Methyl Alcohol And Salicylic Acid Reaction
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
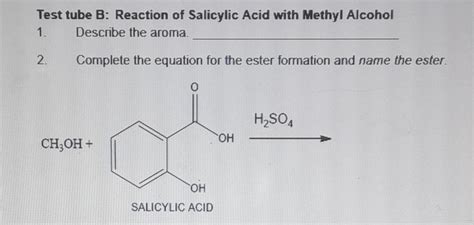
Table of Contents
Methyl Alcohol and Salicylic Acid Reaction: A Deep Dive into Esterification
The reaction between methyl alcohol (methanol) and salicylic acid is a classic example of esterification, a crucial process in organic chemistry with widespread applications in various industries. This article delves deep into the intricacies of this reaction, exploring its mechanism, reaction conditions, applications, and safety considerations. Understanding this reaction is pivotal for anyone working with organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, or materials science.
Understanding the Reactants: Methanol and Salicylic Acid
Before we delve into the reaction itself, let's examine the properties of the reactants:
Methanol (Methyl Alcohol)
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest alcohol with the chemical formula CH₃OH. It's a colorless, volatile, and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor. Methanol is a crucial industrial chemical used as a solvent, antifreeze, and fuel. However, it's highly toxic and should be handled with extreme caution. Ingestion of even small amounts can lead to blindness or death.
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid (C₇H₆O₃) is a naturally occurring phenolic acid with potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. It's a key component of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) and is also used in various skincare products due to its keratolytic effects (ability to remove dead skin cells). In its pure form, salicylic acid is a colorless crystalline solid that's slightly soluble in water but readily dissolves in organic solvents like methanol.
The Esterification Reaction: Mechanism and Conditions
The reaction between methanol and salicylic acid produces methyl salicylate, an ester with a distinct wintergreen odor. This reaction is an example of Fischer esterification, a reversible reaction catalyzed by an acid.
Reaction Mechanism: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The Fischer esterification proceeds through a series of steps:
-
Protonation of the carbonyl group: The carboxylic acid group of salicylic acid is protonated by the acid catalyst (typically sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid). This makes the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic.
-
Nucleophilic attack: The oxygen atom of methanol, acting as a nucleophile, attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. This forms a tetrahedral intermediate.
-
Proton transfer: A proton is transferred from the hydroxyl group of the tetrahedral intermediate to one of the oxygen atoms.
-
Elimination of water: A molecule of water is eliminated, resulting in the formation of methyl salicylate.
-
Deprotonation: The protonated methyl salicylate is deprotonated by a base (often the conjugate base of the acid catalyst), yielding the final product.
Reaction Conditions: Optimizing the Yield
Several factors influence the yield and rate of the esterification reaction:
-
Acid Catalyst: A strong acid catalyst, such as concentrated sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, is essential to facilitate the reaction. The acid catalyst increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon, promoting the nucleophilic attack by methanol.
-
Temperature: The reaction is typically carried out at elevated temperatures (e.g., refluxing conditions) to increase the reaction rate. Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of the molecules, leading to more frequent collisions and a higher probability of successful reaction.
-
Molar Ratio: Using an excess of methanol can help drive the equilibrium towards the formation of methyl salicylate. This is based on Le Chatelier's principle.
-
Reaction Time: Sufficient reaction time is crucial to ensure a high yield. The reaction time can range from several hours to days depending on the reaction conditions.
-
Removal of Water: Removing the water produced during the reaction is beneficial as it shifts the equilibrium towards the product side, improving the yield. This can be achieved through techniques like Dean-Stark apparatus.
Applications of Methyl Salicylate
Methyl salicylate, the product of the methanol and salicylic acid reaction, finds numerous applications:
-
Flavoring Agent: Its distinct wintergreen odor makes it a popular flavoring agent in candies, chewing gums, and other food products.
-
Fragrance: It's also used in perfumes and cosmetics to impart a refreshing, minty scent.
-
Pharmaceutical Applications: Methyl salicylate possesses analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a component in some topical pain relief ointments and balms.
-
Liniments and Rubs: Its counterirritant properties are utilized in liniments and rubs to relieve muscle aches and pains.
-
Insect Repellent: Some studies suggest methyl salicylate might have repellent properties against certain insects.
-
Industrial Applications: It's used as a solvent and intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals.
Safety Precautions: Handling Methanol and Salicylic Acid
Both methanol and salicylic acid require careful handling due to their inherent properties:
-
Methanol Toxicity: Methanol is highly toxic. Inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact should be avoided. Adequate ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and respirators, are crucial when handling methanol.
-
Salicylic Acid Irritation: Salicylic acid can cause skin and eye irritation. Skin contact should be minimized, and appropriate PPE should be used.
-
Acid Catalyst Handling: Strong acid catalysts like sulfuric acid are corrosive and require careful handling. Appropriate PPE and safety measures are necessary to prevent accidents.
-
Waste Disposal: Proper disposal of chemical waste, including unreacted methanol, salicylic acid, and the acid catalyst, is essential to minimize environmental impact.
Advanced Considerations: Reaction Optimization and Variations
The basic Fischer esterification can be optimized and modified in several ways:
-
Enzyme Catalysis: Enzymes, such as lipases, can be used as catalysts for esterification. This offers advantages like higher selectivity and milder reaction conditions compared to traditional acid catalysis.
-
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Microwave irradiation can significantly reduce reaction times and improve yields in esterification reactions.
-
Solvent Selection: The choice of solvent can affect the reaction rate and yield. Appropriate solvents should be selected based on the solubility of the reactants and the desired reaction conditions.
-
Purification Techniques: The crude methyl salicylate produced needs purification, typically through techniques like distillation or recrystallization to obtain a high-purity product.
Conclusion: A Versatile Reaction with Broad Applications
The reaction between methyl alcohol and salicylic acid, resulting in methyl salicylate, serves as a prime example of Fischer esterification. This reaction is widely applied in various industries, from food and fragrance to pharmaceuticals. However, it's crucial to adhere to strict safety procedures when handling the reactants and catalysts due to their potential hazards. Understanding the reaction mechanism, optimizing the reaction conditions, and employing appropriate safety measures are essential for successful and safe synthesis of methyl salicylate. Further research continues to explore variations and optimizations of this reaction, constantly expanding its industrial applications and relevance in organic chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Suppose That An Electric Charge Is Produced
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is Carbon A Conductor Of Electricity
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Are Raw Materials Needed For Photosynthesis
Apr 01, 2025
-
Square Root Of 7 Rational Or Irrational
Apr 01, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast Evaporation And Boiling
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Methyl Alcohol And Salicylic Acid Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
