Labelled Diagram Of A Sperm Cell
News Leon
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
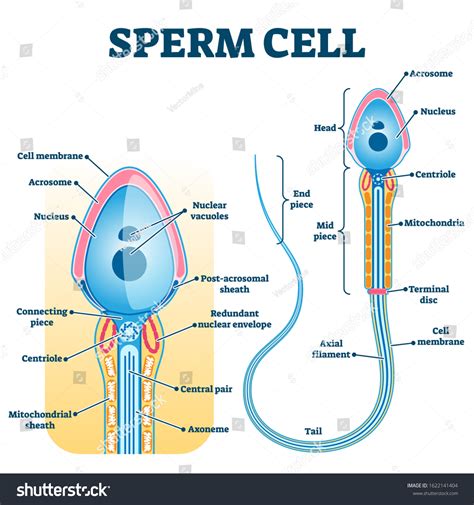
Table of Contents
A Deep Dive into the Sperm Cell: A Labeled Diagram and Comprehensive Guide
The human sperm cell, also known as a spermatozoon, is a remarkable cell, a tiny powerhouse of biological engineering designed for a single, crucial purpose: fertilization. Understanding its structure is key to understanding reproduction. This article provides a detailed labeled diagram of a sperm cell, followed by an in-depth exploration of each component and its role in the complex process of conception.
Labeled Diagram of a Sperm Cell
(Unfortunately, I cannot create visual diagrams directly within this text format. However, I strongly encourage you to search online for "labeled diagram of a sperm cell" using your preferred search engine. You will find many high-quality images illustrating the components described below.)
Components of a Sperm Cell: A Detailed Breakdown
The sperm cell is far from simple; its structure is highly specialized to facilitate its journey to the egg. Let's dissect the major components:
1. Head: The Guiding Star
The head of the sperm cell is the most recognizable part, housing the essential genetic material and the enzymes necessary for fertilization.
-
Acrosome: This cap-like structure covering the anterior part of the head is crucial for fertilization. It contains enzymes, including hyaluronidase and acrosin, which are essential for breaking down the protective layers surrounding the egg (cumulus oophorus and zona pellucida) to allow sperm penetration. Think of it as the sperm's specialized "drill bit." The acrosome reaction, the release of these enzymes, is a critical step in fertilization. Without a functional acrosome, fertilization cannot occur.
-
Nucleus: The nucleus is the command center, containing the tightly packed paternal DNA (23 chromosomes in humans). This genetic material is condensed to maximize space and protect it during its journey. The DNA's integrity is paramount for successful fertilization and the development of a healthy embryo. Any damage to the DNA can result in genetic abnormalities.
2. Neck: Connecting the Powerhouse
The neck is the short, narrow region connecting the head to the midpiece. It's a transition zone, playing a crucial role in anchoring the different components and transmitting energy.
- Centrioles: Located near the neck, centrioles are crucial for cell division. Though the sperm contributes a centriole, it's the oocyte's centriole that is primarily involved in the first few cleavages of the zygote.
3. Midpiece: The Energy Factory
The midpiece is the powerhouse of the sperm cell, packed with mitochondria.
- Mitochondria: These organelles are responsible for generating the adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's primary energy currency. The sperm requires immense energy to propel itself through the female reproductive tract, making the high density of mitochondria in the midpiece essential for its long journey. Mitochondrial dysfunction can impair sperm motility and lead to infertility. Importantly, mitochondrial DNA is maternally inherited, not paternally.
4. Tail (Flagellum): The Propulsion System
The tail is the long, whip-like structure responsible for the sperm's motility, enabling it to swim towards the egg.
-
Axoneme: The core of the flagellum is the axoneme, a complex microtubule structure that enables movement through coordinated beating. The axoneme's structure and function are intricately regulated, ensuring efficient propulsion. Defects in the axoneme's structure can result in immotile sperm, a significant cause of male infertility.
-
Fibrous Sheath: Surrounding the axoneme, the fibrous sheath provides structural support and contributes to the flagellum's movement.
Sperm Cell Motility: A Marathon, Not a Sprint
The journey of a sperm cell is a challenging one. It needs to navigate the complex environment of the female reproductive tract, a journey that demands incredible stamina and efficiency. The coordinated beating of the flagellum propels the sperm forward, navigating a complex landscape of mucus, fluids, and other barriers. This motility is crucial for reaching the egg and successfully fertilizing it.
Several factors influence sperm motility:
-
Seminal fluid: The composition of seminal fluid significantly impacts sperm motility. Its pH, viscosity, and nutrient content are crucial for maintaining sperm viability and motility.
-
Temperature: Optimal temperature is essential for sperm survival and function. Even slight deviations can significantly affect motility.
-
Genetics: Genetic factors can influence the structure and function of the flagellum, impacting sperm motility.
-
Environmental factors: Exposure to toxins, radiation, and certain medications can impair sperm motility.
The Significance of Sperm Cell Structure in Fertility
The intricacies of the sperm cell's structure highlight its remarkable specialization. Any defects or abnormalities in any of these components can significantly impair its function, leading to infertility. This is why the assessment of sperm morphology (structure) and motility is crucial in evaluating male fertility.
Common abnormalities include:
-
Abnormal head morphology: Head size, shape, and acrosome integrity are crucial. Defects in these aspects can affect the sperm's ability to penetrate the egg.
-
Midpiece defects: Abnormalities in the mitochondria can impair energy production, reducing motility and viability.
-
Tail defects: Defects in the flagellum's structure or function severely impact motility, making fertilization impossible.
The Fertilization Process: A Symphony of Events
The sperm cell's journey culminates in the fertilization process. After reaching the egg, the acrosome reaction is initiated, allowing the sperm to penetrate the protective layers surrounding the egg. Once inside, the sperm's nucleus fuses with the egg's nucleus, combining the paternal and maternal genetic material to form a zygote, the first cell of a new human life.
Conclusion: A Marvel of Biological Engineering
The sperm cell, with its intricate structure and remarkable function, is a testament to the sophistication of biological engineering. Understanding its components, their individual roles, and how they work together to achieve fertilization is crucial in understanding human reproduction and addressing infertility. Further research continues to unveil the complexities of this microscopic powerhouse, promising advancements in reproductive medicine and our understanding of human life's beginnings. Remember to consult reliable sources, such as medical textbooks and peer-reviewed scientific articles, for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unlike A Eukaryotic Cell A Prokaryotic Cell Does Not Have
Mar 31, 2025
-
Find The Value Of In The Triangle Shown Below
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Discrete Variable
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is Another Name For Krebs Cycle
Mar 31, 2025
-
Is Boiling Point Chemical Or Physical
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Labelled Diagram Of A Sperm Cell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
