Element With Properties Similar To Sulfur.
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
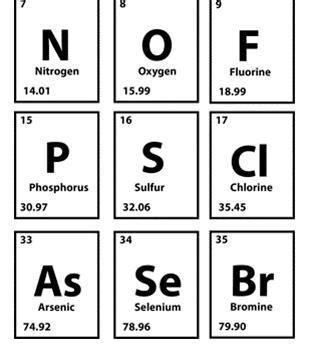
Table of Contents
Elements with Properties Similar to Sulfur: A Deep Dive into Chalcogens and Beyond
Sulfur, a vibrant yellow nonmetal, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Its chemical properties, driven by its six valence electrons, lead to a rich array of compounds and applications. Understanding sulfur's behavior is crucial across numerous fields, from industrial processes to biological systems. But sulfur isn't alone in its fascinating reactivity and characteristics. Several other elements exhibit similarities, making them valuable substitutes or offering insights into sulfur's own behavior. This article delves into the elements with properties similar to sulfur, focusing on their chemical similarities, differences, and applications.
The Chalcogen Family: Sulfur's Closest Relatives
The most obvious place to look for sulfur-like elements is within its own family: the chalcogens. This group (Group 16) comprises oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), polonium (Po), and livermorium (Lv). While livermorium is a synthetic, highly radioactive element with limited understanding, the other chalcogens share several key characteristics with sulfur:
Similarities within the Chalcogen Family:
- Valence Electrons: All chalcogens possess six valence electrons, leading to a tendency to form two covalent bonds (like oxygen in water) or gain two electrons to achieve a stable octet (like sulfide ions). This fundamental similarity underpins much of their chemical behavior.
- Allotropes: Sulfur, selenium, and tellurium all exhibit allotropy – the existence of different structural forms of the same element. Sulfur's most common allotrope is the S₈ ring, but it can also form chains and other structures. Selenium and tellurium also have various allotropic forms, highlighting the complexity of their bonding capabilities.
- Oxidation States: Chalcogens can exhibit various oxidation states, ranging from -2 (common in sulfides, selenides, and tellurides) to +6 (found in sulfates, selenates, and tellurates). This versatility allows them to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions.
- Formation of Anionic Species: Chalcogens readily form anions (negatively charged ions), like sulfide (S²⁻), selenide (Se²⁻), and telluride (Te²⁻). These anions are crucial components in various minerals and compounds.
Differences within the Chalcogen Family:
Despite their similarities, significant differences exist among the chalcogens:
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity decreases down the group. Oxygen is the most electronegative, followed by sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium. This trend influences the polarity of their bonds and the reactivity of their compounds.
- Reactivity: Reactivity generally decreases down the group. Oxygen is highly reactive, while polonium is less so due to relativistic effects impacting its valence electrons. Sulfur exhibits intermediate reactivity, making it versatile in many applications.
- Metallic Character: Metallic character increases down the group. Oxygen and sulfur are nonmetals, while tellurium and polonium display semimetallic and metallic properties, respectively. This trend affects their conductivity and other physical characteristics.
- Toxicity: The toxicity of chalcogens generally increases down the group. While sulfur is relatively non-toxic in its elemental form, selenium and tellurium exhibit varying degrees of toxicity, requiring careful handling. Polonium is highly radioactive and extremely dangerous.
Beyond the Chalcogens: Elements with Partial Sulfur-Like Properties
While the chalcogens are the closest relatives, other elements also exhibit some similarities to sulfur in specific contexts:
Phosphorus (P):
Phosphorus, a group 15 element, shares some similarities with sulfur in its ability to form multiple allotropes (white, red, black phosphorus) and various oxidation states. Both elements can form covalent bonds and participate in diverse chemical reactions. However, phosphorus's greater tendency to form catenated chains (chains of phosphorus atoms) differentiates it from sulfur. Furthermore, phosphorus is a crucial element in biological systems (DNA, RNA), unlike sulfur, which while essential, has a different biological role.
Arsenic (As) and Antimony (Sb):
These group 15 elements exhibit some similarities to sulfur in their ability to form sulfides and other chalcogenides. Arsenic and antimony sulfides are found in nature and possess semiconducting properties, making them relevant in materials science. However, arsenic and antimony are significantly more toxic than sulfur.
Chlorine (Cl):
Chlorine, a halogen (group 17), shows some analogous behavior to sulfur in terms of its ability to form covalent bonds and participate in redox reactions. Both elements can form strong acids (sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid) and participate in numerous industrial processes. However, chlorine is much more electronegative than sulfur, resulting in very different chemical behaviors.
Applications Leveraging Sulfur-Like Properties:
The unique properties of sulfur and elements with similar characteristics find numerous applications across diverse fields:
Industrial Applications:
- Sulfuric Acid Production: The cornerstone of many industries, sulfuric acid production relies heavily on sulfur's reactivity. Its versatility makes it crucial in fertilizers, batteries, and countless other products.
- Vulcanization of Rubber: Sulfur's cross-linking capability revolutionized the rubber industry, creating stronger, more durable materials.
- Metallurgy: Sulfides of various metals are important ore sources for extracting metals like copper, lead, and zinc.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sulfur compounds find applications in several pharmaceuticals, often related to their antimicrobial or other therapeutic properties.
- Pyrotechnics: Sulfur's role in combustion reactions makes it a component in fireworks and other pyrotechnic devices.
Biological Applications:
- Amino Acids: Methionine and cysteine, sulfur-containing amino acids, are essential building blocks of proteins.
- Enzymes: Many enzymes contain sulfur-containing groups that are crucial for their catalytic activity.
- Trace Minerals: Sulfur is a vital micronutrient for plant growth and overall health. Selenium also has some important biological functions, albeit in much smaller quantities.
Materials Science Applications:
- Semiconductors: Selenium and tellurium find use in semiconductors and photovoltaic devices, capitalizing on their semimetallic properties.
- Pigments: Certain sulfur and selenium compounds serve as pigments in paints and inks.
- Lubricants: Sulfur and selenium compounds can be incorporated into lubricants to enhance their properties.
Conclusion: A Diverse Group with Shared Traits
Elements with properties similar to sulfur, particularly within the chalcogen family, share fundamental traits stemming from their similar valence electron configurations. However, the differences in electronegativity, reactivity, and metallic character lead to a fascinating diversity in their chemical behavior and applications. From industrial processes to biological systems, sulfur and its analogs play crucial roles, highlighting the importance of understanding their similarities and differences. Further research into the unique properties of these elements will likely uncover even more applications and deepen our understanding of their fundamental chemistry. Understanding these similarities and differences is key to developing new materials, technologies, and treatments. Future exploration into the less-understood chalcogens, like polonium, despite the inherent safety challenges, could potentially reveal even more exciting possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Matter Is Made Up Of Small Particles Called
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Is The Melting Of Ice Not A Chemical Reaction
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Is Voltmeter Connected In Parallel
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is Ferment A Physical Or Chemical Change
Apr 03, 2025
-
Give An Example Of A Homologous Structure From This Activity
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Element With Properties Similar To Sulfur. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
