Electric Charges That Are Different Attract Each Other. True False
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
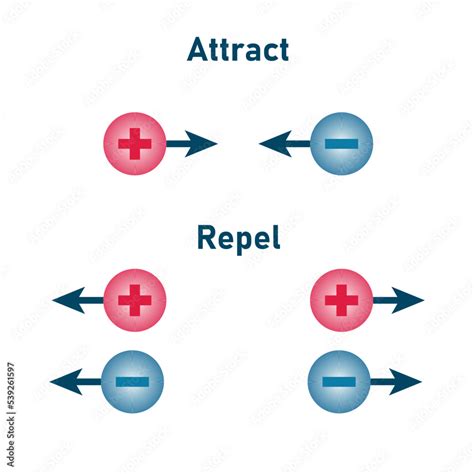
Table of Contents
Electric Charges: Opposites Attract – True or False?
The statement "electric charges that are different attract each other" is unequivocally true. This fundamental principle of electrostatics governs countless phenomena in our universe, from the simple workings of a light switch to the complex interactions within atoms and molecules. This article will delve into the intricacies of electric charges, explaining why opposite charges attract, exploring the forces involved, and examining real-world applications of this principle.
Understanding Electric Charge
Before diving into the attraction of opposite charges, it's crucial to grasp the concept of electric charge itself. Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter, much like mass. It's a quantized property, meaning it exists in discrete units, the smallest being the elementary charge, carried by a single proton or electron.
Two Types of Charge: Positive and Negative
There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative. These terms are somewhat arbitrary, but the convention is firmly established. Protons, found in the nucleus of an atom, carry a positive charge, while electrons, orbiting the nucleus, carry a negative charge. Neutrons, also found in the nucleus, are electrically neutral, possessing no charge.
The magnitude of charge carried by a proton and an electron is exactly the same; however, their signs are opposite. This fundamental difference leads to the attractive force between them.
The Significance of Coulomb's Law
The relationship between electric charges and the forces they exert on each other is beautifully described by Coulomb's Law. This law states that the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically, it's expressed as:
F = k * |q1 * q2| / r²
Where:
- F represents the electrostatic force
- k is Coulomb's constant (a proportionality constant)
- q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the two charges
- r is the distance between the charges
The absolute value signs (| |) indicate that the force is always positive, representing the magnitude of the force. The direction of the force is determined by the signs of the charges.
Opposite Charges Attract, Like Charges Repel
Coulomb's Law elegantly explains why the statement "electric charges that are different attract each other" is true. When two charges have opposite signs (one positive and one negative), the product of their charges (q1 * q2) is negative. However, the absolute value makes the overall force positive, representing an attractive force.
Conversely, when two charges have the same sign (both positive or both negative), the product of their charges is positive, resulting in a repulsive force. Like charges repel each other. This fundamental interaction is the basis for many electrical phenomena.
Real-World Examples of Opposite Charges Attracting
The attraction of opposite charges is not a theoretical concept confined to physics textbooks. It's a ubiquitous phenomenon with numerous real-world applications:
1. Static Electricity: The Everyday Attraction
We experience the effects of static electricity frequently. When you rub a balloon against your hair, electrons transfer from your hair to the balloon, leaving your hair with a net positive charge and the balloon with a net negative charge. The oppositely charged hair and balloon then attract each other, causing the hair to stand on end or the balloon to stick to a wall.
2. The Structure of Atoms and Molecules: The Glue of Matter
The attraction between oppositely charged protons and electrons is what holds atoms together. The positive nucleus attracts the negatively charged electrons, creating a stable atomic structure. Similarly, the interactions between oppositely charged ions (atoms that have lost or gained electrons) form ionic bonds, which are crucial for the formation of many compounds. Think of table salt (NaCl): the positive sodium ion (Na⁺) is strongly attracted to the negative chloride ion (Cl⁻).
3. Lightning: A Dramatic Display of Attraction
Lightning is a spectacular example of electrostatic discharge. A build-up of static electricity in clouds, typically with a negative charge at the bottom, induces a positive charge on the ground. When the potential difference between the cloud and ground becomes sufficiently large, a massive discharge occurs – lightning – as electrons flow from the cloud to the ground, attracted by the opposite charge.
4. Capacitors: Storing Electrical Energy
Capacitors are electronic components that store electrical energy by exploiting the attraction between opposite charges. A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator. When a voltage is applied, one plate accumulates a positive charge, and the other a negative charge. The attraction between these opposite charges allows the capacitor to store energy.
5. Electrochemical Cells: Powering Devices
Batteries and other electrochemical cells work on the principle of attraction between opposite charges. Chemical reactions within the cell generate a potential difference, leading to a build-up of positive charge at one electrode and negative charge at the other. The attraction between these charges drives the flow of electrons through an external circuit, providing electrical power.
Beyond the Basics: More Complex Interactions
While Coulomb's Law provides a fundamental understanding of the forces between charges, the real world is often more complex. The presence of multiple charges, the influence of dielectric materials (materials that reduce the electric field strength), and quantum effects can significantly influence the interactions.
The Superposition Principle
When dealing with multiple charges, the superposition principle applies. This principle states that the net force on a charge due to multiple other charges is the vector sum of the individual forces exerted by each charge. This means that the forces from different charges add up, both in magnitude and direction. Calculating these forces accurately can be challenging in systems with many interacting charges.
Dielectric Materials: Modifying the Force
The presence of dielectric materials between charges affects the strength of the electrostatic force. These materials reduce the electric field strength, effectively weakening the attraction or repulsion between charges. This is because the dielectric material's molecules become polarized in the presence of an electric field, partially counteracting the field.
Quantum Effects: A Deeper Dive
At the atomic and subatomic levels, quantum mechanics plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of electric charges. Quantum effects such as tunneling and quantum fluctuations modify the classical picture described by Coulomb's Law. These effects are crucial in understanding phenomena such as chemical bonding and the behavior of semiconductors.
Conclusion: A Powerful Fundamental Force
The statement "electric charges that are different attract each other" is a cornerstone of physics, explaining a vast array of phenomena, from the stability of matter to the workings of electronic devices. Understanding this fundamental principle, coupled with Coulomb's Law and the principles of superposition and dielectric effects, opens doors to comprehending a wide range of electrical and electronic systems. Further exploration into the quantum mechanical aspects deepens our understanding of these interactions at the atomic level, offering a more complete picture of the world around us. The intricate dance of attraction and repulsion between charges is a testament to the elegance and power of fundamental forces in shaping our universe. It is a powerful force shaping our understanding of the physical world, and continued research and exploration continually refine our understanding of this essential concept.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Electric Charges That Are Different Attract Each Other. True False . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
