How Many Valence Electrons In Copper
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
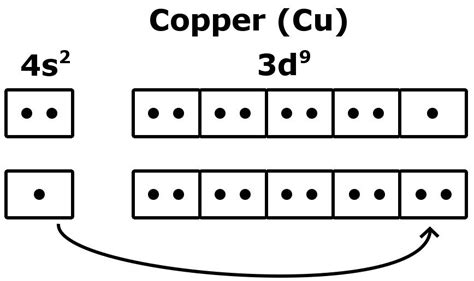
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Copper Have? A Deep Dive into Electronic Configuration and Properties
Copper, a reddish-orange metal known for its excellent electrical conductivity and malleability, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic configuration is crucial to comprehending its remarkable properties. This article will delve deep into the question: how many valence electrons does copper have? We'll explore its electron configuration, exceptions to the octet rule, and how its valence electrons influence its behavior in various chemical and physical contexts.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we address copper specifically, let's clarify the concept of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (or energy level) of an atom. These electrons are the primary participants in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, metallic). The number of valence electrons typically dictates the group number of an element in the periodic table (with some exceptions).
Copper's Electronic Configuration: The Unexpected Twist
Copper's atomic number is 29, indicating it has 29 electrons. Based on the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, you might expect its electronic configuration to be: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d⁹. However, this is not the actual configuration. Copper exhibits an exception to the expected filling order. Its actual electronic configuration is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s¹3d¹⁰.
Why the Exception?
The discrepancy arises from the relative stability of a completely filled d subshell. A filled d subshell (d¹⁰) is significantly more stable than a partially filled d subshell (d⁹). The energy difference between the 4s and 3d orbitals is relatively small. Therefore, one electron from the 4s orbital "jumps" to the 3d orbital to achieve the more stable, completely filled d¹⁰ configuration. This energy gain outweighs the slight increase in energy associated with moving the electron.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Copper Have? The Answer
Now, we can finally answer the central question. While initially it might seem that copper has 11 valence electrons (4s¹ + 3d¹⁰), this is a misconception. In chemical bonding, the 3d electrons participate much less actively than the 4s electron. Therefore, copper typically has only one valence electron. This is reflected in its +1 oxidation state in many compounds.
Copper's Properties and its Single Valence Electron
The single valence electron in copper is responsible for many of its characteristic properties:
1. Excellent Electrical Conductivity:
The loosely held valence electron can move freely through the copper lattice, contributing to its exceptional electrical conductivity. This makes copper an ideal material for electrical wiring and other electrical applications.
2. Malleability and Ductility:
The metallic bonding in copper, facilitated by the shared valence electron, allows the copper atoms to slide past each other relatively easily. This is what gives copper its malleability (ability to be shaped) and ductility (ability to be drawn into wires).
3. Thermal Conductivity:
Copper's high thermal conductivity is also linked to its mobile valence electrons. These electrons can efficiently transfer thermal energy throughout the material.
4. Oxidation States:
While copper primarily exhibits a +1 oxidation state due to its single valence electron, it can also exist in a +2 oxidation state. In this case, both the 4s and one 3d electron are involved in bonding. This results in different chemical behaviors and compound formations. Examples of +1 oxidation state compounds include cuprous oxide (Cu₂O) and cuprous chloride (CuCl), while +2 oxidation state compounds include cupric oxide (CuO) and cupric sulfate (CuSO₄).
Applications of Copper and its Valence Electrons
The unique properties stemming from copper's electronic configuration and single valence electron lead to its widespread use in numerous applications:
- Electrical wiring: Copper's excellent conductivity makes it the material of choice for electrical wiring in homes, buildings, and power grids.
- Plumbing: Copper pipes are used extensively in plumbing systems due to their corrosion resistance and durability.
- Electronics: Copper is crucial in electronics manufacturing, found in printed circuit boards, integrated circuits, and connectors.
- Coins and alloys: Copper is a component of various alloys, such as brass and bronze, used in coinage, and other industrial applications.
- Medical applications: Copper is used in medical devices and instruments due to its antimicrobial properties.
Comparing Copper to Other Elements
Understanding copper's valence electrons allows us to compare it to other elements in the periodic table. For instance, silver (Ag) and gold (Au), which are in the same group as copper, also have one valence electron, contributing to their high conductivity. However, their differences in electronic configuration and atomic size lead to variations in their properties.
Conclusion: The Significance of Copper's Single Valence Electron
In conclusion, despite its initial appearance, copper possesses only one valence electron, which plays a pivotal role in its unique properties and extensive applications. This single electron facilitates excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, and ductility. The understanding of this seemingly simple fact unveils the complexity and importance of the electronic structure in determining the characteristics of this vital metal. While the 3d electrons are involved in chemical bonding under specific circumstances (leading to the +2 oxidation state), it’s the behavior of the 4s electron that primarily defines copper’s chemical and physical characteristics. Therefore, the simple answer – one valence electron – holds profound implications for our understanding of copper's behavior and its myriad applications in our modern world. Further studies into copper's intricacies continue to reveal new possibilities and innovations, driven by the fundamental understanding of its electronic structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Movement Of Earth Around The Sun Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Ph Of A Neutral Solution
Mar 17, 2025
-
Did The Ussr Imiss The Great Depression
Mar 17, 2025
-
Choose The Components Of A Respiratory Membrane
Mar 17, 2025
-
Dendrite Is To Axon As Is To
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons In Copper . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
