One Of Chargaff's Rules States That
News Leon
Apr 04, 2025 · 7 min read
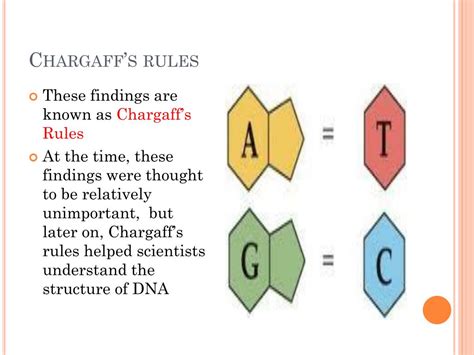
Table of Contents
One of Chargaff's Rules States That… A Deep Dive into DNA Composition
Erwin Chargaff, a renowned biochemist, made groundbreaking discoveries in the field of molecular biology. His meticulous work, primarily focused on the composition of DNA, led to the formulation of two crucial rules, now famously known as Chargaff's rules. These rules were pivotal in understanding the structure and function of DNA, paving the way for Watson and Crick's iconic double helix model. Let's delve deeper into one of Chargaff's rules: the equivalence of purine and pyrimidine bases.
Understanding Chargaff's First Rule: The 1:1 Ratio
Chargaff's first rule states that in a DNA molecule, the amount of guanine (G) is equal to the amount of cytosine (C), and the amount of adenine (A) is equal to the amount of thymine (T). This can be mathematically represented as:
A = T and G = C
This seemingly simple equation holds profound implications for DNA structure and function. This equivalence is not a coincidence; it's a direct consequence of the specific base pairing within the DNA double helix.
The Significance of Base Pairing
The equal ratios of A-T and G-C are dictated by the way the nitrogenous bases pair up to form the iconic double helix. Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) through two hydrogen bonds, while guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C) through three hydrogen bonds. This specific base pairing is crucial for the stability and fidelity of DNA replication and transcription.
The hydrogen bonds are essential for:
- Maintaining the double helix structure: The hydrogen bonds between the base pairs act like molecular "glue," holding the two strands of the DNA molecule together.
- Accurate DNA replication: During DNA replication, the two strands of the DNA molecule separate, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The precise base pairing ensures that the new strands are exact copies of the original strands.
- Faithful transcription: During transcription, the DNA sequence is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Accurate base pairing ensures that the mRNA sequence is a faithful copy of the DNA sequence.
Implications of Deviations from Chargaff's Rule
While Chargaff's rules generally hold true for most DNA, there can be minor deviations under specific circumstances. These deviations don't invalidate the rules but offer insights into potential complexities within the genome. These deviations might be observed in:
- Single-stranded DNA: Viruses and some other organisms possess single-stranded DNA. In these cases, the A=T and G=C ratios won't necessarily hold true.
- Organelle DNA: The DNA found in mitochondria and chloroplasts may exhibit slight variations in base composition compared to nuclear DNA.
- Errors during DNA replication: Rare errors during DNA replication can lead to temporary deviations from Chargaff's rules, but these are usually corrected by cellular repair mechanisms.
Understanding these potential exceptions allows for a more nuanced interpretation of DNA composition and highlights the dynamic nature of genomic processes.
Chargaff's Second Rule: The Base Composition Varies Between Species
Chargaff's second rule adds another layer of complexity to our understanding of DNA. It states that although the A=T and G=C ratios are constant within a given species, the overall base composition (the percentage of A, T, G, and C) can vary significantly between different species. This variation underscores the genetic diversity among different life forms.
Species-Specific Base Composition
This variation in base composition reflects the unique genetic makeup of each species. The specific sequence of bases along the DNA molecule determines the genetic code, dictating the production of proteins and ultimately influencing the organism's traits and characteristics.
-
Evolutionary implications: The differences in base composition between species reflect the evolutionary relationships between them. Closely related species tend to have more similar base compositions than distantly related species. This supports evolutionary theory by providing molecular evidence for common ancestry and divergence.
-
Taxonomic applications: Analysis of DNA base composition has become a valuable tool in taxonomy and phylogenetic studies. By comparing the base composition of different organisms, scientists can infer evolutionary relationships and classify organisms more accurately.
The Role of GC Content
The percentage of guanine and cytosine bases (GC content) in DNA is particularly significant. This is because G-C base pairs are linked by three hydrogen bonds, making them stronger than A-T base pairs, which are linked by only two hydrogen bonds.
-
Melting temperature: DNA with a higher GC content has a higher melting temperature (the temperature at which the double helix separates into single strands). This is because the additional hydrogen bond in G-C base pairs contributes to greater stability. The melting temperature is crucial in various molecular biology techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
-
Environmental adaptations: The GC content of an organism's DNA can be influenced by environmental factors. Organisms thriving in high-temperature environments, for instance, often have a higher GC content in their DNA, conferring greater thermal stability to their genomes.
The Impact of Chargaff's Rules on Molecular Biology
Chargaff's rules were instrumental in the development of our understanding of DNA's structure and function. Before Chargaff's work, the precise composition and structure of DNA remained largely mysterious. His discoveries provided crucial clues that were essential for the subsequent breakthroughs in molecular biology.
The Double Helix Model
Watson and Crick famously used Chargaff's rules as a key constraint in their model-building efforts. The A=T and G=C base pairing ratios were crucial in establishing the complementary nature of the two DNA strands and in determining the diameter of the double helix. Without Chargaff's data, the double helix model would have been impossible to construct.
DNA Replication and Transcription
Chargaff's rules are also essential for understanding the mechanisms of DNA replication and transcription. The specific base pairing dictates the accuracy of these processes, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information. Errors in base pairing can lead to mutations, which can have significant consequences for the organism.
Modern Applications of Chargaff's Rules
Chargaff's rules are not merely historical artifacts; they continue to hold significance in modern molecular biology.
-
Genome sequencing: The principles underlying Chargaff's rules are fundamental to genome sequencing technologies. Analyzing the base composition of sequenced genomes provides insights into gene structure, regulatory regions, and evolutionary relationships.
-
DNA fingerprinting: DNA fingerprinting techniques rely on the analysis of variations in DNA sequences, including variations in base composition.
-
Forensic science: The application of Chargaff's rules extends into forensic science, where DNA profiling is used to identify individuals and solve crimes.
-
Medical diagnostics: Analyzing the base composition of DNA samples can be crucial in medical diagnostics, aiding in the detection and diagnosis of various genetic diseases.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Discovery
Chargaff's rules, seemingly simple yet profound, represent a cornerstone of modern molecular biology. These rules, far from being mere observations, provide fundamental insights into the structure, function, and evolution of DNA. Their impact extends from the conceptual framework of the double helix to countless practical applications in fields ranging from medicine to forensic science. Erwin Chargaff's meticulous work continues to shape our understanding of life's fundamental building block and provides a powerful testament to the power of precise observation and rigorous scientific inquiry. The legacy of his discoveries remains as relevant and vital as ever in the ongoing quest to unravel the complexities of the genetic code. The elegance and simplicity of his rules belie the profound impact they've had on our comprehension of the molecular basis of life. The equal ratios of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine are not just a set of rules, but a fundamental principle underpinning the entire world of genetics and molecular biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
13 Protons 14 Neutrons And 10 Electrons
Apr 05, 2025
-
After Mitosis How Many Chromosomes Are In Each Daughter Cell
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Are The Products Of The Following Reaction
Apr 05, 2025
-
The Patella Is An Example Of Which Type Of Bone
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is Correct Regarding Rna
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One Of Chargaff's Rules States That . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
