Mountain Range That Separates Europe From Asia
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
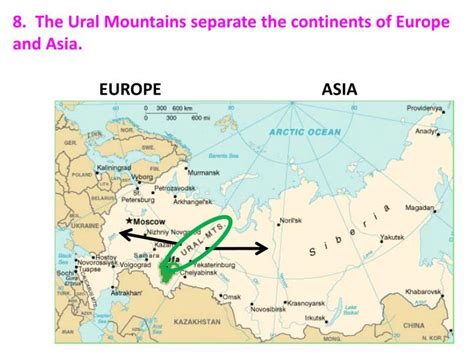
Table of Contents
The Ural Mountains: Dividing Europe and Asia – A Natural Boundary and Cultural Crossroads
The Ural Mountains, a seemingly unassuming range stretching over 2,500 kilometers (1,550 miles) from the Arctic Ocean to the steppes of Kazakhstan, hold a position of immense geographical and historical significance. They form the conventionally accepted boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia, a line drawn not in stone, but in the rugged peaks and rolling foothills of this ancient mountain range. However, the designation as a continental divide is more of a convenient convention than a strictly defined geological reality, adding a layer of complexity to their already fascinating story.
A Geological Timeline: Formation and Evolution of the Urals
The Ural Mountains are far older than many of their more imposing counterparts, like the Himalayas or the Alps. Their formation began around 300 million years ago during the Permian period, a period of intense tectonic activity. The collision of two ancient continents, Baltica and Siberia, resulted in the crumpling and uplifting of the Earth's crust, creating the Uralian orogeny – the process that birthed this majestic mountain range. Unlike younger mountain ranges, the relentless forces of erosion over millions of years have significantly worn down the Urals, resulting in a generally lower elevation compared to other major mountain chains.
A Diverse Landscape: From Arctic Tundra to Steppes
The Urals boast a remarkably diverse landscape, reflecting their vast geographical spread and varied geological composition. The northernmost section is characterized by rugged, high-altitude peaks and valleys, often covered in snow and ice. This area is part of the Arctic tundra, a harsh but beautiful ecosystem that supports a unique array of flora and fauna. As one travels south, the mountains gradually decrease in altitude, transitioning into rolling hills and foothills, eventually merging with the vast Eurasian steppes. This transition reveals a remarkable change in vegetation, with the barren tundra giving way to taiga forests (coniferous forests) and eventually, further south, to more temperate mixed forests and grasslands.
Rich Mineral Resources: A Driving Force of History and Industry
The Ural Mountains have been a significant source of mineral wealth for centuries. The collision of the tectonic plates during the orogeny not only created mountains but also deposited vast quantities of valuable minerals within the Earth's crust. This region is abundant in iron ore, copper, gold, platinum, chromium, and various other minerals. These resources have fueled industrial growth throughout Russian history, leading to the development of numerous mining towns and industrial centers along the range. From the early days of mining to the modern era, the extraction of these resources has significantly shaped the economic and demographic landscape of the region. This abundance of minerals is an integral part of the Urals’ history, intrinsically linking its geological formation to its human story.
A Shifting Boundary: The Complexities of Defining Europe and Asia
While the Ural Mountains are widely accepted as the boundary between Europe and Asia, the demarcation is not without its complexities. The geological definition of continents is often less clear-cut than geographical or political divisions. The Urals don't represent a sharp geological division; rather, they mark a transition zone. The geological structures and formations of the Ural range gradually transition across the boundary, blurring the lines between the two continents. Furthermore, many geographical features extend across the purported boundary, making the line somewhat arbitrary. This has led to different interpretations of the continental divide, with some geographers proposing alternative boundaries like the Ural River or the Emba River. The fluidity of the boundary underscores the limitations of simple geographical classification.
Beyond the Mountains: Cultural Crossroads and Historical Significance
The Urals have played a pivotal role throughout history, serving as both a barrier and a conduit for migration, trade, and cultural exchange. They have been a natural defense, hindering the movement of armies and influencing the development of settlements and civilizations. However, the mountains also acted as a corridor, facilitating the movement of people, ideas, and goods between Europe and Asia. Many ancient trade routes traversed these mountains, fostering interaction and exchange between different cultures. The richness of the region's mineral resources also spurred significant migration and development of industries, further contributing to the area’s importance.
A Tapestry of Cultures: Peoples and Languages of the Urals
The region boasts a vibrant and diverse cultural heritage, with numerous ethnic groups calling the Ural Mountains home. This area showcases a blend of European and Asian influences, reflecting centuries of interactions and cultural exchange. The Uralic language family, which includes Finnish and Hungarian, among others, has its origins in the region, demonstrating the area's long history as a hub for human settlement. This linguistic diversity highlights the complex population history and the interconnectedness of human migrations that have contributed to the rich cultural mosaic of this region. Throughout history, many groups have left their indelible mark on the region's landscape, society, and cultural traditions, creating a fascinating interweaving of cultures.
The Urals Today: Environmental Challenges and Sustainable Development
The rich mineral resources of the Ural Mountains have fueled industrial growth for centuries, but this economic activity has also come at a cost. Decades of heavy industrial activity have left their mark on the environment, resulting in widespread pollution and environmental degradation. The legacy of industrial pollution is visible in degraded landscapes, polluted waterways, and reduced biodiversity. However, in recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the need for sustainable development in the region. Efforts are underway to promote responsible resource management, implement environmental protection measures, and develop sustainable industries. This represents a crucial shift, attempting to balance the economic benefits of the region’s resources with environmental preservation and sustainability.
Preserving the Heritage: National Parks and Conservation Efforts
The unique biodiversity and rich natural landscapes of the Ural Mountains are increasingly recognized as valuable assets. The establishment of national parks and protected areas highlights a growing commitment to conservation. These protected areas serve as vital habitats for various species of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to the region. The preservation of these natural areas also has significant tourism potential, providing opportunities for recreation, education, and economic growth aligned with sustainable development principles. This focus on preserving the natural heritage is an important aspect of the region's future development, seeking to balance environmental conservation with economic and social progress.
Tourism and Recreation: Exploring the Beauty of the Urals
The Ural Mountains offer a wealth of opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers. From hiking and trekking in the rugged terrain to exploring the pristine forests and rivers, there’s a wide range of activities to enjoy. The region’s natural beauty, cultural diversity, and historical significance all contribute to its growing appeal as a tourism destination. The development of sustainable tourism practices is crucial to ensure that the beauty of the Urals is preserved for future generations. This balanced approach can contribute to the local economy while safeguarding the region's unique natural and cultural assets.
Conclusion: A Land of Contrasts and Enduring Significance
The Ural Mountains, far from being merely a geographical boundary, represent a rich tapestry of geological history, cultural diversity, and environmental challenges. Their position as the conventional divide between Europe and Asia is a simplification of a complex reality. The mountains themselves are a transition zone, mirroring the cultural and ecological blending that defines the region. Understanding the Ural Mountains requires appreciating their geological evolution, their historical significance, and the ongoing interplay between human activity and environmental sustainability. The future of the Urals will depend on striking a balance between economic development and environmental protection, preserving this remarkable range for generations to come. Their story is a testament to the dynamic interplay between nature and human civilization, a story that continues to unfold.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match The Label To The Correct Structure On The Chloroplast
Mar 28, 2025
-
Longest Cell In The Human Body
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Part Of A Line With Two Endpoints
Mar 28, 2025
-
Choose The Correct Statement From The Following
Mar 28, 2025
-
Find The Perimeter Of The Figure Shown
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mountain Range That Separates Europe From Asia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
