Difference Between True Ribs False Ribs And Floating Ribs
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
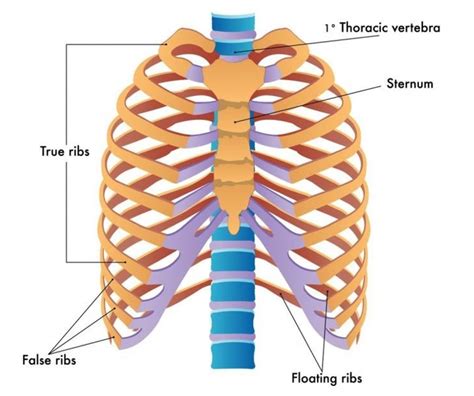
Table of Contents
The Rib Cage: Understanding True, False, and Floating Ribs
The human rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony structure that protects vital organs like the heart and lungs. It's composed of 12 pairs of ribs, each with unique characteristics that contribute to its overall function. Understanding the differences between true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs is crucial to comprehending the intricacies of the skeletal system and its role in respiration, protection, and overall bodily function. This comprehensive guide will delve into the anatomy, differences, and clinical significance of these rib types.
Defining the Three Types of Ribs
Before diving into the specifics, let's establish clear definitions:
-
True Ribs (Vertebrosternal Ribs): These are the first seven pairs of ribs (ribs 1-7). They are directly attached to the sternum (breastbone) via their own costal cartilage. This direct connection provides strong support and stability.
-
False Ribs (Vertebrochondral Ribs): Ribs 8-10 are classified as false ribs. They don't connect directly to the sternum. Instead, their costal cartilages connect to the cartilage of the rib above them, forming a chain-like connection to the sternum. This indirect attachment provides some flexibility.
-
Floating Ribs (Vertebral Ribs): The last two pairs of ribs (ribs 11-12) are called floating ribs because they don't connect to the sternum at all. They are only attached to the vertebrae posteriorly. Their free anterior ends offer greater flexibility and movement.
Anatomical Features and Differences
The differences between true, false, and floating ribs extend beyond their connection to the sternum. Let's explore these anatomical nuances:
1. Attachment to the Sternum: The Key Distinguishing Factor
As previously mentioned, the primary difference lies in their articulation with the sternum. True ribs have a direct, individual connection, providing robust support. False ribs have an indirect connection via the costal cartilage of the rib above them, offering a balance between stability and flexibility. Floating ribs lack any sternal connection, contributing to their enhanced mobility.
2. Costal Cartilage: Length and Flexibility
The costal cartilage plays a vital role in the rib cage's flexibility and resilience. True ribs possess shorter and less flexible costal cartilages compared to false ribs. False ribs have longer and more flexible costal cartilages, allowing for a wider range of motion. Floating ribs, lacking any connection to the sternum, have even longer and more flexible costal cartilages. This contributes to their role in absorbing shock and allowing for respiratory movements.
3. Mobility and Function in Respiration
The varying degrees of mobility are directly related to the ribs' functions in respiration. True ribs provide a stable base for the respiratory muscles to act upon. False ribs allow for greater expansion of the rib cage during inhalation, increasing lung volume. Floating ribs play a crucial role in lateral expansion of the rib cage, particularly during deep breathing. Their mobility allows for significant increase in thoracic volume during forceful inspiration.
4. Protection of Internal Organs
While all ribs contribute to protecting vital organs, the true ribs, with their direct sternal connection, offer the most robust protection for the heart and lungs in the anterior region of the thoracic cavity. The false and floating ribs still offer a degree of protection, particularly on the sides and posteriorly, but their increased mobility makes them slightly less effective at shielding organs from direct impacts.
Clinical Significance and Potential Issues
Understanding the differences between rib types is crucial for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
1. Rib Fractures: Location Matters
Rib fractures are common injuries, and their location can provide clues to the mechanism of injury. Fractures of the true ribs are often associated with direct anterior trauma, whereas fractures of the false and floating ribs may result from lateral or posterior impacts. Floating rib fractures, due to their lack of anterior support, are sometimes more prone to complications like delayed healing or lung injury.
2. Costochondritis: Inflammation of the Costal Cartilage
Costochondritis is an inflammation of the costal cartilages, characterized by chest pain. It can affect any of the ribs, but it's often associated with the costal cartilages of the true or false ribs near the sternum. Understanding which rib segments are involved is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
3. Flail Chest: A Severe Thoracic Injury
A flail chest is a severe life-threatening condition characterized by multiple rib fractures that allow a segment of the chest wall to move paradoxically during breathing. This typically involves fractures of multiple adjacent ribs in the false rib region and compromises ventilation significantly. Prompt medical intervention is vital.
4. Surgical Procedures: Considerations for Rib Access
Surgeons need to consider the rib types when planning procedures involving the chest cavity. Access to the heart and lungs often requires maneuvering around or through the ribs. The differences in mobility and attachment dictate surgical approaches.
Evolutionary Perspective and Comparative Anatomy
The differentiation of ribs into true, false, and floating types isn't unique to humans. It's a common feature in many mammals, reflecting evolutionary adaptations to enhance respiratory function and provide protection. The relative proportions and characteristics of each rib type vary among different species, reflecting their specific locomotor and respiratory needs. For instance, animals with greater reliance on rib cage expansion for breathing tend to have more flexible false and floating ribs.
Conclusion: A Complex yet Harmonious System
The human rib cage is a complex and fascinating structure, with the three types of ribs playing distinct yet complementary roles. True ribs provide strong anterior support, false ribs contribute to flexible expansion, and floating ribs allow for lateral mobility. Understanding their individual characteristics and their interactions is crucial for comprehending respiratory mechanics, the protection of vital organs, and the diagnosis and treatment of various thoracic injuries and conditions. This detailed examination helps paint a picture of the rib cage's integrated function and the importance of each individual rib in maintaining health and well-being. The subtle yet significant differences between true, false, and floating ribs contribute to the intricate and remarkable design of the human body. Further exploration into the biomechanics of the rib cage and its intricate relationships with surrounding structures continues to reveal new insights into its role in maintaining human health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Square Root Of 0 09
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Is A Democracy Different From A Dictatorship
Apr 03, 2025
-
This Industry Is Characterized As
Apr 03, 2025
-
Mass Of A Grain Of Sand
Apr 03, 2025
-
Describe How Phospholipids Are Arranged In The Cell Membrane
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between True Ribs False Ribs And Floating Ribs . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
