Excited State Of Oxygen Electron Configuration
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
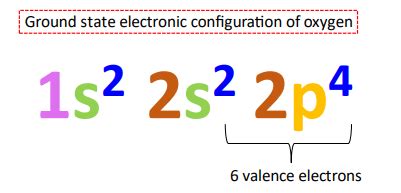
Table of Contents
Excited State of Oxygen: Electron Configuration and its Implications
Oxygen, a vital element for life on Earth, boasts a fascinating electron configuration that dictates its chemical behavior and reactivity. While its ground state configuration is well-known, understanding its excited states is crucial for comprehending a wide range of phenomena, from the aurora borealis to the functioning of certain chemical reactions. This article delves deep into the excited states of oxygen, exploring their electron configurations, energy levels, and the significant roles they play in various scientific fields.
Understanding Ground State Electron Configuration
Before exploring the intricacies of excited states, it's essential to establish a firm understanding of oxygen's ground state electron configuration. Oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, possesses eight electrons. Following the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, these electrons are distributed across its energy levels as follows: 1s²2s²2p⁴.
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the lowest energy level (1s orbital).
- 2s²: Two electrons fill the next energy level (2s orbital).
- 2p⁴: Four electrons occupy the 2p orbitals. According to Hund's rule, these electrons initially occupy separate 2p orbitals with parallel spins before pairing up. This results in two unpaired electrons in the 2p orbitals, contributing to oxygen's paramagnetism and high reactivity.
Transition to Excited States: The Role of Energy Absorption
The ground state represents the lowest energy configuration of an atom. However, by absorbing energy, an electron can jump to a higher energy level, resulting in an excited state. This energy absorption can occur through various mechanisms, including:
- Photon Absorption: Exposure to electromagnetic radiation (light) of a specific frequency can provide the necessary energy to promote an electron to a higher energy level. This is a fundamental principle behind spectroscopic techniques used to study atomic structures.
- Collisional Excitation: Collisions between oxygen atoms and other particles (atoms, ions, or electrons) can transfer kinetic energy, exciting an electron to a higher energy level. This is common in high-energy environments like plasmas and the upper atmosphere.
Excited State Electron Configurations: Variety and Complexity
Unlike the single ground state configuration, oxygen possesses numerous excited states, each with a unique electron configuration. The complexity arises from the various ways an electron can be promoted to higher energy levels. For example:
-
Promoting a 2p electron to a higher energy level (e.g., 3s, 3p): This is the most common type of excitation. The resulting configurations could be 1s²2s²2p³3s¹, 1s²2s²2p³3p¹, etc., depending on the specific energy level the electron transitions to. Each of these configurations corresponds to a different excited state with a different energy level.
-
Simultaneous excitation of multiple electrons: It's possible for more than one electron to be simultaneously excited to higher energy levels. This leads to even more complex excited state configurations and significantly higher energy levels.
-
Spin changes: During excitation, the spin of the excited electron can change, resulting in different spin multiplicity (e.g., singlet, triplet) of the excited state. This impacts the allowed transitions between excited states and ground states.
Energy Levels and Term Symbols: A Deeper Dive
Describing oxygen's excited states requires using term symbols, which concisely represent the quantum numbers associated with the excited state. These symbols provide information on the total orbital angular momentum (L), the total spin angular momentum (S), and the total angular momentum (J). The general form is ²S+¹L<sub>J</sub>, where:
- 2S+1: Represents the spin multiplicity (singlet, doublet, triplet, etc.).
- L: Represents the total orbital angular momentum (S, P, D, F, etc.).
- J: Represents the total angular momentum.
Determining the term symbols for various excited states of oxygen necessitates a detailed understanding of quantum mechanics and spectroscopic principles. This is often a complex process, often aided by computational methods. For example, an oxygen atom with one electron excited to a 3s orbital could have a variety of term symbols depending on the quantum numbers.
Spectroscopic Studies: Unveiling Excited State Properties
Spectroscopy plays a crucial role in studying oxygen's excited states. Techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) allow researchers to identify and characterize the various excited states. By analyzing the wavelengths of light absorbed or emitted during electronic transitions, researchers can determine the energy differences between the ground state and various excited states.
The Significance of Excited States in Various Phenomena
Oxygen's excited states play crucial roles in various natural and technological processes:
1. Aurora Borealis:
The stunning auroras are a direct result of energized particles from the sun interacting with atoms and molecules in Earth's upper atmosphere. Oxygen atoms in excited states are responsible for the characteristic green and red emissions observed in the aurora. The transitions from these excited states back to the ground state release photons of light at specific wavelengths, creating the breathtaking displays.
2. Combustion and Flames:
The excited states of oxygen play a critical role in combustion processes. During burning, oxygen molecules react with fuels, often leading to the formation of excited oxygen atoms and other species. The transitions from these excited states to the ground state contribute to the light emitted in flames.
3. Atmospheric Chemistry:
Oxygen's excited states influence various atmospheric chemical reactions. These reactions can involve the formation of ozone (O₃), which plays a vital role in protecting the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. The photochemical reactions involving excited oxygen are complex and vital for understanding atmospheric processes.
4. Laser Technology:
Oxygen's excited states can be utilized in laser technology. Specific transitions between excited states can be exploited to generate laser light at specific wavelengths. While not as common as other elements used in lasers, oxygen’s excited states remain a potential area of laser technology development.
5. Plasma Physics:
In plasma environments, oxygen atoms are frequently in excited states due to the high energy conditions. The properties of oxygen plasma are greatly influenced by the presence of excited oxygen atoms and their interactions with other plasma components. This is relevant to applications such as plasma etching in semiconductor manufacturing.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Secrets of Oxygen's Excited States
The excited states of oxygen represent a complex and fascinating area of study. While the ground state configuration provides a fundamental understanding of oxygen's behavior, it's the excited states that reveal its full potential for reactivity and its involvement in diverse phenomena. Through spectroscopic techniques and advanced computational methods, scientists continue to unravel the secrets of oxygen's excited states, leading to a deeper understanding of its role in various natural processes and technological applications. Further research will undoubtedly reveal even more about this fundamental element and its impact on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Are In One Cubic Foot
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Diodes Are Required To Form A Bridge Rectifier
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Graph Of The X Component Of The Electric Field
Mar 14, 2025
-
Reactions Which Do Not Continue To Completion Are Called Reactions
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is Five Hours
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Excited State Of Oxygen Electron Configuration . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
