Largest Satellite In The Solar System
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
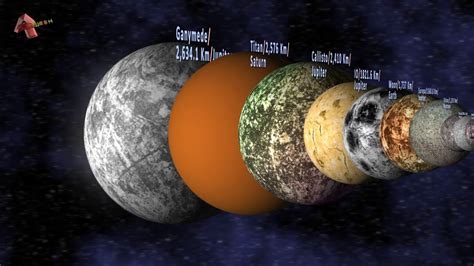
Table of Contents
Ganymede: The Solar System's Largest Moon
Ganymede, the largest moon in our solar system, is a world of captivating contrasts. Larger than the planet Mercury and even dwarf planet Pluto, it boasts a fascinating geological history, a unique magnetic field, and a potential subsurface ocean – making it a prime target for future exploration. This exploration of Ganymede delves into its size, composition, atmosphere, magnetic field, potential for life, and future missions, providing a comprehensive overview of this celestial giant.
Ganymede's Immense Size and Composition
Ganymede's sheer size is staggering. With a diameter of 5,268 kilometers (3,273 miles), it's significantly larger than both Mercury and Pluto. Its mass is also impressive, accounting for over 25% of the total mass of all the moons orbiting Jupiter. This monumental size significantly impacts its internal structure and geological activity.
The moon is differentiated, meaning it possesses distinct layers: a core, mantle, and crust. Scientists believe its core is primarily iron and likely molten, contributing to its surprisingly powerful magnetic field. The mantle is thought to be composed of silicate rock, while the crust is a complex mixture of ice and rock. Evidence suggests significant tectonic activity throughout Ganymede's history, evidenced by its heavily fractured surface.
Evidence of Tectonic Activity and Surface Features
Ganymede's surface is a stunning tapestry of dark and light regions, revealing a complex geological history. The dark regions, known as "dark terrains," are older and heavily cratered, providing a record of ancient impacts. In contrast, the lighter regions, called "light terrains," exhibit extensive grooves and ridges, signifying significant tectonic activity and resurfacing events.
These light terrains are characterized by complex systems of long, parallel grooves and ridges, indicative of extensional tectonic processes. Some regions show evidence of faulting and folding, indicating significant stress and strain within the moon's icy crust. The surface also reveals evidence of past volcanic activity, although it's thought to be largely cryovolcanic—involving the eruption of water, ammonia, or other volatile substances rather than molten rock.
Ganymede's Unique Atmosphere and Magnetic Field
While Ganymede's atmosphere is incredibly thin, it's nevertheless significant. This extremely tenuous atmosphere is primarily composed of oxygen, which is generated through the radiolysis of water ice on the surface by radiation from Jupiter's magnetosphere. This atmospheric oxygen is not breathable by Earth-based life.
Ganymede stands apart among the moons in our solar system due to its intrinsic magnetic field. This is a remarkable feature, as it's the only moon known to possess such a field. This magnetic field is generated by the movement of conductive fluids, likely salty water, within its metallic core. This magnetic field interacts with Jupiter's much stronger magnetosphere, creating a complex and dynamic interplay.
The Interaction with Jupiter's Magnetosphere
Ganymede's magnetic field is embedded within Jupiter's vast magnetosphere, leading to fascinating interactions. As Ganymede orbits Jupiter, its magnetic field interacts with the Jovian magnetic field lines, creating currents and auroras at its poles. These auroras, detectable in the ultraviolet spectrum, provide valuable insights into the dynamics of both Ganymede's and Jupiter's magnetic fields. Studying these auroras helps scientists understand the complex processes occurring within the moon's interior and its environment.
The Potential for Subsurface Oceans
Perhaps the most exciting aspect of Ganymede's composition is the strong evidence for a subsurface ocean, potentially containing more water than all of Earth's oceans combined. This massive ocean is believed to be sandwiched between layers of ice, creating a potentially habitable environment. The existence of this ocean has been inferred from observations made by the Galileo spacecraft and subsequent analysis.
Evidence from Galileo and Future Missions
Data gathered by NASA's Galileo spacecraft provided crucial evidence for the existence of this subsurface ocean. Observations of Ganymede's magnetic field and its interaction with Jupiter's magnetosphere suggested the presence of a highly conductive layer beneath the surface, which is consistent with a salty water ocean. Future missions, such as the European Space Agency's JUICE mission (Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer), are designed to further investigate this ocean and its potential habitability.
JUICE, planned to arrive at Jupiter in 2031, will conduct detailed observations of Ganymede, including high-resolution imaging, spectroscopic analysis, and magnetic field measurements. These observations will significantly enhance our understanding of the moon's geological history, internal structure, and the potential for life.
Ganymede's Habitability and the Search for Life
The presence of a vast subsurface ocean raises the intriguing possibility of life existing on Ganymede. While the ocean is likely to be very cold and under immense pressure, the presence of liquid water, along with potentially other essential elements, suggests the possibility of at least microbial life. However, proving the existence of life remains a major challenge.
Factors influencing habitability
Several factors influence the potential habitability of Ganymede's ocean. The ocean's salinity, temperature, and the availability of essential nutrients are crucial. Hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor could provide a source of heat and energy, creating potentially habitable environments, similar to those found on Earth's ocean floor. Furthermore, the interaction between the ocean and the icy crust could create chemical gradients that support life.
Further investigation is needed to determine if the ocean meets the conditions necessary to support life. The JUICE mission, with its advanced instruments, aims to significantly advance our understanding of Ganymede's habitability. Analysis of the ocean's composition, temperature, and potential for chemical reactions will provide crucial information to address this fascinating question.
Future Missions and the Exploration of Ganymede
Ganymede's immense scientific potential has made it a prime target for future exploration. The European Space Agency's JUICE mission is a significant step forward, providing a comprehensive study of Ganymede and its environment.
The JUICE mission and beyond
JUICE's comprehensive suite of instruments will allow detailed investigations of Ganymede's surface, interior, and magnetosphere. High-resolution imaging will provide detailed maps of its surface features, while spectroscopic analysis will determine the composition of the surface and atmosphere. Magnetic field measurements will help to refine our understanding of the moon's internal structure and its interaction with Jupiter's magnetosphere.
Beyond JUICE, other future missions to the Jovian system are being considered. These missions could involve landers or even subsurface probes to directly explore Ganymede's ocean and search for signs of life. The immense scientific potential of Ganymede ensures that this fascinating moon will continue to be a focus of intense scientific study for decades to come.
Conclusion: Ganymede's Enduring Mystery
Ganymede, the largest moon in our solar system, remains an enigma, a celestial body that defies simple categorization. Its immense size, complex geology, unique magnetic field, and potential for a vast subsurface ocean make it one of the most scientifically compelling objects in our solar system. Future missions, like JUICE, promise to unveil more of Ganymede's secrets, potentially revealing evidence of past or present life and providing a deeper understanding of the diverse worlds that exist beyond our planet. The ongoing exploration of Ganymede promises a wealth of new discoveries, further enriching our understanding of the solar system and our place within it. The mysteries of this colossal moon continue to fuel scientific curiosity and drive the quest for knowledge in the realms of planetary science and astrobiology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Where In A Plant Cell Is Chlorophyll Found
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Monomial
Mar 21, 2025
-
True Or False The Vertical Axis Is Called The Y Axis
Mar 21, 2025
-
Compressing A File Is Also Called
Mar 21, 2025
-
Bundles Of Axons In The Central Nervous System Are Called
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Largest Satellite In The Solar System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
