Is The Paramecium A Unicellular Or Multicellular Organism
News Leon
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
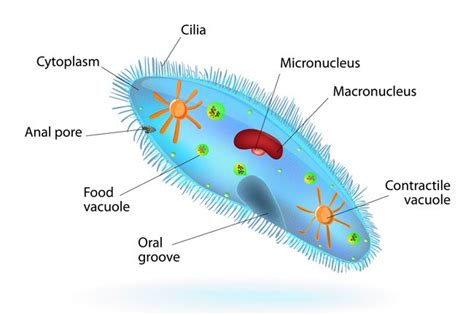
Table of Contents
Is the Paramecium a Unicellular or Multicellular Organism? A Deep Dive into Paramecium Biology
The question, "Is a paramecium unicellular or multicellular?" has a straightforward answer: a paramecium is a unicellular organism. However, the seemingly simple answer opens the door to a fascinating exploration of the complexity of this single-celled marvel. This article will delve into the intricacies of paramecium biology, exploring its structure, functions, and behaviors, to fully appreciate why classifying it as unicellular is accurate, even with its surprisingly sophisticated capabilities.
Understanding Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms
Before diving into the specifics of paramecium, let's establish a clear understanding of the key difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms.
-
Unicellular organisms: These are organisms made up of only one cell. All life processes, including nutrition, excretion, respiration, and reproduction, occur within this single cell. Examples include bacteria, amoeba, and, as we'll explore extensively, paramecium.
-
Multicellular organisms: These are organisms composed of multiple cells, often organized into specialized tissues, organs, and organ systems. Different cells perform specific functions, contributing to the overall organism's survival. Humans, animals, plants, and fungi are all examples of multicellular organisms.
The defining characteristic separating these two types is the number of cells that make up the organism. While complexity of function can vary significantly between unicellular organisms, the fundamental distinction remains the number of cells.
The Paramecium: A Single-celled Powerhouse
Paramecium, a genus of single-celled ciliates, serves as an excellent example of the remarkable capabilities found within a unicellular organism. Its complexity often leads to initial confusion about its classification, but a closer look confirms its unicellular nature. While it might exhibit sophisticated behaviors and intricate internal structures, it remains a single cell performing all life functions within its boundaries.
Paramecium's Cellular Structure: A Microscopic City
Despite being a single cell, the paramecium possesses a surprisingly complex internal structure. Think of it as a tiny, self-contained city with various specialized organelles performing distinct tasks.
-
Cell Membrane: The outer boundary, regulating the passage of substances into and out of the cell. This is vital for maintaining homeostasis and nutrient uptake.
-
Cilia: Numerous hair-like structures covering the cell surface. These cilia beat rhythmically, propelling the paramecium through its aquatic environment. This coordinated movement demonstrates a level of cellular organization remarkable for a single-celled entity.
-
Oral Groove: A funnel-shaped structure leading to the cell's interior. Food particles are swept into the oral groove by the cilia and then ingested. This highlights the sophisticated mechanisms for nutrient acquisition within this single cell.
-
Food Vacuoles: Membrane-bound sacs that form after food is ingested. These vacuoles move around the cell, allowing enzymes to digest the food. The waste products are then expelled. This internal transport system is remarkable considering the scale.
-
Contractile Vacuoles: These specialized organelles are essential for osmoregulation, regulating water balance within the cell. They periodically contract, expelling excess water to prevent the cell from bursting. This precise control is vital for survival in aquatic environments.
-
Nucleus: Paramecia typically have two types of nuclei: a macronucleus and a micronucleus. The macronucleus controls the day-to-day functions of the cell, while the micronucleus is involved in sexual reproduction. The presence of two distinct nuclei further underscores the intricate organization within this single-celled organism.
-
Cytoplasm: The jelly-like substance filling the cell, containing various organelles and enzymes. This is the site of numerous metabolic processes, including protein synthesis and energy production.
Paramecium's Life Processes: All Within One Cell
The impressive aspect of paramecium is that all the essential life processes, usually distributed across multiple cell types in multicellular organisms, occur within this single cell:
-
Nutrition: Paramecium is a heterotroph, obtaining nutrients by consuming other microorganisms. The coordinated action of cilia, oral groove, and food vacuoles ensures efficient feeding.
-
Respiration: Paramecium performs aerobic respiration, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. This gas exchange happens directly across the cell membrane.
-
Excretion: Waste products resulting from digestion and metabolism are expelled through the cell membrane or specialized structures.
-
Reproduction: Paramecium can reproduce both asexually (binary fission) and sexually (conjugation). Asexual reproduction involves the simple division of the cell into two identical daughter cells. Sexual reproduction involves the exchange of genetic material between two individuals, increasing genetic diversity.
-
Response to Stimuli: Paramecium exhibits chemotaxis (movement towards or away from chemicals) and avoids obstacles, demonstrating its ability to sense and respond to its environment. This behavior requires sophisticated internal signaling and coordination.
Why Paramecium is Unequivocally Unicellular
Despite the sophisticated internal organization and remarkable behaviors, the crucial factor in classifying paramecium remains the single-cell structure. All life processes are contained within the boundaries of this one cell. There's no cellular specialization into tissues or organs, a defining characteristic of multicellular organisms. Each paramecium is an independent, self-sufficient unit, capable of carrying out all necessary functions for its survival.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
The complexity of paramecium's internal structure and its sophisticated behaviors can sometimes lead to misconceptions:
-
Colonial Organisms: Some might confuse paramecium with colonial organisms, which are groups of unicellular organisms living together in a colony. While colonial organisms show some level of cooperation, each individual cell remains independent and can survive on its own. Paramecium is not a colony; it's a single, independent cell.
-
Cellular Specialization: The presence of specialized organelles within the paramecium might lead one to think of cellular specialization like in multicellular organisms. However, these organelles are all within a single cell; they are not separate cells performing specific functions as in a multicellular organism. There is no differentiation into different cell types.
Conclusion: A Single Cell, a Complex Life
The paramecium, a seemingly simple single-celled organism, reveals the astonishing complexity that can exist within a single cell. Its intricate internal structures, sophisticated behaviors, and efficient life processes demonstrate the remarkable adaptability and functionality of unicellular life. While its capabilities may be impressive, the fundamental defining characteristic—the presence of only one cell—firmly places the paramecium in the category of unicellular organisms. Understanding the distinction between unicellular and multicellular organisms, along with the detailed biology of a fascinating organism like paramecium, provides valuable insight into the diversity and wonder of life on Earth. This detailed exploration has hopefully clarified any doubt about the classification of this fascinating microscopic creature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Do Transverse And Longitudinal Waves Have In Common
Apr 09, 2025
-
What Are The Units Of Potential Energy
Apr 09, 2025
-
Is Dry Ice A Compound Element Or Mixture
Apr 09, 2025
-
Vapour Pressure Of Water In Torr
Apr 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True Regarding Viruses
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Paramecium A Unicellular Or Multicellular Organism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.