Elements And Compounds Are Two Types Of
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
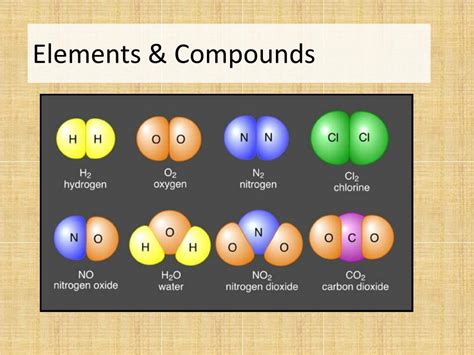
Table of Contents
Elements and Compounds: Two Fundamental Types of Matter
Everything around us, from the air we breathe to the ground we walk on, is made up of matter. Matter, in its simplest form, can be classified into two fundamental categories: elements and compounds. Understanding the differences between these two is crucial to comprehending the complexities of chemistry and the world around us. This article delves deep into the nature of elements and compounds, exploring their properties, differences, and the fundamental principles that govern their interactions.
What are Elements?
Elements are the purest form of matter. They are substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element is characterized by a unique number of protons in its atomic nucleus, known as its atomic number. This atomic number defines the element's identity and distinguishes it from all other elements. The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, organizes and displays all known elements based on their atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
Key Characteristics of Elements:
- Unique Atomic Number: Each element has a distinct number of protons, which determines its place on the periodic table.
- Cannot be Broken Down: Elements are fundamental building blocks; they cannot be further simplified through chemical reactions.
- Specific Properties: Each element possesses unique physical and chemical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, reactivity, and density. These properties are determined by the element's electron configuration and atomic structure.
- Examples: Common examples include oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), carbon (C), iron (Fe), gold (Au), and many more. These elements, individually, exhibit specific behaviors and characteristics.
Exploring Different Element Types:
Elements are further categorized into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals, like iron and copper, are typically shiny, conductive, and malleable. Nonmetals, such as oxygen and chlorine, tend to be poor conductors and exist in various states. Metalloids, like silicon and germanium, possess properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. Understanding these classifications helps predict the behavior of elements in chemical reactions.
What are Compounds?
Compounds are substances formed when two or more elements chemically combine in fixed proportions. This chemical combination involves the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of chemical bonds. Unlike elements, compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical processes.
Key Characteristics of Compounds:
- Fixed Composition: Compounds always have a precise and constant ratio of elements. For example, water (H₂O) always contains two hydrogen atoms for every one oxygen atom.
- Chemical Bonds: Atoms within a compound are held together by chemical bonds, either ionic or covalent bonds. These bonds determine the compound's properties.
- Different Properties from Constituent Elements: The properties of a compound are often drastically different from the properties of the elements that make it up. For instance, sodium (Na) is a highly reactive metal, and chlorine (Cl) is a toxic gas, but their combination forms sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt, a relatively inert and edible substance.
- Can be Broken Down: Compounds can be decomposed into their constituent elements through chemical reactions, such as electrolysis or thermal decomposition.
- Examples: Water (H₂O), carbon dioxide (CO₂), sodium chloride (NaCl), glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), and countless others are examples of compounds.
The Difference Between Elements and Compounds: A Detailed Comparison
The table below summarizes the key differences between elements and compounds:
| Feature | Element | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purest form of matter; cannot be broken down chemically | Formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements |
| Composition | Single type of atom | Two or more types of atoms in fixed proportions |
| Chemical Bonds | No chemical bonds between different atoms | Chemical bonds (ionic or covalent) hold atoms together |
| Properties | Unique properties determined by atomic structure | Properties different from constituent elements |
| Decomposition | Cannot be broken down chemically | Can be broken down chemically into constituent elements |
| Examples | Oxygen (O), Iron (Fe), Gold (Au) | Water (H₂O), Salt (NaCl), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) |
Types of Chemical Bonds in Compounds:
The formation of compounds is governed by the interaction of atoms through chemical bonds. Two primary types exist:
1. Ionic Bonds:
Ionic bonds are formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms. One atom loses electrons (becoming a positively charged ion or cation) while another atom gains these electrons (becoming a negatively charged ion or anion). The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms the ionic bond. Ionic compounds are typically solids at room temperature and often dissolve readily in water. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and magnesium oxide (MgO).
2. Covalent Bonds:
Covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms. Atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling the electron configuration of a noble gas. Covalent compounds can exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature and often have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds. Examples include water (H₂O), methane (CH₄), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
The Importance of Understanding Elements and Compounds:
Understanding the distinction between elements and compounds is fundamental to many scientific disciplines. This knowledge is essential for:
- Chemistry: The foundation of chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and chemical bonding relies heavily on understanding elements and compounds.
- Materials Science: Designing new materials with specific properties involves careful selection and manipulation of elements and compounds.
- Biology: The building blocks of living organisms are complex molecules, which are themselves compounds made up of various elements.
- Medicine: Understanding the chemical properties of elements and compounds is crucial for developing new drugs and therapies.
- Environmental Science: Studying the composition and reactions of compounds in the environment is critical for addressing environmental challenges.
Conclusion:
Elements and compounds represent the fundamental building blocks of matter. Elements are the simplest form of matter, while compounds are formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements. The differences in their properties, bonding, and decomposition behavior are crucial to understanding the world around us. Their importance spans across various scientific fields, highlighting the necessity of grasping these core chemical concepts. This in-depth exploration emphasizes the foundational role of elements and compounds in chemistry and beyond, encouraging further exploration of their fascinating properties and interactions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Muscles
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Atmospheric Layer Prevents Meteoroids From Reaching Earths Surface
Mar 22, 2025
-
Reaction Of Ammonia With Sulfuric Acid
Mar 22, 2025
-
In Glycolysis There Is A Net Gain Of Atp
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True Of Rna Processing
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Elements And Compounds Are Two Types Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
