
-
Parallax Using Nearby Stars: More recently, measuring the distance to nearby stars using parallax has provided a more precise determination of the astronomical unit. By observing the apparent shift in a star's position against the background of more distant stars as Earth orbits the Sun, astronomers can use trigonometry to calculate the distance to the star. This, in turn, can be used to refine the calculation of the AU.
The Importance of Accurate Measurement
Accurately measuring the Sun-Earth distance is vital for numerous reasons:
-
Understanding Planetary Orbits: The AU is fundamental to understanding the orbital mechanics of planets in our solar system. Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion rely on accurate distance measurements to predict planetary positions and movements.
-
Celestial Navigation: Accurate knowledge of the Sun's distance is essential for celestial navigation, guiding ships and spacecraft through space.
-
Space Exploration: Precise measurements are crucial for planning and executing space missions, ensuring spacecraft reach their intended targets.
-
Understanding Solar Physics: The distance helps us understand the Sun's properties, including its luminosity and its influence on Earth's climate and weather patterns.
The Sun's Influence on Earth
The Sun's relatively close proximity to Earth is not just a matter of measurement; it's a defining factor for life on our planet. The Sun's energy drives our climate, powers photosynthesis in plants, and shapes our daily cycles. The consistent supply of solar radiation, at a distance that isn't too close or too far, is a crucial ingredient for the habitability of Earth.
A closer distance would lead to extreme heat, rendering the planet uninhabitable, while a further distance would result in freezing temperatures and an inability to support life as we know it. The delicate balance of the Sun-Earth distance is a testament to the unique conditions that have allowed life to flourish on our planet.
Beyond Our Solar System: Light-Years Take Center Stage
While AUs are perfect for our solar system, as we move beyond our immediate cosmic neighborhood, light-years become indispensable. When we talk about distances to other stars and galaxies, the vastness of space necessitates a larger unit of measurement. The distances are so immense that using kilometers or even AUs would lead to unwieldy and unmanageable numbers. The nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, is approximately 4.37 light-years away – a distance far beyond anything we can comprehend within our solar system.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Unit
In summary, while the Sun's distance from Earth can technically be expressed in light-years, it's far more practical and informative to use Astronomical Units (AU). Light-years are more suited for discussing the distances between stars and galaxies. The Sun's proximity to Earth, measured in AUs, is a crucial factor in understanding our planet's climate, life, and place within the solar system. The precise measurement of this distance has been a driving force in the advancements of astronomy and continues to be essential for our ongoing exploration of the cosmos. Choosing the right unit of measurement, be it AU or light-years, depends entirely on the scale of the distances being discussed. Using the appropriate unit ensures clarity, accuracy, and a more effective understanding of the vastness and wonder of the universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Solid Sphere Of Uniform Density Has A Mass Of
Mar 19, 2025
-
In A Two Digit Number The Tens Digit
Mar 19, 2025
-
In The Figure Pq Is Parallel To Rs
Mar 19, 2025
-
I Am Who I Am Essay
Mar 19, 2025
-
Inertia Is A Property Of Matter
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sun Distance From Earth In Light Years . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
