How To Find The Resonant Frequency
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
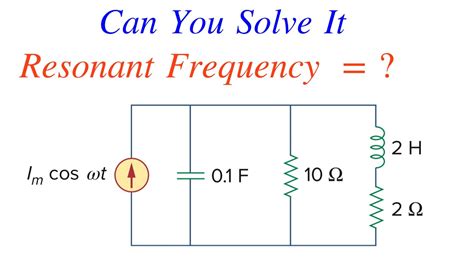
Table of Contents
How to Find the Resonant Frequency: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the resonant frequency of a system is crucial in various fields, from engineering and physics to music and acoustics. Resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate with greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. Understanding how to find this frequency is essential for optimizing performance, predicting behavior, and preventing catastrophic failures. This comprehensive guide will explore various methods for determining resonant frequencies, covering both theoretical calculations and practical experimental techniques.
Understanding Resonance
Before diving into the methods, let's establish a firm understanding of resonance. Resonance occurs when the frequency of an external force matches the natural frequency of a system. This natural frequency is determined by the system's physical properties, such as mass, stiffness, and damping. When the frequencies align, the system absorbs energy efficiently, leading to a significant increase in amplitude of oscillation. Think of pushing a child on a swing – you achieve the maximum amplitude by applying force at the swing's natural frequency.
Factors Affecting Resonant Frequency
Several factors influence the resonant frequency of a system:
- Mass: In simpler systems, like a mass-spring system, a higher mass results in a lower resonant frequency.
- Stiffness: Increased stiffness leads to a higher resonant frequency. A stiffer spring will oscillate faster.
- Damping: Damping reduces the amplitude of oscillations. While it doesn't directly change the resonant frequency, it broadens the resonance peak, making it less sharp.
- Geometry: The shape and dimensions of an object significantly affect its resonant frequency. For example, the length of a string determines the frequencies at which it will resonate.
- Material Properties: The material's Young's modulus (a measure of stiffness) and density play crucial roles in determining the resonant frequency.
Methods for Finding Resonant Frequency
There are two primary approaches to finding resonant frequency: theoretical calculation and experimental measurement.
1. Theoretical Calculation
Theoretical calculations rely on mathematical models to predict the resonant frequency. The complexity of the calculation depends on the system's complexity.
a) Simple Mass-Spring System
For a simple mass-spring system, the resonant frequency (f) can be calculated using the following formula:
f = 1 / (2π) * √(k/m)
Where:
- f is the resonant frequency in Hertz (Hz)
- k is the spring constant (N/m) – a measure of the spring's stiffness
- m is the mass (kg)
This formula assumes negligible damping.
b) LCR Circuit
In an electrical circuit containing an inductor (L), capacitor (C), and resistor (R), the resonant frequency is given by:
f = 1 / (2π) * √(1/LC)
Again, this formula assumes negligible resistance (R). The resistor introduces damping, affecting the sharpness of the resonance.
c) More Complex Systems
For more complex systems like beams, plates, or complex structures, the theoretical calculation becomes significantly more intricate. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and other computational methods are often employed to model the system's behavior and determine its resonant frequencies. These methods involve dividing the system into smaller elements and solving the equations of motion for each element.
2. Experimental Measurement
Experimental methods directly measure the resonant frequency of a physical system. Several techniques are available:
a) Frequency Sweep Method
This method involves applying a sinusoidal force or signal to the system while gradually changing its frequency. The amplitude of the system's response is monitored. The frequency at which the amplitude is maximum corresponds to the resonant frequency. This technique is widely used in various applications, including characterizing mechanical systems and electronic circuits.
b) Impulse Response Method
An impulse (a short, sharp force or signal) is applied to the system, and the system's response is measured. The Fourier Transform of the response reveals the system's frequency spectrum, with the peak corresponding to the resonant frequency. This method is particularly useful for systems with short response times.
c) Resonance Testing Machines
Specialized resonance testing machines are available for accurately determining the resonant frequencies of various materials and structures. These machines apply controlled vibrations and precisely measure the system's response, providing accurate measurements of resonant frequencies and damping ratios. These machines are commonly used in material science and engineering for quality control and material characterization.
d) Using a Sound Level Meter and a Sound Source
For acoustic systems like musical instruments or rooms, a sound level meter and a sound source (like a speaker) can be used. Varying the frequency of the sound source and measuring the sound pressure level with the sound level meter will reveal the resonant frequencies as peaks in the sound pressure level.
Practical Considerations and Applications
The choice of method for determining resonant frequency depends heavily on the system's complexity, available resources, and desired accuracy.
Practical Considerations:
- Damping: The presence of damping affects the sharpness of the resonance peak. High damping will broaden the peak, making it harder to pinpoint the exact resonant frequency.
- Measurement Accuracy: The accuracy of both theoretical and experimental methods depends on the precision of the input parameters and measuring instruments.
- Non-linearity: In some systems, the resonant frequency might change with the amplitude of vibration. This non-linear behavior needs to be considered when selecting a method.
- Environmental Factors: External factors like temperature and humidity can affect the system's properties and hence its resonant frequency.
Applications:
Determining resonant frequencies has a wide range of applications across various disciplines:
- Structural Engineering: Understanding the resonant frequencies of bridges, buildings, and other structures is crucial for preventing resonance-induced failures.
- Mechanical Engineering: Designing machines and components that avoid resonant frequencies ensures smooth operation and prevents vibrations that could damage the equipment.
- Acoustics: Resonant frequencies play a critical role in the design of musical instruments, concert halls, and noise-cancellation technologies. Understanding these frequencies is essential for optimizing sound quality and minimizing unwanted noise.
- Electronics: In electronic circuits, resonant frequencies are utilized in filters, oscillators, and other components. Accurate determination of resonant frequency ensures the circuit operates as intended.
- Medical Imaging: Medical imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI utilize resonant frequencies for creating images of internal organs.
Conclusion
Finding the resonant frequency of a system is a fundamental task in many scientific and engineering disciplines. The methods discussed in this guide, ranging from simple calculations to sophisticated experimental techniques, provide a comprehensive overview of how to achieve this. The selection of the most appropriate method depends heavily on the specific system and its characteristics. By understanding resonance and employing the correct techniques, engineers and scientists can design and optimize systems to avoid potential failures and achieve desired performance. Remember to carefully consider all factors influencing resonant frequency and select the most appropriate method for achieving the required level of accuracy and detail. Always prioritize safety and follow appropriate procedures when conducting experimental measurements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is A Webcam An Input Or Output Device
Mar 17, 2025
-
Word For A Person Who Uses Big Words
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 375 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Is The Correct Order Of The Scientific Method
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Long Is A Thousand Days
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find The Resonant Frequency . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
