Calculate The Molar Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2
News Leon
Apr 07, 2025 · 4 min read
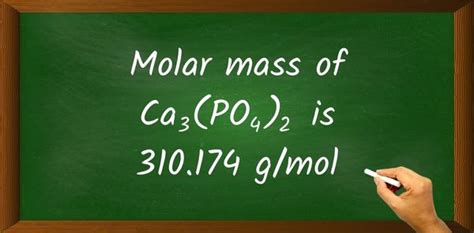
Table of Contents
Calculating the Molar Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂: A Step-by-Step Guide
Determining the molar mass of a compound is a fundamental skill in chemistry, crucial for various calculations, including stoichiometry, solution preparation, and analyzing chemical reactions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of calculating the molar mass of calcium phosphate, Ca₃(PO₄)₂, step-by-step, explaining the underlying principles and offering valuable insights along the way.
Understanding Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). One mole is defined as the amount of a substance that contains Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³) of elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). Essentially, the molar mass tells us how many grams there are in one mole of a particular substance.
For elements, the molar mass is numerically equal to the atomic weight (relative atomic mass) found on the periodic table. For compounds, we need to consider the molar mass of each constituent element and their respective quantities within the compound's chemical formula.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂
Calcium phosphate, Ca₃(PO₄)₂, is an ionic compound composed of calcium cations (Ca²⁺) and phosphate anions (PO₄³⁻). To calculate its molar mass, we need to consider the molar mass of each element present:
- Calcium (Ca): According to the periodic table, the molar mass of calcium is approximately 40.08 g/mol.
- Phosphorus (P): The molar mass of phosphorus is approximately 30.97 g/mol.
- Oxygen (O): The molar mass of oxygen is approximately 16.00 g/mol.
Step 1: Identify the number of atoms of each element.
The chemical formula Ca₃(PO₄)₂ tells us:
- There are 3 calcium (Ca) atoms.
- There are 2 phosphorus (P) atoms (because of the subscript 2 outside the parenthesis).
- There are 8 oxygen (O) atoms (because there are 4 oxygen atoms within each phosphate ion (PO₄) and there are 2 phosphate ions).
Step 2: Calculate the mass contribution of each element.
- Calcium (Ca): 3 atoms × 40.08 g/mol/atom = 120.24 g/mol
- Phosphorus (P): 2 atoms × 30.97 g/mol/atom = 61.94 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 8 atoms × 16.00 g/mol/atom = 128.00 g/mol
Step 3: Sum the mass contributions of all elements.
Total molar mass = Mass of Ca + Mass of P + Mass of O
Total molar mass = 120.24 g/mol + 61.94 g/mol + 128.00 g/mol = 310.18 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is approximately 310.18 g/mol.
Significance of Molar Mass Calculations
The accurate determination of molar mass is paramount in numerous chemical calculations and applications. Here are some key examples:
1. Stoichiometry:
Stoichiometry involves the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Molar mass is crucial for converting between the mass of a substance and the number of moles, allowing us to determine the amounts of reactants needed or products formed in a reaction.
For instance, if we want to determine how many grams of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ are required to react with a specific amount of another reactant, we would use the molar mass (310.18 g/mol) as a conversion factor.
2. Solution Preparation:
Molar mass is essential in preparing solutions with specific concentrations. For example, to prepare a 1 M (molar) solution of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, we need to dissolve 310.18 grams of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ in enough solvent to make one liter of solution.
3. Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas:
Molar mass plays a vital role in determining the empirical and molecular formulas of a compound. The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound, while the molecular formula represents the actual number of atoms in a molecule. By comparing the molar mass of the compound with its empirical formula mass, we can determine the molecular formula.
4. Analyzing Chemical Reactions:
Molar mass allows for the accurate analysis of chemical reactions, providing quantitative data on reactant consumption and product formation. This is critical in various fields, including industrial chemistry, environmental science, and biochemistry.
Advanced Considerations and Potential Errors
While the calculation above is straightforward, several factors can influence accuracy:
-
Significant Figures: Pay close attention to significant figures throughout the calculation. The final answer should reflect the precision of the least precise measurement used (in this case, the molar masses of the elements from the periodic table).
-
Isotopic Abundance: The molar masses used are average atomic weights, considering the natural abundance of different isotopes of each element. In highly precise calculations, considering the specific isotopic composition of the sample may be necessary.
-
Purity of the Sample: The calculated molar mass assumes the sample is pure Ca₃(PO₄)₂. Impurities in the sample will affect the experimental molar mass determination.
Conclusion
Calculating the molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is a straightforward yet fundamental process in chemistry. Mastering this skill is crucial for a solid understanding of stoichiometry, solution preparation, and various other chemical calculations. By understanding the steps involved and considering potential sources of error, you can accurately determine the molar mass of this important compound and apply this knowledge to a wide range of chemical problems. Remember always to refer to an updated periodic table for the most accurate atomic weights. This detailed explanation should equip you with the confidence and knowledge to tackle similar molar mass calculations for other compounds.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Entrepreneurship As A Factor Of Production Refers To
Apr 08, 2025
-
A Group Of Organisms Of The Same Species
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Statements Are True For Chloroplasts
Apr 08, 2025
-
How Does Amoeba Capture Its Food
Apr 08, 2025
-
Cytoplasmic Division Of A Cell Is Called
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Calculate The Molar Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.