How Many Diagonals Does A Regular Pentagon Have
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
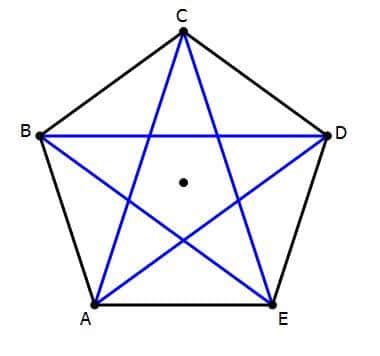
Table of Contents
How Many Diagonals Does a Regular Pentagon Have? A Comprehensive Exploration
The question, "How many diagonals does a regular pentagon have?" might seem simple at first glance. However, exploring this seemingly basic geometric problem opens doors to understanding fundamental concepts in combinatorics, geometry, and even graph theory. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the underlying principles, exploring different methods of calculation and extending the concept to polygons with more sides. We will also examine the significance of diagonals in various geometric contexts.
Understanding Diagonals
Before we tackle the pentagon, let's define what a diagonal is. In any polygon (a closed figure with straight sides), a diagonal is a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices (corners). Crucially, it's internal to the polygon; it lies within the shape's boundaries. A side of the polygon is not considered a diagonal.
Calculating Diagonals in a Pentagon
A regular pentagon is a five-sided polygon with all sides equal in length and all interior angles equal. Let's find out how many diagonals it has.
One approach is to use a visual method. Draw a regular pentagon and try to draw all possible diagonals from each vertex. You'll find that from each vertex, you can draw two diagonals. Since there are five vertices, you might initially think there are 5 x 2 = 10 diagonals. However, this method counts each diagonal twice (once for each endpoint). Therefore, the correct number of diagonals is half of this, which is 5.
Therefore, a regular pentagon has 5 diagonals.
The Combinatorial Approach: A More General Method
The visual method works well for a pentagon, but it becomes cumbersome for polygons with many sides. A more powerful and general method uses combinatorics, a branch of mathematics dealing with counting.
Consider a polygon with n sides (and therefore n vertices). To form a diagonal, we need to choose two vertices. The number of ways to choose 2 vertices from n vertices is given by the combination formula:
n C 2 = n! / (2! * (n-2)!)
Where:
- n! (n factorial) is the product of all positive integers up to n (e.g., 5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120).
However, this formula includes the sides of the polygon as well. Since we only want diagonals, we must subtract the number of sides (n) from the total number of line segments.
Thus, the general formula for the number of diagonals in a polygon with n sides is:
Number of diagonals = n C 2 - n = n! / (2! * (n-2)!) - n = n(n-3) / 2
Let's apply this formula to the pentagon (n=5):
Number of diagonals = 5(5-3) / 2 = 5(2) / 2 = 5
This confirms our earlier result.
Extending to Other Polygons
This combinatorial approach is incredibly useful. Let's apply it to other polygons:
- Square (n=4): Number of diagonals = 4(4-3)/2 = 2
- Hexagon (n=6): Number of diagonals = 6(6-3)/2 = 9
- Heptagon (n=7): Number of diagonals = 7(7-3)/2 = 14
- Octagon (n=8): Number of diagonals = 8(8-3)/2 = 20
And so on. The formula elegantly handles polygons with any number of sides.
Diagonals and Geometric Properties
The diagonals of a polygon possess various interesting properties depending on the polygon's type and regularity.
-
Regular Polygons: In regular polygons, diagonals often exhibit symmetry and can be used to divide the polygon into smaller, congruent shapes. For instance, the diagonals of a regular pentagon intersect to form a smaller, self-similar pentagon within the original.
-
Convex Polygons: In convex polygons (polygons where all interior angles are less than 180 degrees), all diagonals lie entirely within the polygon.
-
Concave Polygons: In concave polygons (polygons with at least one interior angle greater than 180 degrees), some diagonals may lie partially or entirely outside the polygon.
-
Triangles: Triangles are a special case. They have no diagonals since every line segment connecting two vertices is a side.
Diagonals in Graph Theory
The concept of diagonals extends to graph theory, a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between objects. A polygon can be represented as a graph where the vertices are the polygon's corners and the edges are its sides and diagonals. The number of diagonals becomes relevant when analyzing the connectivity and properties of the graph.
Practical Applications
Understanding the number of diagonals isn't just an academic exercise. It has practical applications in various fields:
-
Computer Graphics: Algorithms for rendering polygons often rely on knowledge of their vertices and diagonals.
-
Engineering: Structural design might involve analyzing the stability of polygonal structures, where diagonals play a crucial role in strength and rigidity.
-
Cartography: Dividing geographical regions into polygons requires understanding their geometric properties, including diagonals.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple question of how many diagonals a regular pentagon has leads to a fascinating exploration of combinatorics, geometry, and graph theory. The formula n(n-3)/2 provides a powerful and general method for calculating the number of diagonals in any polygon. This knowledge extends beyond simple counting, offering insights into geometric properties and having practical implications in diverse fields. Understanding the properties of diagonals helps us to analyze and manipulate polygons efficiently in various applications. The power of this simple formula and the underlying principles demonstrate the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their real-world relevance. From the regular pentagon to complex polygons, the concept of diagonals continues to provide a rich area for mathematical exploration and practical application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Are In One Cubic Foot
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Diodes Are Required To Form A Bridge Rectifier
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Graph Of The X Component Of The Electric Field
Mar 14, 2025
-
Reactions Which Do Not Continue To Completion Are Called Reactions
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is Five Hours
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Diagonals Does A Regular Pentagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
