How Do You Convert Joules To Electron Volts
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
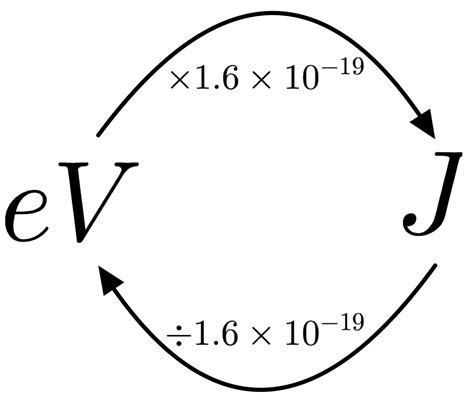
Table of Contents
How Do You Convert Joules to Electron Volts?
Understanding energy units is crucial in various scientific fields, particularly physics. While joules (J) are the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI), electron volts (eV) are frequently used in atomic and nuclear physics, particle physics, and materials science. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of converting joules to electron volts, delving into the underlying concepts and providing practical examples.
Understanding the Joule
The joule (J), named after James Prescott Joule, is the SI unit of energy. It's defined as the work done when a force of one newton is applied over a distance of one meter. This fundamental unit is used across numerous applications, encompassing mechanical, thermal, electrical, and other forms of energy.
Key Characteristics of the Joule:
- SI Unit: It's the standard unit for energy in the International System of Units.
- Versatility: Applicable to diverse energy forms.
- Magnitude: Relatively large compared to the electron volt.
Understanding the Electron Volt
The electron volt (eV) is a unit of energy representing the kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating through an electrical potential difference of one volt. This unit is particularly useful when dealing with atomic and subatomic particles because it reflects the energies typically involved in these interactions.
Key Characteristics of the Electron Volt:
- Atomic and Subatomic Physics: Preferably used in these domains due to its scale.
- Convenience: Offers a more manageable scale for energies at the atomic level.
- Magnitude: Significantly smaller than the joule.
The Conversion Factor: Linking Joules and Electron Volts
The conversion between joules and electron volts hinges on the fundamental charge of an electron (e) and the definition of the volt. The elementary charge (e) is approximately 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs (C). One electron volt is the energy gained by an electron when accelerated through a potential difference of one volt (V).
The relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
1 eV = 1.602 x 10^-19 J
This equation is the cornerstone of our conversion process. It signifies that one electron volt is equivalent to 1.602 x 10^-19 joules.
Converting Joules to Electron Volts: A Step-by-Step Guide
The conversion process itself is straightforward, thanks to the established conversion factor. Let's outline the steps involved:
Step 1: Identify the Energy in Joules
Begin by identifying the energy value you wish to convert from joules to electron volts. This value will be your starting point for the calculation.
Step 2: Apply the Conversion Factor
Use the conversion factor (1 eV = 1.602 x 10^-19 J) to transform the energy from joules to electron volts. This involves dividing the energy value in joules by the conversion factor.
Step 3: Calculate the Energy in Electron Volts
Perform the calculation to obtain the equivalent energy in electron volts. The result will represent the energy expressed in the more convenient electron volt unit.
Example 1: Converting a Large Energy Value
Let's say we have an energy value of 1.0 x 10^-15 joules. To convert this to electron volts, we perform the following calculation:
Energy in eV = (1.0 x 10^-15 J) / (1.602 x 10^-19 J/eV) ≈ 6242 eV
Therefore, 1.0 x 10^-15 joules is approximately equivalent to 6242 electron volts.
Example 2: Converting a Smaller Energy Value
Consider an energy of 5.0 x 10^-20 joules. Following the same steps:
Energy in eV = (5.0 x 10^-20 J) / (1.602 x 10^-19 J/eV) ≈ 0.312 eV
Thus, 5.0 x 10^-20 joules is approximately equivalent to 0.312 electron volts.
Converting Electron Volts to Joules: The Reverse Process
The reverse conversion, from electron volts to joules, is equally straightforward. Simply multiply the energy value in electron volts by the conversion factor (1.602 x 10^-19 J/eV).
Example 3: Converting from Electron Volts to Joules
Suppose we have an energy of 1000 eV. Converting to joules:
Energy in J = 1000 eV * (1.602 x 10^-19 J/eV) = 1.602 x 10^-16 J
Therefore, 1000 electron volts is equivalent to 1.602 x 10^-16 joules.
Practical Applications: Where These Conversions Matter
The ability to convert between joules and electron volts is essential in numerous scientific and technological domains:
- Nuclear Physics: Analyzing nuclear reactions and decays, determining binding energies, and calculating particle energies.
- Particle Physics: Understanding interactions between elementary particles, analyzing particle accelerator data, and studying high-energy collisions.
- Materials Science: Studying electronic band structures, analyzing electron transport in materials, and characterizing semiconductor properties.
- Astrophysics: Analyzing stellar processes, understanding energy production in stars, and characterizing cosmic ray energies.
- Medical Physics: Calculating radiation doses in radiotherapy and other medical applications involving ionizing radiation.
Beyond the Basics: Dealing with Larger Units
For extremely large or small energy values, it’s common to use multiples or submultiples of the electron volt. These include:
- keV (kiloelectronvolt): 1 keV = 1000 eV
- MeV (megaelectronvolt): 1 MeV = 10^6 eV
- GeV (gigaelectronvolt): 1 GeV = 10^9 eV
- TeV (teraelectronvolt): 1 TeV = 10^12 eV
These larger units are crucial when dealing with the high energies encountered in particle physics and astrophysics. Remember to convert to the base unit (eV) before converting to joules to maintain accuracy.
Potential Pitfalls and Considerations
While the conversion itself is simple, some points deserve attention:
- Significant Figures: Maintain appropriate significant figures throughout the calculations to ensure accuracy.
- Unit Consistency: Always double-check that your starting units are consistently joules or electron volts, avoiding mix-ups.
- Scientific Notation: Employing scientific notation can simplify calculations involving very large or small numbers, minimizing errors.
Conclusion: Mastering the Joule-Electron Volt Conversion
The ability to smoothly convert between joules and electron volts is a fundamental skill for anyone working in physics, chemistry, engineering, or related fields. The conversion, while mathematically simple, allows researchers and scientists to effortlessly navigate between the standard SI unit of energy and the unit specifically tailored to the microcosm of atomic and subatomic interactions. By understanding the underlying principles and applying the conversion factor correctly, one can seamlessly move between these energy scales, unlocking deeper insights into the physical world. Remember to practice the steps outlined in this article, focusing on accuracy and careful attention to detail to master this crucial conversion skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If A Pea Plant Shows A Recessive Phenotype
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is A Patent A Current Asset
Mar 15, 2025
-
Why Are Producers So Important To An Ecosystem
Mar 15, 2025
-
Difference Between Interest Groups And Political Parties
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Division Of The Cell Nucleus Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Convert Joules To Electron Volts . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
